Summary
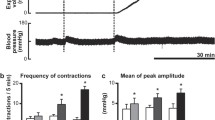
The effect of domperidone, a peripheral antidopaminergic drug, on sigmoid motor activity in the irritable bowel syndrome, has been evaluated by measuring pressures in 3 opentipped tubes perfused with distilled water at a constant flow rate of 0.636 ml/min and inserted into the sigmoid colon. Domperidone 20 mg i.v. in 10 patients, did not induce any significant change in basal motility, but prevented the increase in motor activity produced by the infusion of dopamine 5 µg/kg/min for 10 min. It appears that domperidone had no effect on sigmoid motor activity, although the inhibition of dopamine-induced motility confirms the presence of specific dopaminergic receptors in the colon and the antidopaminergic action of domperidone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van Neuten JM, Schuurkes JAJ (1981) Animal pharmacology of domperidone, antiemetic and gastrokinetic properties. Roy Soc Med ICSS 36: 22–27
Ennis C, Cox B (1980) The dopamine receptor antagonist domperidone is also a competitive antagonist at α1-adrenoceptors. J Pharm Pharmacol 32: 434–438
Costall B, Fortune DM, Naylor RJ (1979) Neuropharmacological studies on the neuroleptic potential of domperidone. J Pharm Pharmacol 31: 344–347
Brock-Utne JG, Downing JW, Dimopoulos GE, Rubin J, Moshal MG (1980) Effect of domperidone on lower oesophageal sphincter tone in late pregnancy. Anesthesiology 52: 321–323
Weihrauch TR, Forster CF, Krieglstein JK (1978) Evaluation of the effect of domperidone on human oesophageal and gastroduodenal motility by intraluminal manometry. Postgrad Med J 55 [Suppl 1]: 7–10
Lux G, Engel H, Rosch W (1981) The stimulation of oesophageal motility with bromopride, domperidone, and metoclopramide. Roy Soc Med ICSS 36: 29–31
Valenzuela JE, Defilippi C, Gutierrez F (1980) Effect of domperidone on patients with symptomatic gastro-oesophageal reflux. Dig Dis Sci (abstract) 25: 716
Blackwell JN, Heading RC, Fettes MR (1981) Effects of domperidone on lower oesophageal sphincter pressure and gastro-oesophageal reflux in patients with peptic oesophagitis. Roy Soc Med ICSS 36: 57–60
Malagelada JR (1979) Physiologic basis and clinical significance of gastric emptying disorders. Dig Dis Sci 24: 657
Valenzuela JE, Miranda M, Ansari AN, Lim BR (1981) Delayed gastric emptying in patients with reflux oesophagitis. Gastroenterology 80: 1307
Jacobs F, Akkermans LMA, Yol OH, Wittebol P (1981) Effects of domperidone on gastric emptying of semi solid and solid food. Roy Soc Med ICSS 36: 11–20
Valenzuela JE, Liu DP (1981) Studies on intragastric pressure and gastric emptying of liquid in man. Gastroenterologie 19: 449–450
Baeyens R, Reyntjens A, Van Velde E, De Schepper A, Wollaert F (1978) Effects of intravenous and oral domperidone on the motor function of the stomach and small intestine. A double blind evaluation against placebo. Postgrad Med J 54: 17–21
Weihrauch TR, Ehl W (1981) Effect of domperidone on the motility of antrum, pylorus and duodenum in man. Scand J Gastroenterol 16 [Suppl 67]: 195
Schuurkes JAJ, Van Neuten JM (1981) Is dopamine an inhibitory modulator of gastrointestinal motility? Scand J Gastroenterol 16 [Suppl 67]: 33–36
Schuurkes JAJ, Helsen LFM, Van Neuten JM (1982) Improved gastroduodenal coordination by the peripheral dopamine antagonist domperidone. In: Wienbeck (ed) Motility of digestive tract. Raven Press, New York, 565–572
Broekaert A (1979) Effect of domperidone on gastric emptying and secretion. Postgrad Med J 55 [Suppl 1]: 11–14
Lanfranchi GA, Marzio L, Cortini C, Moreno Osset E (1978) Motor effect of dopamine on human sigmoid colon: Evidence for specific receptors. Am J Dig Dis 23: 257–263
Milo R (1980) Use of the peripheral dopamine antagonist, domperidone, in the management of gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Curr Med Res Opin 6: 577–584
Fielding JF (1982) Domperidone treatment in the irritable bowel syndrome. Digestion 23: 125–127
Cann PA, Read WW, Holdsworth CD (1983) Oral domperidone: Double blind comparison with placebo in irritable bowel syndrome. Gut 24: 1135–1140
Schulze-Delrieu K (1979) Metoclopramide. Gastroenterology 77: 768–779
Lechin F, Gomez F, Van Der Dijs B, Lechin E (1980) Distal colon motility in schizophrenic patients. J Clin Pharmacol 20: 459–464
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lanfranchi, G.A., Bazzocchi, G., Fois, F. et al. Effect of domperidone and dopamine on colonic motor activity in patients with the irritable bowel syndrome. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 29, 307–310 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00544085
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00544085