Summary
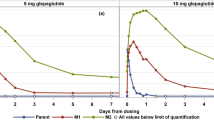
To determine the local gastrointestinal absorption of a new synthetic somatostatin analogue (SMS 201-995 = Sandostatin), an intestinal tube was passed in eight healthy volunteers and on different days an aqueous solution was administered at four different locations: stomach, proximal duodenum, ligament of Treitz and jejunum. In a follow-up study, an oro-ileal tube was passed in six of the original volunteers and the drug solution was administered in to the terminal ileum.
The aqueous solution of SMS was rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract after local application, and it was well tolerated. Absorption of the drug from the different sites was comparable, although there was a tendency to decreased peptide absorption after ileal administration. Absorption of the drug was quite variable between the subjects and the different locations. The dose-corrected systemic availability relative to subcutaneous administration in another study was 0.28%.
However, significant plasma SMS concentrations were achieved, suggesting that oral delivery of the polypeptide may eventually be possible for long-term treatment of a variety of disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold R, Lankisch PG (1980) Somatostatin and the gastrointestinal tract. Clin Gastroenterol 9: 733–753
Reichlin S (1983) Somatostatin. N Engl J Med 309: 1495–1501
Lamberts SWJ, Vitterlinden P, Verschoor L, van Dongen KJ, del Pozo E (1985) Long-term treatment of acromegaly with the somatostatin analogue SMS 201-995. N Engl J Med 313: 1576–1580
Reichlin S (1983) Somatostatin. N Engl J Med 309: 1556–1563
Bonfils S (1985) New somatostatin molecule for management of endocrine tumours. Gut 26: 433–437
Wood SM, Kraenzlin ME, Adrian TE, Bloom SR (1985) Treatment of patients with pancreatic endocrine tumours using a new long-acting somatostatin analogue symptomatic and peptide responses. Gut 26: 438–444
Kayasseh L, Gyr K, Keller U, Stalder GA, Wall M (1980) Somatostatin and cimetidine in peptic-ulcer haemorrhage. Lancet 1: 844–846
Magnusson I, Ihre T, Johansson C, Seligson U, Törngren S, Uvnäs-Moberg K (1985) Randomised double blind trial of somatostatin in the treatment of massive upper gastrointestinal haemorrhage. Gut 26: 221–226
Williams S, Cooper JC, Axon ATR, King RFG, Barker M (1984) Use of a long-acting somatostatin analogue in controlling life threatening ileostomy diarrhea. Br Med J 289: 1027–1028
Vallot T, Hardy N, Bonfils S (1981) Inhibition des sécrétions gastriques de l'homme par la somatostatine cyclique administrée par voie sous-cutanée. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 5: 728–732
Bauer W, Briner U, Doepfner W, Haller R, Huguenin R, Marbach P, Petcher TJ, Pless J (1982) SMS 201-995: A very potent and selective octapeptide analogue of somatostatin with prolonged action. Life Sci 31: 1133–1140
Alric R, Mariani MM, Loubatières A (1965) Importance de l'état des éléments figurés du sang et en particulier de celui des globules rouges sur les valeurs du glucose sanguin mesuré par auto-analyseur Technicon. Pathol Biol 13: 506–511
Hales CN, Randle PJ (1963) Immunoassay of insulin with insulin antibody precipitate. Biochem J 88: 137–146
Sachs L (1984) Angewandte Statistik. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Whitehouse I, Beglinger C, Rüttimann G, Gyr K (1986) Inhibition of pentagastrin-stimulated acid secretion after subcutaneous administration of a new somatostatin analogue. Gut 27: 141–146
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Köhler, E., Duberow-Drewe, M., Drewe, J. et al. Absorption of an aqueous solution of a new synthetic somatostatin analogue administered to man by gavage. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 33, 167–171 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00544562
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00544562