Summary
The effects of oral dilevalol (an R, R-isomer of labetalol), a new β-adrenoceptor blocker with β2-receptor stimulating and α-recepter blocking properties on blood pressure, renal function, plasma renin activity (PRA) and plasma aldosterone have been studied in 15 patients with mild-to-moderate essential hypertension treated with it for 6 weeks.
Two patients with apparent treatment failure and one patient who developed muscle pain and cramps, and had an elevated creatine phosphokinase level, were excluded from the study.
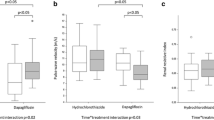
Dilevalol monotherapy 100 mg once daily for 6 weeks significantly lowered both the systolic and diastolic blood pressure compared to placebo. Total renal vascular resistance was significantly reduced, and RBF and GFR remained unchanged. Dilevalol significantly decreased PRA.
The results suggest that prolonged daily treatment with dilevalol preserves renal function and produces a concomitant hypotensive action in patients with mild-to-moderate essential hypertension. The ancillary pharmacological properties of dilevalol rather than PRA suppression may be relevant to its renal effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weber MA, Drayer JIM (1980) Renal effects of beta-adrenoceptor blockade. Kidney Int 18: 686–699
Bernstein KN, O'Connor DT (1984) Antiadrenergic anti-hypertensive drugs: Their effect on renal function. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 24: 105–120
Bauer JH, Brooks CS (1979) The long-term effect of propranolol therapy on renal function. Am J Med 66: 405–410
Warren SE, O'Connor DT, Cohen IM, Mitas JA (1981) Renal hemodynamic changes during long-term antihypertensive therapy. Clin Pharmacol Ther 29: 310–317
Wilkinson R, Stevens IM, Pickering M, Robson V, Hawkins T, Kerr DNS, Harry JD (1980) A study of the effects of atenolol and propranolol on renal function in patients with essential hypertension. Br J Clin Pharmacol 10: 51–59
Ibsen H, Sederberg-Olsen P (1973) Changes in glomerular filtration rate during long-term treatment with propranolol in patients with arterial hypertension. Clin Sci 44: 129–134
O'Connor DT, Preston RA, Sasso EH (1979) Renal perfusion changes during treatment of essential hypertension: Prazosin versus propranolol. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1 [Suppl 6]: S38-S42
Falch DK, Ødegaard AE, Norman N (1979) Decreased renal plasma flow during propranolol treatment in essential hypertension. Acta Med Scand 205: 91–95
Malini PL, Strocchi E, Negroni S, Ambrosioni E, Magnani B (1982) Renal haemodynamics after chronic treatment with labetalol and propranolol. Br J Clin Pharmacol 13 [Suppl 1]: 123S-126S
Rasmussen S, Nielsen PE (1981) Blood pressure, body fluid volumes and glomerular filtration rate during treatment with labetalol in essential hypertension. Br J Clin Pharmacol 12: 349–353
Cruz F, O'Neill WM Jr, Clifton G, Wallin JD (1981) Effects of labetalol and methyldopa on renal function. Clin Pharmacol Ther 30: 57–63
Larsen JS, Pedersen EB (1980) Comparison of the effects of propranolol and labetalol on renal haemodynamics at rest and during exercise in essential hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 18: 135–139
Wainer E, Boner G, Rosenfeld JB (1980) Effects of pindolol on renal function. Clin Pharmacol Ther 28: 575–580
Boner G, Wainer E, Rosenfeld JB (1982) Effects of pindolol on renal function. II. Effects of intravenous and prolonged oral dosing. Clin Pharmacol Ther 32: 423–427
van der Meulen J, Reijn E, Heidendal GAK, Oe PL, Donker AJM (1986) Comparison of the effects of penbutolol and propranolol on glomerular filtration rate in hypertensive patients with impaired renal function. Br J Clin Pharmacol 22: 469–474
Fabre J, Wintsch J, Peter-Contesse R, Bouchardy C, Liniger C, Favre L, Donath A (1986) Effects of bopindolol on renal function. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 8 [Suppl 6]: S45-S50
Hollenberg NK, Adams DF, McKinstry DN, Williams G, Borucki LJ, Sullivan JM (1979) β-Adrenoceptor-blocking agents and the kidney: Effect of nadolol and propranolol on the renal circulation. Br J Clin Pharmacol 7 [Suppl 2]: 219S-224S
Textor SC, Fouad FM, Bravo EL, Tarazi RC, Vidt DG, Gifford RW (1982) Redistribution of cardiac output to the kidneys during oral nadolol administration. N Engl J Med 307: 602–605
Sybertz EJ, Sabin CS, Pula KK, Vliet GV, Glennon J, Gold EH, Baum T (1981) Alpha-beta-adrenoceptor blocking properties of labetalol and its R, R-isomer, SCH 19927. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 218: 435–443
Baum T, Watkins RW, Sybertz EJ, Vemulapalli S, Pula KK, Eynon E, Nelson S, Vliet GV, Glennon J, Moran RM (1981) Antihypertensive and hemodynamic actions of SCH 19927, the R, R-isomer of labetalol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 218: 444–452
Baba T, Boku A, Ishizaki T, Sone K, Takebe K (1986) Renal effects of nicardipine in patients with mild-to-moderate essential hypertension. Am Heart J 111: 552–557
Baba T, Ishizaki T, Ido Y, Aoyagi K, Murabayashi S, Takebe K (1986) Renal effects of nicardipine, a calcium entry blocker, in hypertensive Type II diabetic patients with nephropathy. Diabetes 35: 1206–1214
Willassen Y, Ofstad J (1983) Intrarenal pressure and sodium excretion in hypertension of chronic glomerulonephritis in humans. Hypertension 5: 375–384
Haber E, Koerner T, Page LB, Klinman B, Purnode A (1969) Application of a radioimmunoassay for angiotensin I to the physiologic measurements of plasma renin activity in normal human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 29: 1349–1355
Ogihara T, Iinuma K, Nishi K, Arakawa Y, Takagi A, Kurata K, Miyai K, Kumahara Y (1977) A non-chromatographic non-extraction radioimmunoassay for serum aldosterone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 45: 726–731
Mercier DE, Feld RD, Witte DL (1978) Comparison of dewpoint and freezing point osmometry. Am J Med Technol 44: 1066–1069
Wallin JD, O'Neill WM Jr (1983) Labetalol. Current research and therapeutic status. Arch Int Med 143: 485–490
Riddell JG, Harron DWG, Shanks RG (1987) Clinical pharmacokinetics of β-adrenoceptor antagonists. An update. Clin Pharmacokinet 12: 305–320
Heel RC, Brogden RN, Speight TM, Avery GS (1979) Atenolol: A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy in angina pectoris and hypertension. Drugs 17: 425–460
Karch FE, Lasagna L (1975) Adverse drug reactions. A critical review. J Am Med Assoc 234: 1236–1241
Carr AA, Mulligan OF, Sherill LN (1982) Pindolol versus methyl-dopa for hypertension: Comparison of adverse reactions. Am Heart J 104: 482–486
Lehtonen A, Kanto J, Kleimola T (1977) Plasma concentrations of propranolol in patients with essential hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 11: 155–157
von Bahr C, Collste P, Frisk-Holmberg M, Haglund K, Jorfelt L, Orme M, Östman J, Sjöqvist F (1976) Plasma levels and effects ot metoprolol on blood pressure, adrenergic betareceptor blockade, and plasma renin activity in essential hypertension. Clin Pharmacol Ther 20: 130–137
Ishizaki T, Oyama Y, Suganuma T, Sasaki T, Nakaya H, Shibuya T, Sato T (1983) A dose ranging study of atenolol in hypertension: Fall in blood pressure and plasma renin activity, beta-blockade and steady-state pharmacokinetics. Br J Clin Pharmacol 16: 17–25
Cannon PJ (1977) The kidney in heart failure. New Engl J Med 296: 26–32
Bühler FR, Laragh JH, Baer L, Vaughan ED Jr, Brunner HR (1972) Propranolol inhibition of renin secretion. N Engl J Med 287: 1209–1214
Bauer JH (1983) Effects of propranolol therapy on renal function and body fluid composition. Arch Int Med 143: 927–931
O'Connor DT, Preston RA (1982) Urinary kallikrein activity, renal hemodynamics, and electrolyte handling during chronic beta blockade with propranolol in hypertension. Hypertension 4: 742–749
Dreslinski GR, Aristimuro GG, Messerli FH, Suarez DH, Frohlich ED (1979) Effects of beta-blockade with acebutolol on hypertension, hemodynamics, and fluid volume. Clin Pharmacol Ther 26: 562–565
Epstein SE, Braunwald E (1966) The effect of beta-adrenergic blockade on patterns of urinary sodium excretion: Studies in normal subjects and in patients with heart disease. Ann Int Med 65: 20–27
Epstein M, Oster JR (1982) Beta-blockers and the kidney. Miner Electrolyte Metab 8: 237–254
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baba, T., Murabayashi, S., Aoyagi, K. et al. Effects of dilevalol, an R, R-isomer of labetalol, on blood pressure and renal function in patients with mild-to-moderate essential hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 35, 9–15 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00555500
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00555500