Summary
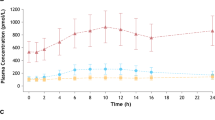
Pharmacokinetic and metabolic studies with3H-etilefrine were performed to assess the importance of a first-pass effect on the pharmacodynamic action of this sympathomimetic amine. Identical amounts of3H-activity, ca. 80% of the dose, were excreted in the urine after intravenous or oral administration, which indicates complete enteral absorption of the drug. Comparison of the areas under the plasma curves of unchanged etilefrine after both routes of administration resulted in a bioavailability factor of 0.55, which can be explained by an extensive first-pass effect. The time curve of plasma levels of etilefrine was compatible with an open 2-compartment model characterized by a rather large volume of distribution (Vd, β) of 160 1, and a predominant half life of 2 hours. The pharmacodynamic action corresponded to the amount of drug in the central compartment. The major pathway of metabolism of etilefrine was conjugation to form the phenolic sulphate, and a very minor proportion of the drug was excreted as the corresponding hydroxymandelic acid. This metabolic pattern seems to confirm our hypothesis that phenylalkylamines with the hydroxyl group in the m-position of the benzene ring are predominantly conjugated in contrast to p-hydroxylated compounds which are mainly deaminated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray, G.A.: A simple efficient liquid scintillator for counting aqueous solutions in a liquid scintillation counter. Analyt. Biochem.1, 279–285 (1960)
Dost, F.H.: Grundlagen der Pharmakokinetik. Stuttgart: Georg Thieme Verlag 1968
Hengstmann, J.H., Konen, W., Konen, C., Eichelbaum, M., Dengler, H.J.: The physiological disposition ofp-octopamine in man. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol.283, 93–106 (1974)
Hengstmann, J.H., Konen, W., Konen, C., Eichelbaum, M., Dengler, H.J.: Bioavailability ofm-octopamine in man related to its metabolism. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol.8, 33–39 (1975)
Hengstmann, J.H.: Microcomputer program for the calculation of the parameters of the two-compartment open model and the amount of drug in central and peripheral compartment after repetitive dosing. (in preparation)
Lang, V.O.: Blutdruckwirksamkeit oraler Kreislaufmittel. Intern. Praxis9, 7–9 (1969)
Rangno, R.E., Kaufmann, J.S., Cavanaugh, J.H., Island, D., Watson, J.T., Oates, J.: Effects of a false neurotransmitter, phydroxynorephedrine, on the function of adrenergic neurons in hypertensive patients. J. clin. Invest.52, 952–960 (1973)
Schneider, K.W.: Untersuchungen über Veränderungen einiger Kreislaufgrößen unter der Wirkung sympathikomimetischer Substanzen. Arch. Kreisl. Forsch.255, 1–101 (1957)
Wagner, J.G.: Biopharmaceutics and relevant pharmacokinetics. Hamilton, III.: Drug Intelligence Publications 1971
Coleman, A.J., Leary, W.P., Asmal, A.C.: The cardiovascular effects of etilefrine. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol.8, 41–45 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Parts of these results have been presented as a thesis for the MD degree of the University of Giessen
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hengstmann, J.H., Weyand, U. & Dengler, H.J. The physiological disposition of etilefrine in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 9, 179–187 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00614015
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00614015