Abstract
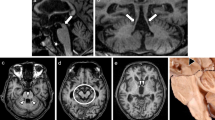
Our purpose was to investigate brain atrophy and signal intensity changes on MRI in patients with progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) and to correlate them with pathological features. We reviewed MRI and brain specimens of six patients with PSP, nine with Parkinson's disease (PD) and six with striatonigral degeneration (SND). Sagittal T1-weighted images showed that four patients with PSP had obvious reduction of anteroposterior midbrain diameter. T2-weighted images demonstrated diffuse high-signal lesions in the tegmentum and tectum of the midbrain of four patients, the upper pontine tegmentum of four, and the lower pontine tegmentum of two, but in no patient with PD or SND. The inferior olivary nuclei gave high signal intensity on T2-weighted images in one patient with PSP These signal intensity changes were consistent with the pathological findings. One patient with PSP showed abnormal signal intensity in the upper pontine tegmentum without atrophy of the midbrain. Midbrain atrophy and diffuse high-signal lesions on T2-weighted images in the tegmentum and tectum of the brain stem are characteristic of PSP
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steele JC, Richardson JC, Olszewski J (1964) Progressive supranuclear palsy. Arch Neurol 10: 333–359
Cardoso F, Jankovic J (1994) Progressive supranuclear palsy. In: Calne DB (ed) Neurodegenerative disease. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 769–786
Agid Y (1992) Conclusions. In: Litvan I, Agid Y (eds) Progressive supranuclear palsy. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 270–273
Lees AJ (1987) The Steele-RichardsonOlszewski syndrome. In: Marsden CD, Fahn S (eds) Movement disorders, vol 2. Butterworths, London, pp 272–287
Schonfeld SM, Golbe LI, Sage JI, Safer JN, Duvoisin RC (1987) Computed tomographic findings in progressive supranuclear palsy: correlation with clinical grade. Mov Disord 2: 263–278
Gibb WRG (1992) Neuropathology of Parkinson's disease and related syndromes. Neurol Clin 10: 361–376
House EA, Pansky B (1967) A functional approach to neuroanatomy, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 36–37
Carpenter MB, Sutin J (1983) Human neuroanatomy, 8th edn. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, p 524
Nolte J (1988) The human brain, 2nd edn. Mosby, St. Louis, pp 150, 274, 239
Truwit CL, Lempert TE (1994) High resolution atlas of cranial neuroanatomy. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 267, 456
Rutledge JN, Hilal SK, Silver AJ, Defendini R, Fahn S (1987) Study of movement disorders and brain iron by MR. AJNR 8: 397–411
Drayer PB, Olanow W, Burger P, Johnson GA, Herfkens R, Riederer S (1986) Parkinson plus syndrome: diagnosis using high field MR imaging of brain iron. Radiology 159: 493–498
Savoiardo M, Strada L, Girotti F, et al (1989) MR imaging in progressive supranuclear palsy and Shy-Drayer syndrome. J Comput Assist Tomogr 13: 555–560
Coffey CE, Alston S, Heinz ER, Burger PC (1989) Brain iron in progressive supranuclear palsy: clinical, magnetic resonance imaging, and neuropathological findings. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 1: 400–404
Giaccone G, Tagliavini F, Street JS, Ghetti B, Bugiani O (1988) Progressive supranuclear palsy with hypertrophy of the olives — an immunocytochemical study of the cytoskeleton of argyrophilic neurons. Acta Neuropathol 77: 14–20
Braffman BH, Grossman RI, Goldberg HI, et al (1988) MR imaging of Parkinson disease with spin-echo and gradient-echo sequences. AJNR 9: 1093–1099
Stern MB, Braffman BH, Skolnick BE, Hurtig HI, Grossmann RI (1989) Magnetic resonance imaging in Parkinson's disease and parkinsonian syndromes. Neurology 39: 1524–6
Aoki S, Okada Y, Nishimura K, et al (1989) Normal deposition of brain iron in childhood and adolescence: MR imaging at 1.5 T. Radiology 172: 381–385
Jellinger KA, Bancher C (1992) Neuropathology. In: Litvan I, Agid Y (eds) Progressive supranuclear palsy. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 44–88
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yagishita, A., Oda, M. Progressive supranuclear palsy: MRI and pathological findings. Neuroradiology 38 (Suppl 1), S60–S66 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02278121
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02278121