Abstract
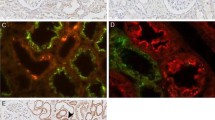
N-Acetylneuraminic acids (NANA) promote binding of calcium ions to macromolecules and cells, increase the intrinsic viscosity of glycoproteins and facilitate gel formation in water. Since these properties are crucial in urinary calculogenesis, we evaluated NANA levels in urine and serum as well as their expression in kidney tissues. Using a modified thiobarbituric acid assay, the evaluation of free and bound NANA in 24-h urine samples revealed a ratio of 1.87 in 33 non-stone-formers but a reversed ratio of 0.84 in 41 recurrent calcium oxalate stone-formers. Time kinetics revealed a gradual rise in NANA expression until 48 h of culture and a significantly higher release into supernatants of papillary renal epithelial cells (REC) when compared with cortical REC. To examine NANA distribution in kidney tissues, paraffin-embedded biopsies from five normal and six stone-forming kidneys were labeled with the biotinylated NANA-specific lectins Maackia amurensis (MAA) and Sambucus nigra (SNA). Immunohistochemistry revealed intense luminal MAA reactivity of distal tubular REC and collecting ducts in 96.7% and 91.5% of normal and stone-forming kidneys respectively. By contrast, there was a marked difference between normal and stone-forming kidneys for SNA reactivity (17.7% vs 95%) at the same locations. Finally, the glycocalyx of recurrent stone-formers showed altered sialylglycoside linkages [α(2,6) instead of α(2,3)] that may indicate an altered REC function. Given the calcium-binding potential of NANA, their increased local concentration within the glycocalyx layer in the distal nephron may either initiate stone formation or facilitate attachment of microcrystals to REC.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 14 November 1996 / Accepted: 17 June 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hofbauer, J., Fang-Kircher, S., Steiner, G. et al. N -Acetylneuraminic acids (nana): a potential key in renal calculogenesis. Urological Research 26, 49–56 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002400050023
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002400050023