Abstract
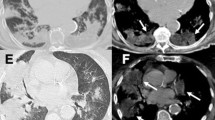
A series of nine infants, 2–8 months of age, with a history of animal or vegetable fat intake within 10 days after birth, is presented. The infants developed respiratory problems and failure to thrive. Plain films and computed tomography showed areas of consolidation in the medial-posterior parts of the lungs. The areas of consolidation showed three types of changes at computed tomography. Attentuation measurements did not reveal fat. Toestablish the diagnosis, fine needle aspiration biopsy, tru-cut biopsy and/or open lung biopsy was done in eight infants and bronchopulmonary lavage in one patient. The pathological findings were an intense lymphocytic infiltration with scattered granulomas which contained lipid deposit.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Laughlen GF (1925) Studies on pneumonia following naso-pharyngeal injections of oil. Am J Pathol 1:407
Ikeda K (1935) Oil aspiration pneumonia (Lipoid pneumonia): Clinical, Pathologic, and Experimental Consideration. Am J Dis Child 49:985
Goodwin TC (1934) Lipoid cell pneumonia. Am J Dis Child 48: 309
Pinkerton H (1927) Oils and fats; their entrance into and fate in the lungs of infants and children: A clinical and pathologic report. Am J Dis Child 33:259
Balakrishnan S (1973) Lipoid pneumonia in infants and children in South India. Br Med J 4:329
Bromer RS, Wolman IJ (1939) Lipoid pneumonia in infants and children. Radiology 32:1
Riff EJ, Moore CCM, Tufenkeji HT, Harfi H (1990) Infantile lipoid pneumonia. Ann Saudi Med 10:378
Gilbert A, Jomier J (1905) J Compt rend Soc Biol 19:87 (cited by Laughlen GF 1925)
Pinkerton H (1928) The reaction to oils and fats in the lungs. Arch Pathol 5:380
Corper HJ, Fried H (1922) Intratracheal injection of oils for therapeutic purposes. JAMA 79:1739
Wolfson BJ, Allen JL, Panitch HB, Karmazin N (1989) Lipid aspiration pneumonia due to gastroesophageal reflux. Pediatr Radiol 19:545
Pierson JW (1932) Some unusual pneumonias associated with the aspiration of fats and oils in the lungs. AJR 27:572
Brimblecombe FSW, Crome L, Tizard JPM (1951) Oil aspiration pneumonia in infancy, Arch Dis Childhood 25:141
Bakshi S, Bhakoo ON, Singh S, Bannerjee AK (1971) Lipoid Pneumonia. Indian Pediatr 8:793
Wheeler PS, Stitik FP, Hutchins GM, Klinefelter HF, Siegelmann SS (1981) Diagnosis of Lipoid pneumonia by computed tomography. JAMA 245:65
Joshi RR, Cholankeril JV (1985) Computed tomography in Lipoid Pneumonia. J Comput Assis Tomogr 9:211
de Oliveira GA, Del Caro SR, Bender Lamego CM, Mercon de Vargas PR, Vervloet VEC (1985) Radiographic plain film and CT findings in lipoid pneumonia in infants following aspiration of mineral oil used in the treatment of partial small bowel obstruction by Ascaris Lumbricoides. Pediatr Radiol 15:157
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hugosson, C.O., Riff, E.J., Moore, C.C.M. et al. Lipoid pneumonia in infants: a radiological-pathological study. Pediatr Radiol 21, 193–197 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02011045
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02011045