Abstract
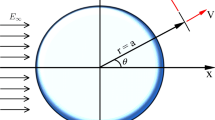
We observed that particles, suspended in an electrolyte and brought into crossed magnetic and electric fields of low intensities, will deviate in the central part of the electrophoresis chamber of a standard Zeiss Cytopherometer with a component vertical to both fields. The direction and magnitude, however, were sharply at variance with what would be expected by the action of the Lorentz force (EMF) on the surface of the particles. The magnitude of the deviation depends upon the magnetic and electric field strength, the ion concentration of the suspension medium and the geometry of the chamber. The movement of the particles is due to streaming of the electrolyte which is mainly caused by inhomogeneities of the electric field in the electrophoresis chamber. The magnitude of the effect is high enough to occur under physiological conditions. Magneto-electrophoretic streaming might eventually act as a transducer mechanism which could explain the ability of some animals to orientate themselves in the geomagnetic field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brauer, G.: Handbuch der prÄparativen anorganischen Chemie, 2. Aufl., p. 925. Stuttgart: Enke 1962
Cole, K. S.: Membranes, ions and impulses, p. 522. Berkeley: University of California Press 1968
Emlen, S. T., Wiltschko, W., Demong, N. J., Wiltschko, R., Bergman, S.: Magnetic direction finding: Evidence for its use in migratory indigo buntings. Science 193, 505–508 (1976)
Fuhrmann, G. F., Ruhenstroth-Bauer, G.: Cell electrophoresis empoying a rectangular measuring cuvette. In: Cell electrophoresis (ed. E. J. Ambrose), p. 22–25. London: Churchill 1965
Gak, E. Z.: Magnetohydrodynamic effect in strong electrolytes. Sov. Electrochem. 3, 75–78 (1967); Translation of: Elektrokhimiya 3, 89–93 (1967)
Hjerten, S.: Free zone electrophoresis, p. 51. Upsala: Almqvist & Wiksells Boktryckeri 1967
Kolin, A., Leenov, D., Lichten, W.: Electromagnetically engendered convection in electromagnetophoresis. Biochim. biophys. Acta 32, 535–538 (1959)
Kolin, A.: Continuous electrophoretic fractionation stabilized by electromagnetic rotation. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 46, 509–523 (1960)
Mehrishi, J. N., Gunter, R. C., Jr., Ruhenstroth-Bauer, G., LeBeau, R. J., Gunter, K. D., Bajorin, D. F.: The effect of low magnetic fields on the electrophoretic trajectories of blood elements, tumor cells, and other particles in electrophoresis chambers of rectangular and circular cross sections. Int. Congr. on Thrombosis and Haemostasis, Washington, D.C. 1972
Mohanta, S., Fahidy, T. Z.: The hydrodynamics of a magnetoelectric cell. J. Appl. Electrochem. 6, 211–220 (1976)
Presman, H. S.: Electromagnetic fields and life. New York: Plenum Press 1970
Ruhenstroth-Bauer, G., Gunter, R. C., Jr., Dimich, R., Jaeger, H.: Some observations on the trajectories of particles in crossed electric and magnetic fields. Int. Kongr. Physiologie, München 1971
Ruhenstroth-Bauer, G.: Der Einflu\ von kombinierten elektrischen und magnetischen Feldern auf biologische Zellen und andere Partikel. Haematologia 8, 517–521 (1974)
Smoluchowski, M. von: Elektrische Endosmose und Strömungsströme. Graetz Hdb. ElektrizitÄt und Magnetismus, Bd. 2, p. 366. Leipzig: Barth 1922
Wiltschko, W.: Kompa\systeme in der Orientierung von Zugvögeln. Schriftenreihe: Informationsaufnahme und Informationsverarbeitung im lebenden Organismus 2, Akademie der Wissenschaften. Wiesbaden: Steiner 1973
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gunter, R.C., Bamberger, S., Valet, G. et al. The trajectories of particles suspended in electrolytes under the influence of crossed electric and magnetic fields. Biophys. Struct. Mechanism 4, 87–95 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00538842
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00538842