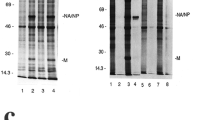
Abstract
Lentinan, a β-1,6;1,3-glucan, is tumor-specific for transplantable mouse solid-type tumors and it also stimulates the production of acute phase proteins (APPs). The APP response to lentinan is of the delayed type (DT-APR) and differs from that to lipopolysaccharide, which is acute. We found that the responses were genetically controlled in mice and that low responsiveness is dominant (Maeda et al. 1991). Using 123 segregants of crosses between SWR/J (a high responder) andMus spretus (a low responder), we analyzed the linkage between DT-APR responsiveness and the DNA polymerase chain reaction-simple sequence lenght polymorphism (PCR-SSLP) phenotype using 80 chromosome-specific microsatellite markers. We identified two loci (ltn1.1 andltn1.2) responsible for DT-APR.ltn1.1 is closely linked toD3Mit11 on chromosome 3 andltn1.2 toD11Nds9 on chromosome 11 (P<0.001). The linkage analysis also suggested thatltn1.2 is the major determinant for DT-APR. Correlation between lentinan-specific IL-6 mRNA expression (the late expression) controlled recessively and DT-APR induction suggests that theltn1 loci control some process(es) of IL-6 expression in the regulation step before NF-IL6.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avner, P., Amar, L., Dandolo, L., and Guenet, J. L. Genetic analysis of the mouse using interspecific crosses.Trends Genet 4: 18–23, 1988
Bretz, J. D., Williams, S. C., Baer, M., Johnson, P. F., and Schwartz, R. C. C/EBP-related protein 2 confers lipopolysaccharide-inducible expression of interleukin 6 and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 to a lymphoblastic cell line.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 7306–7310, 1994
Chihara, G., Hamuro, J., Maeda, Y. Y., Arai, Y., and Fukuoka, F. Fractionation and purification of the polysaccharides with marked antitumor activity, especially lentinan, fromLentinus edodes (Berk.) Sing. (an edible mushroom).Cancer Res 30: 2776–2781, 1970
Chihara, G., Maeda, Y. Y., and Hamuro, J. Current status and perspectives of immunomodulators of microbial origin.Int J Tiss Reac 4: 207–225, 1982
Chirgwin, J. M., Przybyla, A. E., MacDonald, R. J., and Rutter, W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease.Biochemistry 18: 5294–5299, 1979
Chiu, C.-P., Moulds, C., Coffman, R. L., Rennick, D., and Lee, F. Multiple biological activities are expressed by a mouse interleukin 6 cDNA clone isolated from bone marrow stromal cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 7099–7103, 1988
Dresser, D. W. and Phillips, J. M. The orientation of the adjuvant activities ofSalmonella typhosa lipopolysaccharide and lentinan.Immunology 27: 895–902, 1974
Fourney, R. M., Miyakoshi, J., Day, R. S., III, and Paterson, M. C. Northern blotting: efficient RNA staining and transfer.Focus 10: 5–7, 1988
Hamuro, J., Röllinghoff, M., and Wagner, H. Induction cytotoxic peritoneal exudate cells by T-cell immune adjuvants of the β (1→3) glucan-type lentinan and its analogues.Immunology 39: 551–559, 1980
Maeda, Y. Y. and Chihara, G. Lentinan, a new immunoaccelerator of cell-mediated responses.Nature 229: 634, 1971
Maeda, Y. Y., Chihara, G., and Ishimura, K. Unique increase of serum proteins and action of antitumor polysaccharides.Nature 252: 250–252, 1974
Maeda, Y. Y., Sakaizumi, M., Moriwaki, K., and Yonekawa, H. Genetic control of the expression of two biological activities of an antitumor polysaccharide, lentinan.Int J Immunopharmac 13: 977–986, 1991
Manabe, T., Takahashi, Y., Okuyama, T., Maeda, Y. Y., and Chihara, G. Identification of mouse serum proteins increased by the administration of antitumor polysaccharide lentinan, by micro two-dimensional electrophoresis.Electrophoresis 4: 242–246, 1983
Oliviero, S. and Cortese, R. The human haptoglobin gene promoter: interleukin-6-responsive elements interact with a DNA-binding protein induced by interleukin-6.EMBO J 8: 1145–1151, 1989
Paul, W. E. and Seder, R. A. Lymphocyte responses and cytokines.Cell 76: 241–251, 1994
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F., and Maniatis, T.Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual,2nd edn, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, 1989
Yoshioka, O., Abe, S., Masuko, Y., and Mizuno, D. Typing of immunomodulators in terms of their effects on the electrophoretic pattern of serum proteins and antitumor combination therapy based on this typing.Jpn J Canc Res 72: 471–478, 1981
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maeda, Y.Y., Takahama, S., Kohara, Y. et al. Two genes controlling acute phase responses by the antitumor polysaccharide, lentinan. Immunogenetics 43, 215–219 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587302
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587302