Abstract
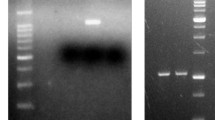
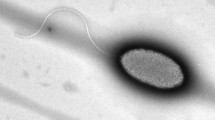
A polymerase chain reaction (PCR) protocol was developed for the specific detection of genes coding for type II polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) synthases. The primer-pair, I-179L and I-179R, was based on the highly conserved sequences found in the coding regions of Pseudomonas phaC1 and phaC2 genes. Purified genomic DNA or lysate of colony suspension can serve equally well as the target sample for the PCR, thus affording a simple and rapid screening of phaC1/C2-containing microorganisms. Positive samples yield a specific 540-bp PCR product representing partial coding sequences of the phaC1/C2 genes. Using the PCR method, P. corrugata 388 was identified for the first time as a medium-chain-length (mcl)-PHA producer. Electron microscopic study and PHA isolation confirmed the production of mcl-PHA in P. corrugata 388. The mcl-PHA of this organism has a higher molecular weight than that of similar polymers produced by other pseudomonads.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 16 August 1999 / Received revision: 23 December 1999 / Accepted: 4 January 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solaiman, D., Ashby, R. & Foglia, T. Rapid and specific identification of medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase gene by polymerase chain reaction. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 53, 690–694 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530000332
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530000332