Abstract
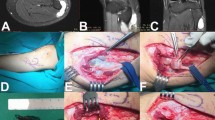
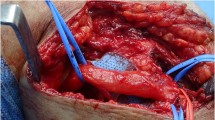
A case of peroneal nerve palsy caused by an intraneural ganglion is presented. The cystic mass was located posterolateral to the lateral femoral condyle and extended along the common peroneal nerve distal to the origin of the peroneus longus muscle. The nerve was compressed in the narrow fibro-osseous tunnel against the fibula neck and the tight origin of the peroneus longus muscle. The nerve was decompressed by complete tumor excision and transection of the origin of the peroneus longus muscle. Full recovery of nerve function was obtained in 6 months.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamazaki, H., Saitoh, S., Seki, H. et al. Peroneal nerve palsy caused by intraneural ganglion. Skeletal Radiol 28, 52–56 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002560050473
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002560050473