Summary
Intraosseus venography and measurement of intramedullary pressure have been carried out in the metaphyses of 55 patients with unilateral Perthes' disease.
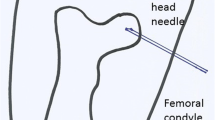
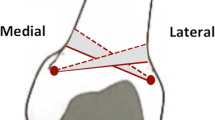
Flow of the opaque medium into the diaphysis is the most important finding in intraosseous venography of the metaphysis. This was related to a rise of intramedullary pressure which indicates the presence of venous congestion within the metaphysis. While such congestion was seen both in the sclerotic stage and the segmentation stage, it was not related to the severity of Perthes' disease as judged by Catterall's [1] classification. Such venous congestion could be relevant to the pathogenesis of Perthes' disease, but there are probably different factors which determine the prognosis.
Résumé
On a réalisé des phlébographies intra-osseuses et mesuré la pression intra-médullaire au niveau de la métaphyse chez 55 patients atteints d'une maladie de Perthes unilatérale.
L'irruption du produit opaque dans la diaphyse constitue le signe le plus important au cours de la phlébographie osseuse métaphysaire. Elle s'accompagne d'une élévation de la pression intramédullaire, ce qui traduit l'existence d'une congestion veineuse métaphysaire. Comme cette congestion s'observe aussi bien au stade de sclérose qu'à celui de segmentation, elle ne peut préjuger de la gravité de la maladie, selon la classification de Catterall [1]. La congestion veineuse peut jouer un rôle dans la pathogénie de la maladie de Perthes, mais le pronostic relève probablement de facteurs différents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Catterall, A.: The natural history of Perthes' disease. J. Bone Joint Surg. [Br.] 53, 37–53 (1971)
Hulth, A.: The vessel anatomy of the upper femur end with special regard to the mechanism of origin of different vascular disorders. Acta Orthop. Scand. 27, 192–209 (1958)
Inoue, A., Freeman, M. A. R., Mizuno, S.: The pathogenesis of Perthes' disease. J. Bone Joint Surg. [Br.] 58, 453–461 (1976)
Iwasaki, K.: Intraosseous venography of Perthes' disease. (in Japanese with English summary). J. Jpn. Orthop. Assoc. 51, 1361–1373 (1977)
Iwasaki, K.: The role of blood vessels within the ligamentum teres in Perthes' disease. Clin. Orthop. 159, 248–256 (1981)
McKibbin, B.; Ráliš, Z.: Pathological changes in a case of Perthes' disease. J. Bone Joint Surg. [Br.] 56, 438–447 (1974)
Mizuno, S.: Fallacy of phlebography for estimating the blood flow of the femoral head. Int. Surg. 52, 22–28 (1969)
Shiba, T.: Study on the Legg-Perthes' disease (in Japanese with English summary). J. Jpn. Orthop. Assoc. 39, 377–400 (1965)
Suramo, I., Puranen, J., Heikkinen, E., Vuorinen, P.: Disturbed patterns of venous drainage of the femoral neck in Perthes' disease. J. Bone Joint Surg. [Br.] 56, 448–453 (1974)
Trueta, J.: The normal vascular anatomy of the human femoral head during growth. J. Bone Joint Surg. [Br.] 39, 358–394 (1957)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iwasaki, K., Suzuki, R., Okazaki, T. et al. The haemodynamics of perthes' disease. International Orthopaedics 6, 141–148 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00267723
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00267723