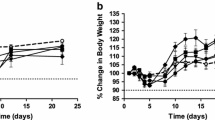
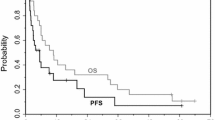
Abstract
The camptothecin analogues topotecan and irinotecan (CPT-11) are active anticancer drugs. This article reviews the accumulated results of clinical and laboratory studies performed with these agents at The Johns Hopkins Oncology Center. In a phase I clinical and pharmacology trial of topotecan given as a 30-min infusion daily for 5 days every 3 weeks, profound neutropenia precluded dose escalation above 1.5–2.0 mg/m2 per day, the maximum tolerated dose (MTD). The daily ×5 schedule has been developed further with dose escalation using granulocytecolony-stimulating factor support in patients who have kidney or liver dysfunction and given in combination with cisplatin. In addition, a phase I trial of topotecan given as a 5-day continuous intravenous infusion to patients with refractory leukemia has had promising antileukemic responses. A separate series of in vitro studies indicates that a modest degree of resistance to the cytotoxicity of topotecan can be mediated by P-glycoprotein. A phase I and pharmacology study of irinotecan given as a 90-min infusion every 3 weeks has defined an MTD of 240 mg/m2, with dose escalation being limited by several toxicities. These included an acute treatment-related syndrome of flushing, warmth, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea; a subacute combination of nausea, diarrhea, anorexia, and weight loss; and/or neutropenia. Antitumor activity has been observed with topotecan and irinotecan in patients with a variety of solid tumors and refractory leukemia in our studies, which supports the widespread enthusiasm for this group of compounds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burris HA, Rothenberg ML, Kuhn JG, Von Hoff DD (1992) Clinical trials with the topoisomerase I inhibitors. Semin Oncol 19:663–669
Chen AY, Yu C, Potmesil M, Wall ME, Wani MC, Liu LF (1992) Camptothecin overcomes MDR-1 mediated resistance in human KB carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 51:6039–6044
Culine S, DeForni M, Extra JM, Chabot GG, Madelaine I, Heriat P, Bugat R, Marty M, Mathieu-Boué A (1992) Phase I study of the camptothecin analogue CPT-11, using a weekly schedule. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 11:110
Gandia D, Armand JP, Chabot G (1992) Phase I study of the new camptothecin analogue CPT-11 administered every 3 weeks. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 33:260
Grochow LB, Rowinsky EK, Johnson R, Ludeman S, Kaufmann SH, McCabe FL, Smith BR, Hurowitz L, DeLisa A, Donehower RC, Noe DA (1992) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of topotecan in patients with advanced cancer. Drug Metab Dispos 20:706–712
Grochow LB, Slichenmyer WJ, Rowinsky EK, Donehower RC, Forastiere A, Chen T-L (1994) Phase I clinical and pharmacologic study of topotecan in patients with hepatic or renal dysfunction (abstract). In: Henrar REC (ed) Proceedings of the 8th NCI-EORTC Symposium on New Drugs in Cancer Therapy. March 15–18, 1994, Kluwer, Amsterdam, p 191
Hendricks CB, Rowinsky EK, Grochow LB, Donehower RC, Kaufmann SH, (1992) Effect of P-glycoprotein expression on the accumulation and cytotoxicity of topotecan (SK&F 104864), a new camptothecin analogue. Cancer Res 52:2268–2278
Hsaing Y-H, Hertzberg R, Hecht S, Liu LF (1985) Camptothecin induces protein-linked DNA breaks via mammalian DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem 260:14873–14878
Johnson R, McCabe F, Yu Y (1992) Combination regimens with topotecan in animal tumor models. Proceedings, 7th NCI-EORTC Symposium on New Drugs in Cancer Therapy, Amsterdam, March 17–20, 1992, p 5
Kano Y, Suzuki K, Akutsu M, Suda K, Inoue Y, Yoshida M, Sakamoto S, Miura Y (1992) Effects of CPT-11 in combination with other anti-cancer agents in culture. Int J Cancer 50:604–610
Katz EJ, Vick JS, Kling KM, Andrews PA, Howell SB (1990) Effect of topoisomerase modulators on cisplatin cytotoxicity in human ovarian carcinoma cells. Eur J Cancer 26:724–727
Kingsbury WD, Boehm JC, Jakas DR, Holden KG, Hecht SM, Gallagher G, Caranfa MJ, McCabe FL, Faucette LF, Johnson RK, Hertzberg RP (1991) Synthesis of water-soluble (aminoalkyl)camptothecin analogues: inhibition of topoisomerase I and antitumor activity. J Med Chem 34:98–107
Kuhn J, Burris S, Wall J, et al (1990) Pharmacokinetics of the topoisomerase I inhibitor, SK and F 104864. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 9:70
Kunimoto T, Nitta K, Tanaka T, Uehara N, Baba H, Takeuchi M, Yokokura T, Sawada S, Miyasaka T, Mutai M (1987) Antitumor Activity of 7-ethyl-10-[4-(1-piperidino)-1-piperidino]-carbonyloxy-camptothecin, a novel water-soluble derivative of camptothecin, against murine tumors. Cancer Res 47:5944–5947
Liu LF (1989) DNA topoisomerase I poisons as antitumor drugs. Annu Rev Biochem 58:351–375
Mattern MR, Hofmann GA, Polsky RM, Johnson RK (1993) Cross resistance of MDR, P-glycoprotein overexpressing CHO cells to camptothecin analogues (abstract 2529). Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 34:424
Miller AA, Hargis JB, Fields S, Lilenbaum RC, Rosner GL, Schilsky RL (1993) Phase I study of topotecan and cisplatin in patients with advanced cancer (CALGB 9261) (abstract 1367). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 12:399
Naito M, Hamada H, Tsuruo T (1988) ATP/Mg2+-dependent binding of vincristine to the plasma membrane of multidrug-resistant k562 cells. J Biol Chem 26:11887–11891
Ohe Y, Sasaki Y, Shinkai T, Eguchi K, Tamura T, Kojima A, Oshita F, Miya T, Okamoto H, Yoshioka H, Fukuoka M, Niitani H, Taguchi T, Saijo N (1991) Pharmacokinetics with a 5-day continuous infusion of a camptothecin derivative, CPT-11. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 10:117
Rothenberg ML, Burris HA III, Eckardt JR, Rinaldi DA, Weiss GR, Smith S, Jones K, Johnson RK, Von Hoff DD (1993) Phase I/II study of topotecan + cisplatin in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (abstract 423). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 12:156
Rowinsky EK, Grochow LB, Hendricks CB, Ettinger DS, Forastiere AA, Hurowitz LA, McGuire WP, Sartorius SE, Lubejko BG, Kaufmann SH, Donehower RC (1992) Phase I and pharmacologic study of topotecan: a novel topoisomerase I inhibitor. J Clin Oncol 10:647–656
Rowinsky E, Sartorius S, Grochow L, Forastiere A, Lubejko B, Hurowitz L, Donehower R (1992) Phase I and pharmacologic study of topotecan, an inhibitor of topoisomerase I, with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF): toxicologic differences between concurrent and post-treatment G-CSF administration. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 11:116
Rowinsky EK, Grochow LB, Ettinger DS, Sartorius SE, Lubejko BG, Chen T-L, Rock M, Donehower RC (1994) Phase I and pharmacologic study of the novel topoisomerase I inhibitor CPT-11 administered as a 90 minute infusion every three weeks. Cancer Res (in press)
Rowinsky E, Grochow L, Kaufmann S, Bowling K, Lubejko B, Chen T, Ettinger D, Peereboom D, Sartorius S, Donehower R (1994) Sequence-dependent effects of topotecan (T) and cisplatin (C) in a phase I and pharmacological study (abstract). In: Henrar REC (ed) Proceedings of the 8th NCI-EORTC Symposium on New Drugs in Cancer Therapy. March 15–18, 1994, Kluwer, Amsterdam, p 192
Saltz L, Sirott M, Young C, Tong W, Niedzwiecki D, Tzy-Jyun Y, Tao Y, Trochanowski B, Wright P, Barbosa K, Toomasi F, Kelsen D (1993) Phase I clinical and pharmacology study of topotecan given daily for 5 consecutive days to patients with advanced solid tumors, with attempt at dose intensification using recombinant granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. J Natl Cancer Inst 85: 1499–1507
Slichenmyer WJ, Rowinsky ER, Donehower RC, Kaufman SH (1993) The current status of camptothecin analogues as antitumor agents. J Natl Cancer Inst 85:271–92
Verweij J, Lund B, Beynen J, et al (1992) Clinical studies with topotecan: the EORTC experience. Proceedings 7th NCI-EORTC Symposium on New Drugs in Cancer Therapy, Amsterdam, March 17–20, 1992, p 118
Wall ME, Wani MC, Cook CE, Palmer KH, McPhail AT, Sim GA (1966) Plant antitumor agents. I. The isolation and structure of camptothecin, a novel alkaloidal leukemia and tumor inhibitor fromCamptotheca acuminata. J Am Chem Soc 88:3888–3890
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Slichenmyer, W.J., Rowinsky, E.K., Grochow, L.B. et al. Camptothecin analogues: studies from The Johns Hopkins Oncology Center. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 34 (Suppl 1), S53–S57 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00684864
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00684864