Abstract
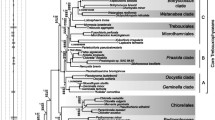
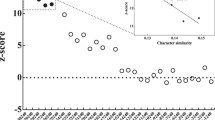
We have generated secA sequence data from a number of photosynthetic prokaryotes and carried out a phylogenetic analysis using secA sequences from prokaryotes, green plants, and red and brown algae. We have studied the substitution patterns that give rise to the apparent phylogenetic structure. We show that the high AT content of the plastid sequences significantly affects the amino-acid composition. We also show that most of the apparent evidence for an edge separating red and brown plastids from green plants within the phylogenetic tree is due to differences in nucleotide composition. The remaining apparent evidence is likely to be due, at least in part, to differences in the distribution of sites free to vary. We discuss the implications of this study for hypotheses of plastid origins.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 21 May / 8 September 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barbrook, A., Lockhart, P. & Howe, C. Phylogenetic analysis of plastid origins based on secA sequences. Curr Genet 34, 336–341 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002940050404
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002940050404