Summary
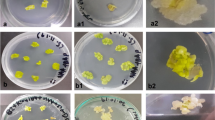
The wild species Solanum integrifolium represents a source of pest and disease resistance genes for breeding strategies of the cultivated species Solanum melongena. Somatic hybridization via protoplast fusion between the two species may provide a valuable tool for transferring polygenic traits into the cultivated species. The availability of S.integrifolium cells carrying dominant selectable markers would facilitate the heterokaryon rescue. An appropriate methodology for in vitro culture and plant regeneration from leaf explants of S.integrifolium is reported. Efficient leaf-disk transformation via co-cultivation with Agrobacterium tumefaciens led to the regeneration of transformed plants carrying the reporter genes GUS and NPT-II. Transformed individuals were obtained through selection on kanamycin-containing medium. Stable genetic transformation was assessed by histochemical and enzymatic assays for GUS and NPT-II activity, by the ability of leaf disks to initiate callus on Km-containing medium, Southern blot analyses of the regenerated plants, and genetic analysis of their progenies. Selfed-seed progeny of individual transformed plants segregated seedlings capable to root and grow in selective condition, while untransformed progeny did not. Genetic analyses of progeny behaviour showed that the reporter gene NPT-II segregated as single as well as two independent Mendelian factors. In two cases an excess of kanamycin-sensitive seedlings was obtained, not fitting into any genetic hypothesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog (1962) medium
- NOS:
-
nopaline synthase
- NPT-II:
-
neomycin phosphotransferase
- GUS:
-
beta-glucuronidase
- LB:
-
Luria and Bertani medium
- KIN:
-
6-furfurylaminopurine
- BAP:
-
6-benzylaminopurine
- 2iP:
-
N6-(2-isopentyl)adenine
- ZEA:
-
zeatin
- TDZ:
-
Thidiazuron
References
Akamatsu T, Yoshida M, Shiga T (1989) In: Iyama S, Takeda G (eds) Breeding Research: The key to the survival of the earth. SABRAO, Japan, pp 463–466
Chambonnet D (1985) Ph D Thesis, Academie de Montpellier, France
Deblaere R, Bytebier B, De Greve A, Deboeck F, Schell J, Van Montagu M, Leemans J (1985) Nucleic Acids Res 13:4777–4788
Dikii SP, Voronina MV (1985) Trudy Prikl Botan Genet Selek 81:71–75
Draper J, Scott R, Armitage P, Walden R (1988) Plant Genetic Transformation and Gene Expression. Blackwell Sci. Publ., Oxford.
Heller R (1953) Ann Sci Nat Bot Biol Veg 14:1–22
Hoekema A, Hirsch PR, Hooykaas PJJ (1983) Nature 303:179–180
Horsch RB, Fry JE, Hoffmann N, Wallroth M, Eichholtz D, Rogers SG, Fraley RT (1985) Science 227:1229–1231
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) Embo J 6:3901–3907
Matzke MA, Matzke AJM (1991) Plant Mol Biol 16:821–830
McCormick S, Niedermeyer J, Fry J, Barnason A, Horsch R, Fraley R (1986) Plant Cell Rep 5:81–84
McDonnell RE, Clark RD, Smith WA, Hinchee MA (1987) Plant Mol Biol Rep 5:380–386
Morel G, Wetmore RH (1951) Am J Bot 38:141–143
Müller-Gensert E, Schieder O (1987) Mol Gen Genet 208:235–241
Murashige T, Skoog F (1982) Physiol Plant 15:473–498
Nevers P, Shepard N, Saedler H (1986) Adv Bot Res 12:103–203
Okimura M, Matsuo S, Arai K, Okitsu S (1986) Bull Veg Ornam Crops Res Stat (Kurume) 9:43–58
Rotino GL, Gleddie S (1990) Plant Cell Rep 9:26–29
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KM, Jorgensen RA, Allard RW (1984) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:8014–8018
Schmidt R, Willmitzer L (1988) Plant Cell Rep 7:583–586
Southern EM (1975) J Mol Biol 98:503–517
Vancanneyt G, Schmidt R, O'Connor-Sanchez A, Willmitzer L, Rocha-Sosa M (1990) Mol Gen Genet 220:245–250
Yamakawa K, Mochizuki H (1979) Bull Veget Ornam Crops Res Stat (Yasai) 6:19–27
Zambryski P, Joos H, Genetello C, Leemans J, Van Montagu M, Schell J (1983) Embo J 2:2143–2150
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by H. Lörz
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rotino, G.L., Perrone, D., Ajmone-Marsan, P. et al. Transformation of Solanum integrifolium poir via Agrobacterium tumefaciens: Plant regeneration and progeny analysis. Plant Cell Reports 11, 11–15 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231831
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231831