Abstract
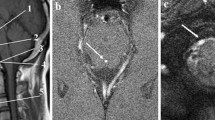
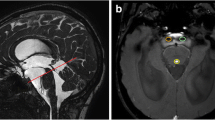
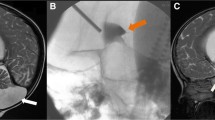
Fifteen patients with solid and cystic occlusions of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) circulation pathways were examined with MRI using an ECG retrogated two-dimensional FISP sequence to determine whether there are certain defined pathological CSF flow patterns in these patients. All patients were clinically still compensated. The results of the measurements of CSF flow velocities at different locations in the CSF system were compared with the results from 8 healthy volunteers. In all patients with occlusive processes of the intraventricular CSF pathways (4 aqueduct stenoses, 1 membranous occlusion of the fourth ventricular outlets, 1 solid tumour at the foramen of Monro and 1 solid fourth ventricular tumour) we observed hyperdynamic CSF pulsation above the lesion. This was transmitted into the spinal canal. Close by a solid occlusion within the aqueduct the flow velocity curve over the RR cycle was typically shifted, resulting in a mirroring of the flow velocity curve compared with normals. In cystic lesions (n = 4) there was transmission of the pulsation wave through the lesion and therefore no mirroring of the flow velocity curve. This technique allows very good delineation of cystic structures in the peripineal region (n = 4), also due to the opposite direction of flow within the cyst compared with the surrounding CSF spaces, depending on the extent of communication.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Du Boulay GH (1966) Pulsatile movements in the CSF pathways. Br J Radiol 39: 255–262
Du Boulay GH, O'Connel J, Currie J, Bostick T, Verity P (1972) Further investigations on pulsatile movements in the cerebrospinal fluid pathways. Acta Radiol 13: 496–523
Bradley WG Jr, Kortman KE, Burgoyne B (1986) Flowing cerebrospinal fluid in normal and hydrocephalic states: appearance of MR images. Radiology 159: 611–616
Kunz U, Heintz P, Ehrenheim C, Dietz H, Hundeshagen H (1989) CSF-Flow visualization by MR imaging technique. In: Frowein RA, Brock M, Klinger M (eds) Advances in neurosurgery vol 17. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 351–356
Bradley WG Jr (1991) Phase-contrast imaging documents CSF in motion. Diagn Imaging: 116–119
Hennig J, Ott D, Adam T, Friedburg H (1990) Measurement of CSF flow using an interferographic MR technique based on the RARE-FAST imaging sequence. Magn Reson Imaging 8: 543–556
Kunz U, Heintz P, Ehrenheim C, Stolke D, Dietz H (1989) MRI as the primary diagnostic instrument in normal pressure hydrocephalus? Psychiatric Res 29: 287–288
Hofmann E, Meixensberger J, Warmuth-Metz M, Becker T, Pfister K, Jackel M (1993) Aqueductal cerebrospinal fluid flow phenomena on magnetic resonance imaging: comparision with intracranial pressure and cerebrospinal fluid dynamics. In: Lorenz R, Klinger M, Brock M (eds) Advances in neurosurgery vol 21. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 145–150
Schroth G, Klose U (1992) Cerebrospinal fluid flow. III. Pathological cerebrospinal fluid pulsations. Neuroradiology 35: 16–24
Sherman JL, Citrin CM, Gangerosa RE, Bowen BJ (1987) The MR appearance of CSF flow in patients with ventriculomegaly. AJR 148: 193–199
Goldmann A, Kunz U, Rotermund G, Friedrich JM, Schnarkoski P (1992) Magnetresonanztomograpische Darstellung der Liquorpulsbewegung bei Hydrozephalus communicans vor und nachh Shuntanlage. Fortschr Rontgenstr 157: 555–560
Ridgway JP, Turnbull LW, Smith MA (1987) Demonstration of pulsatile cerebrospinal-fluid flow using magentic resonance phase imaging. Br J Radiol 60: 423–427
Enzmann DR, Pelc NJ (1991) Normal flow patterns of intracranial and spinal cerebrospinal fluid defined with phase-contrast cine MR imaging. Radiology 178: 467–474
Nitz WR, Bradley WG Jr, Watanabe AS, Lee RR, Burgoyne B, O'Sullivan RM, Herbst MD (1992) Flow dynamics of cerebrospinal fluid: assessment with phase-contrast velocity MR imaging performed with retrospective cardiac gating. Radiology 183: 395–405
Mascalchi M, Ciraolo L, Tanfani G, Taverni G, Inzitari D, Siracusa GF, Dal Pozzo GC (1988) Cardiac-gated aqueductal CSF flow. J Comput Assist Tomogr 12: 923–926
Schroth G, Klose U (1992) Cerebrospinal fluid flow. I. Physiology of cardiac-related pulsation. Neuroradiology 35: 1–9
Schroth G, Klose U (1992) Cerebrospinal fluid flow. II. Physiology of respiration-related pulsation. Neuroradiology 35: 10–15
Harders A (1986) Neurosurgical applications of transcranial Doppler sonography. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 115–118
Kunz U, Wallner B, Oldenkott P (1993) Endoscopic fenestration of septations in the CSF space. Acta Neurochir (Wien) [Suppl] (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: U. Kunz
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kunz, U., Goldmann, A., Karras, U. et al. CSF pulsation patterns in occlusive hydrocephalus. Eur. Radiol. 4, 133–141 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231199
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231199