Abstract
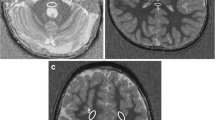
The aim of our work was to determine the efficacy of turbo inversion recovery spin echo (TIRSE) pulse sequences in differentiating patients with normal and abnormal myelination. Twenty neurological normal children (aged 5 months to 12 years) as well as 65 children presenting clinically with neurologic developmental deficits (aged 2 months to 10 years) were examined using TIRSE, T1-weighted SE, and T2-weighted turbo SE pulse sequences. Contrast-to-noise-ratio (CNR) between myelinated white and gray matter was compared for the different pulse sequences. In addition, two readers analyzed all images qualitatively by consensus. The CNR values were significantly higher on TIRSE images as compared with conventional images (p < 0.05). Forty-two neurologically abnormal patients displayed a normal myelination on all sequences, whereas 23 showed an abnormal myelination. The TIRSE sequence provided a sensitive and specific depiction of an abnormal myelination in all of these patients. The TIRSE sequence provided additional information to conventional pulse sequences in determining myelination disorders in children, especially in children older than 2 years.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 13 November 1996; Revision received 12 March 1997; Accepted 11 April 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daldrup, H., Schuierer, G., Link, T. et al. Evaluation of myelination and myelination disorders with turbo inversion recovery magnetic resonance imaging. Eur Radiol 7, 1478–1484 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003300050320
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003300050320