Abstract
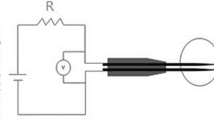
For measuring air velocities in swirling flows a differential pressure probe of small axial length was developed. The determination of the velocity is based on measuring the difference between the stagnation pressure and the base pressure of a circular disk whose surface is perpendicular to the main flow direction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Debler WR (1990) Fluid mechanics fundamentals, Prentice-Hall
Ostowari C;Wentz JrWH (1983) Modified calibration technique of a five-hole probe for high flow angles. Exp Fluids 1: 166–168
Ower E;Pankhurst RC (1977) The measurement of air flow. 5th edition, p. 35. Oxford: Pergamon
Zilliac GG (1993) Modelling, calibration, and error analysis of seven-hole pressure probes. Exp Fluids 14: 104–120
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, U. A differential-pressure probe for velocity measurements in swirling air flows. Experiments in Fluids 20, 134–135 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01061592
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01061592