Summary
-
1.
Radiotracer and cannulation techniques have been used to measure branchial fluxes and internal distributions of sodium in freshwater adapted rainbow trout at rest, during one hour of swimming activity, and during one hour of postexercise recovery.
-
2.
Activity was imposed by manual chasing in a small chamber. Ventilatory and cardiovascular changes occurring during and after this procedure were similar to those associated with normal swimming.
-
3.
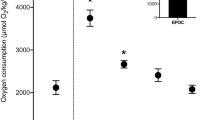
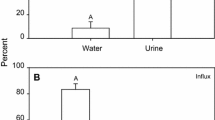
Sodium efflux rate equalled influx at rest, increased 70% during exercise, and returned to slightly below resting levels during recovery; influx rate remained invariant under the three treatments. The switch from a negative to a positive branchial sodium balance at the end of exercise occurred extremely rapidly.
-
4.
Despite the branchial deficit, plasma sodium levels tended to rise in active fish. This effect was associated with an apparent reduction in blood volume.
-
5.
Terminal concentrations of sodium and water in “white” muscle did not differ significantly among treatment groups.
-
6.
Expansion of the radiosodium space in active and recovering trout exceeded that in resting animals because of a faster rate of dispersal of influxed sodium out of the plasma compartment into tissues other than “white” muscle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennion, G.: The control of the function of the heart in teleost fish. M. Sc. Thesis, University of British Columbia, Department of Zoology 1968.
Bentley, P. J.: Permeability of the skin of the cyclostomeLampetra fluviatilis to water and electrolytes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.6, 95–97 (1962).
Brett, J. R.: The respiratory metabolism and swimming performance of young sockeye salmon. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Canada21, 1183–1226 (1964).
Cameron, J. N., Davis, J. C.: Gas exchange in rainbow trout with varying blood oxygen capacity. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Canada27, 1069–1085 (1970).
Conte, F. P.: Salt secretion. In: Fish physiology, vol. I. (W. S. Hoar and D. J. Randall, eds.) New York: Academic Press, Inc. 1969.
Davis, J. C.: The influence of temperature and activity on certain cardiovascular and respiratory parameters in adult sockeye salmon. M. Sc. Thesis, University of British Columbia, Department of Zoology 1968.
Duncan, D. B.: Multiple range and multipleF tests. Biometrics11, 1–42 (1955).
Farmer, G. J., Beamish, F. W. H.: Oxygen consumption ofTilapia nilotica in relation to swimming speed and salinity. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Canada26, 2807–2821 (1969).
Fromm, P. O.: Some quantitative aspects of ion regulation in teleosts. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.27, 865–869 (1968).
Garcia-Romeu, F., Maetz, J.: The mechanism of sodium and chloride uptake by the gills of a fresh-water fish,Carassius auratus. I. Evidence for an independent uptake of sodium and chloride ions. J. gen. Physiol.47, 1195–1207 (1964).
Hildebrandt, J., Young, A. C.: Anatomy and physics of respiration. In: Physiology and biophysics (T. C. Ruch and H. D. Patton, eds.). Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders Co. 1965.
Holeton, G. F., Randall, D. J.: Changes in blood pressure in the rainbow trout during hypoxia. J. exp. Biol.46, 297–305 (1967).
Holmes, W. N.: Studies on the hormonal control of sodium metabolism in the rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Acta endocr. (Kbh.)31, 587–602 (1959).
Houston, A. H.: Osmoregulatory adaptation of steelhead trout (Salmo gairdneri Richardson) to sea water. Canad. J. Zool.37, 729–748 (1959).
Houston, A. H., De Wilde, M. A.: Environmental temperature and the body fluid system of the fresh-water teleost-III. Hematology and blood volume of thermally acclimated brook trout,Salvelinus fontinalis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.28, 877–885 (1969).
Hughes, G. M.: The dimensions of fish gills in relation to their function. J. exp. Biol.45, 177–195 (1966).
Hughes, G. M., Grimstone, A. V.: The fine structure of the secondary lamellae of the gills ofGadus pollachius. Quart. J. micr. Sci.106, 343–353 (1965).
Kerstetter, T. H., Kirschner, L. B., Rafuse, D. D.: On the mechanisms of sodium ion transport by the irrigated gills of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). J. gen. Physiol.56, 342–359 (1970).
Keys, A., Bateman, J. B.: Branchial responses to adrenaline and pitressin in the eel. Biol. Bull.63, 327–336 (1932).
Kirschner, L. B.: On the mechanism of active sodium transport across frog skin. J. cell. comp. Physiol.45, 61–87 (1955).
Kirschner, L. B.: Ventral aortic pressure and sodium fluxes in perfused eel gills. Amer. J. Physiol.217, 596–604 (1969).
Kirschner, L. B.: The study of NaCl transport in aquatic animals. Amer. Zoologist10, 365–376 (1970).
Kramer, C. Y.: Extension of multiple range tests to group means with unequal numbers of replications. Biometrics12, 307–310 (1956).
Krawkow, N. P.: Über die Wirkung von Giften auf die Gefässe isolierter Fischkiemen. Arch. ges. Physiol.151, 583–603 (1913).
Labat, R., Raynaud, P., Serfaty, A.: Réactions cardiaques et variations de masse sanguine chez les téléostéens. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.4, 75–80 (1961).
Maetz, J.: Les échanges de sodium chez le poissonCarassius auratus L. Action d'un inhibiteur de l'anhydrase carbonique. J. Physiol. (Paris)48, 1085–1099 (1956).
Manery, J. F.: Water and electrolyte metabolism. Physiol. Rev.34, 334–417 (1954).
Maren, T. H.: Bicarbonate formation in cerebrospinal fluid: role of sodium transport and pH regulation. Amer. J. Physiol.222, 885–899 (1972).
Mayer, N., Nibelle, J.: Sodium space in fresh-water and sea-water eels. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.31, 589–597 (1969).
Miles, H. M., Smith, L. S.: Ionic regulation in migrating juvenile coho salmon,Oncorhyncus kisutch. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.26, 381–398 (1968).
Morris, R., Bull, J. M.: Studies on fresh-water osmoregulation in the ammocoete larva ofLampetra planeri (Bloch). III. The effect of external and internal sodium concentration on sodium transport. J. exp. Biol.52, 275–290 (1970).
Nakano, T., Tomlinson, N.: Catecholamine and carbohydrate metabolism in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) in relation to physical disturbance. J. Fish Res. Bd. Canada24, 1701–1715 (1967).
Newstead, J. D.: Fine structure of the respiratory lamellae of teleostean gills. Z. Zellforsch.79, 396–428 (1967).
Östlund, E., Fange, R.: Vasodilation by adrenalin and noradrenalin, and the effects of some other substances on perfused fish gills. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.5, 307–309 (1962).
Randall, D. J., Baumgarten, D., Maylusz, M.: The relationship between gas and ion transfer across the gills of fishes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol41A, 629–638 (1972).
Randall, D. J., Holeton, G. F., Stevens, E. D.: The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide across the gills of rainbow trout. J. exp. Biol.46, 339–348 (1967).
Randall, D. J., Smith, L. S.: The effect of environmental factors on circulation and respiration in teleost fish. Hydrobiologia19, 113–124 (1967).
Randall, D. J., Stevens, E. D.: The role of adrenergic receptors in cardiovascular changes associated with exercise in salmon. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.21, 415–424 (1967).
Rao, G. M. M.: Oxygen consumption of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) in relation to activity and salinity. Canad. J. Zool.46, 781–786 (1968).
Rao, G. M. M.: Effect of activity, salinity and temperature on plasma concentrations of rainbow trout. Canad. J. Zool.47, 131–134 (1969).
Richards, B. D., Fromm, P. O.: Patterns of blood flow through filaments and lamellae of isolated-perfused rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) gills. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.29, 1063–1070 (1969).
Richards, B. D., Fromm, P. O.: Sodium uptake by isolated-perfused gills of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Comp. Biochem, Physiol.33, 303–310 (1970).
Saunders, R. L.: The irrigation of gills in fishes. I. Studies of the mechanism of branchial irrigation. Canad. J. Zool.39, 637–653 (1961).
Shehadeh, Z. H., Gordon, M. S.: The role of the intestine in salinity adaptation of the rainbow trout,Salmo gairdneri. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.30, 397–418 (1969).
Smith, L. S.: Blood volume of three salmonids. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Canada23, 1439–1446 (1966).
Smith, L. S., Bell, G. R.: A technique for prolonged blood sampling in freeswimming salmon. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Canada21, 711–717 (1964).
Smith, L. S., Brett, J. R., Davis, J. C.: Cardiovascular dynamics in swimming adult sockeye salmon. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Canada24, 1775–1790 (1967).
Steen, J. B., Kruysse, A.: The respiratory function of teleostean gills. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.12, 127–142 (1964).
Stevens, E. D.: The effect of exercise on the distribution of blood to various organs in rainbow trout. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.25, 615–625 (1968).
Stevens, E. D., Black, E. C.: The effect of intermittent exercise on carbohydrate metabolism in rainbow trout,Salmo gairdneri. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Canada23, 471–485 (1966).
Stevens, E. D., Randall, D. J.: Changes in blood pressure, heart rate, and breathing rate during moderate swimming activity in rainbow trout. J. exp. Biol.46, 307–315 (1967a).
Stevens, E. D., Randall, D. J.: Changes of gas concentrations in blood and water during moderate swimming activity in rainbow trout. J. exp. Biol.46, 329–337 (1967b).
Taylor, W., Houston, A. H., Horgan, J. D.: Development of a computer model simulating some aspects of the cardiovascular-respiratory dynamics of the salmonid fish. J. exp. Biol.49, 477–494 (1968).
Toews, D. P.: The effect of cycling temperatures on electrolyte balance in skeletal muscle and plasma of rainbow trout.Salmo gairdneri. M. Sc. Thesis. University of Alberta, Department of Zoology 1966.
Toews, D. P., Hickman, C. P.: The effect of cycling temperatures on electrolyte balance in skeletal muscle and plasma of rainbow troutSalmo gairdneri. Comp. Biochem. Physiol29, 905–918 (1969).
Wolf, K.: Physiological salines for fresh water teleosts. Progr. Fish. Cult.25, 135–140 (1963).
Wood, C. M., Randall, D. J.: The effect of anaemia on ion exchange in the southern flounder (Paralichthys lethostigma). Comp. Biochem. Physiol.39A, 391–402 (1971).
Wood, C. M., Randall, D. J.: The influence of swimming activity on water balance in the rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). J. comp. Physiol.82, 257–276 (1973a).
Wood, C. M., Randall, D. J.: Sodium balance in the rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) during extended exercise. J. comp. Physiol.82, 235–256 (1973b).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors wish to thank Dr. J. E. Phillips, Dr. D. P. Toews, Dr. J. C. Davis, Dr. J. N. Cameron, and Miss O. Johannsson for their help in various aspects of the project. Constructive criticism of the manuscript by Dr. G. Shelton and Dr. D. R. Jones is also greatly appreciated. The work was supported by grants from the National Research Council of Canada and the B.C. Heart Foundation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wood, C.M., Randall, D.J. The influence of swimming activity on sodium balance in the rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). J. Comp. Physiol. 82, 207–233 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00694237
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00694237