Abstract
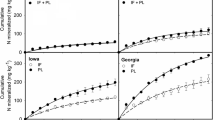
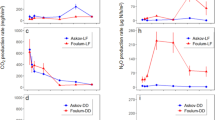
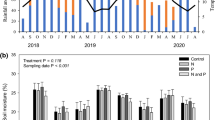
Added N interactions were measured in four soil incubated with 15N-labelled urea or diammonium phosphate. The use of biologically active, γ-irradiated, or reinoculated γ-irradiated samples allowed us to separate added N interactions due to chemical and biological processes, and to distinguish real interactions from apparent effects. Real biologically mediated added N interactions were observed in one soil for both fertilizer sources and in three soils amended with urea. These real interactions increased with the N fertilizer rate, but did not differ significantly between N sources. Fertilizer-induced unlabelled organic N in soil extracts declined during incubation in both sterile and non-sterile samples, but the temporal decline was higher in biologically active soil. Changes in fertilizer-induced unlabelled organic N in the extracts of three soils attributed to biological processes were similar to the measured real biologically mediated added N interactions. The results are consistent with the hypothesis that real biologically mediated added N interactions arise from the mineralization of soil organic N solubilized by alkaline-hydrolysing N fertilizers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreeva EA, Scheglova GM (1968) Uptake of soil nitrogen on application of nitrogen fertilizers and nitrification inhibitors as revealed by greenhouse pot experiments using 15N. Trans 9th Int Congr Soil Sci. The International Society of Soil Science and Angus and Robertson Ltd., Sydney 2:523–532
Azam F, Lodhi A, Ashraf M (1991) Interaction of 15N-labelled ammonium nitrogen with native soil nitrogen during incubation and growth of maize (Zea mays L.). Soil Biol Biochem 23:473–477
Barrow NJ (1960) Stimulated decomposition of soil organic matter during the decomposition of added organic materials. Aust J Agric Res 11:331–338
Bjarnason S (1988) Calculation of gross nitrogen immobilization and mineralization in soil. J Soil Sci 39:393–406
Bremner JM, Mulvaney CS (1982) Nitrogen-total. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties, 2nd edn. Agronomy 9, Am Soc Agron, Madison, Wis. pp 595–624
Broadbent FE, Nakashima T (1971) Effect of added salts on nitrogen mineralization in three California soils. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 35:457–460
Braodbent FE, Norman AG (1946) Some factors affecting the availability of the organic nitrogen in soil—A preliminary report. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 11:264–267
Chalk PM, Victoria RL, Muraoka T, Piccolo MC (1990) Effect of a nitrification inhibitor on immobilization and mineralization of soil and fertilizer nitrogen. Soil Biol Biochem 22:533–538
Chen D, Chalk PM, Freney JR (1990) Release of dinitrogen from nitrite and sulphamic acid for isotope ratio analysis of soil extracts containing nitrogen-15 labelled nitrite and nitrate. Analyst 115:365–370
Hart PBS, Rayner JH, Jenkinson DS (1986) Influence of pool substitution on the interpretation of fertilizer experiments with 15N. J Soil Sci 37:389–403
Hauck RD (1984) Significance of nitrogen fertilizer microsite reactions in soil. In: Hauck RD (ed) Nitrogen in crop production. Am Soc Agron, Crop Sci Soc Am, Soil Sci Soc Am, Madison, Wis, pp 507–519
Hauck RD, Stephenson HF (1965) Nitrification of nitrogen fertilizers. Effect of nitrogen source, size and pH of the granule and concentration. J Agr Food Chem 13:486–492
Jansson SL, Persson J (1982) Mineralization and immobilization of soil nitrogen. In: Stevenson FJ (ed) Nitrogen in agricultural soils. Am Soc Agron, Madison, Wis, pp 229–252
Jenkinson DS, Fox RH, Rayner JH (1985) Interactions between fertilizer nitrogen and soil nitrogen—the so-called ‘priming’ effect. J Soil Sci 36:425–444
Johnson DD, Guenzi WD (1963) Influence of salts on ammonium oxidation and carbon dioxide evolution from soil. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 27:663–666
Keeney DR, Nelson DW (1982) Nitrogen—inorganic forms. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties, 2nd edn. Agronomy 9, Am Soc Agron, Madison, Wis, pp 643–698
Magalhães AMT, Chalk PM (1987) Nitrogen transformations during hydrolysis and nitrification of urea. 2. Effects of fertilizer concentration and nitrification inhibitors. Fert Res 11:173–184
McInnes KJ, Fillery IRP (1989) Modeling and field measurements of the effect of nitrogen source on nitrification. Soil Sci Soc Am J 53:1264–1269
McLaren AD (1969) Radiation as a technique in soil biology and biochemistry. Soil Biol Biochem 1:63–73
McLaughlin M, Fillery IR, Till AR (1992) Operation of the phosphorus, sulphur and nitrogen cycles. In: Gifford RM, Barson MM (eds) Australia's renewable resources: sustainability and global changes. Bureau of Rural Resources Proceedings No 12, Canberra, pp 67–116
Megusar F (1968) The depressing effect on mineralisation caused by the addition of mineral nitrogen to soil. In: Isotopes and radiation in soil organic-matter studies. IAEA and FAO, Vienna, pp 143–149
Norman RJ, Gilmour JT, Gale PM (1988) Transformation of organic matter solubilized by anhydrous ammonia. Soil Sci Soc Am J 52:694–697
Pruden G, Powlson DS, Jenkinson DS (1985) The measurement of 15N in soil and plant material. Fert Res 6:205–218
Rao ACS, Smith JL, Papendick RI, Parr JF (1991) Influence of added nitrogen interactions in estimating recovery efficiency of labeled nitrogen. Soil Sci Soc Am J 55:1616–1621
Reeder JD (1988) Transformations of nitrogen-15-labelled fertilizer nitrogen and carbon mineralization in incubated coal mine spoils and disturbed soil. J Environ Qual 17:291–298
Sen S, Chalk PM (1993) Chemical interactions between soil N and alkaline-hydrolysing N fertilizers. Fert Res 36:239–248
Sen S, Chalk PM (1994) Solubilization of soil organic N by alkaline-hydrolysing N fertilizers. Fert Res 38:131–139
Shen SM, Pruden G, Jenkinson DS (1984) Mineralisation and immobilization of nitrogen in fumigated soil and the measurement of microbial biomass nitrogen. Soil Biol Biochem 16:437–444
Singh BR, Agarwal AS, Kanehiro Y (1969) Effect of chloride salts on ammonium nitrogen release in two Hawaiian soils. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 33:557–560
Stace HCT, Hubble GD, Brewer R, Northcote KH, Sleeman JR, Mulcahy MJ, Hallsworth EG (1968) A handbook of Australian soils. Rellim Technical Publications, Glenside, South Australia
Weier KL, Gilliam JW (1986) Effect of acidity on nitrogen mineralization and nitrification in Atlantic coastal plain soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 50:1210–1214
Westerman RL, Kurtz LT (1973) Priming effect of 15N-labeled fertilizers on soil nitrogen in field experiments. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 37:725–727
Wickramasinghe KN, Rodgers GA, Jenkinson DS (1985) Transformation of nitrogen fertilizers in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 17: 625–630
Wollum AG II (1982) Cultural methods for soil microorganisms. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties, 2nd edn. Agronomy 9, Am Soc Agron, Madison, Wis, pp 781–802
Woods LE, Cole CV, Porter LK, Coleman DC (1987) Transformation of added and indigenous nitrogen in gnotobiotic soil: A comment on the priming effect. Soil Biol Biochem 19:673–678
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sen, S., Chalk, P.M. Biological interactions between soil nitrogen and alkaline-hydrolysing nitrogen fertilizers. Biol Fert Soils 20, 41–48 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307839
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307839