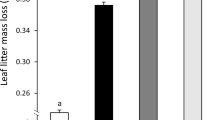
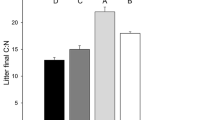
Summary
Feeding by the isopod, Oniscus asellus, produced changes in the sulfur constituents of leaf litter substrates (Acer negundo, A. saccharum, Fagus grandifolia, Picea rubens, and Tsuga canadensis). Isopod consumption of leaf litter generally accelerated the mineralization of carbon-bonded S and increased the formation of ester sulfate in all substrates. After the isopod egestion of A. negundo leaves, fecal decomposition over 6 weeks increased total S concentration from 68 to 120 μmol S/g due to the catabolism of organic carbon. During the same period sulfate decreased from 34 to 20 μmol S/g and carbon-bonded S increased from 34 to 100 μmol S/g. Thus the total S pool in aged feces became enriched with organic S (83% of total S). Macroinvertebrate consumption accelerated the transformation of S constituents and the carbon-bonded S concentration approached that of the Oa organic horizon of a northern hardwood forest.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atlas R, Bartha R (1981) Microbial ecology. Addison-Wesley, Reading, Massachusetts
Bocock KL (1963) The digestion and assimilation of food by Glomeris. In: Doeksen J, Van der Drift J (eds) Soil organisms. North Holland, Amsterdam, pp 85–91
Coleman DC (1986) The role of microfloral and faunal interactions in affecting soil processes. In: Mitchell MJ, Nakas JP (eds). Mierofloral and faunal interactions in natural and agro-ecosystems. Martinus Nijhoff/Dr. W. Junk, Dordrecht, pp 285–348
David MB, Mitchell MJ, Nakas JP (1982) Organic and inorganic sulfur constituents of a forest soil and their relationship to microbial activity. Soil Sci Soc Am J 46:847–852
David MB, Mitchell M, Schindler SC (1984) Dynamics of organic and inorganic sulfur constituents in a hardwood forest soil and their relationship to nutrient cycling. In: Stone EL (ed) Forest soils and treatment impacts. Sixth North American Forest Soils Conference, Knoxville, Tennessee pp 221–245
Edwards CA (1974) Macroarthropods. In: Dickinson CH, Pugh GJF (eds) Biology of plant litter decomposition, vol 2. Academic Press, New York, pp 533–554
Fitzgerald JW (1978) Naturally occurring organosulfur compounds in soil. In: Nriagu JO (ed). Sulfur in the environment. Wiley, New York, pp 391–443
Fitzgerald JW, Strickland TC, Swank WT (1982) Metabolic fate of inorganic sulphate in soil samples from undisturbed and managed forest ecosystems. Soil Biol Biochem 14:529–536
Freney JR (1961) Some observations on the nature of organic sulfur compounds in soil. Aust J Agr Res 12:424–432
Freney JR, Stevenson FJ (1966) Organic sulfur transformations in soils. Soil Sci 101:307–316
Hornor SG, Mitchell MJ (1981) Effect of the earthworm Eisenia foetida (Oligochaeta) on fluxes of volatile carbon and sulfur compounds from sewage sludge. Soil Biol Biochem 13:367–372
Ivanov MV, Freeney JR (eds) (1983) The global biogeochemical sulphur cycle. Wiley, New York
Johnson DW (1984) Sulfur cycling in forests. Biogeochemistry 1:2943
Krivolutzky DA, Pokarzhevsky AD (1977) The role of soil animals in nutrient cycling in forest and steppe. In: Lohm U, Persson T (eds) Soil organisms as components of ecosystems. Ecol Bull 25:253–260
Landers DH, David MB, Mitchell MJ (1983) Analysis of organic and inorganic sulfur constituents on sediments, soils, and water. Intern J Environ Anal Chem 14:245–256
Lawrence GB, Mitchell MJ (1985) Use of 35S to determine the influence of Hexagenia on sulfur cycling in lake sediments. Hydrobiologia 128:91–95
Lawrence GB, Mitchell MJ, Larders DH (1982) Effects of the burrowing mayfly Hexagenia, on nitrogen and sulfur fractions in lake sediment microcosms. Hydrobiologia 87:273–283
Lee KE (1985) Earthworms, their ecology and relationships with soils and land use. Academic Press, New York
Mitchell MJ (1979) Functional relationships of macroinvertebrates in heterotrophic systems with emphasis on sewage sludge decomposition. Ecology 60:1270–1283
Mitchell MJ, Horror SG, Abrams BI (1980) Decomposition of sewage sludge in drying beds and the potential role of the earthworm Eisenia foetida. J Environ Qual 9:373–378
Mitchell MJ, Lawrence GB, Landers DH, Stucker KA (1981) Role of a benthic invertebrate, Hexagenia, in affecting sulfur and nitrogen dynamics of lake sediments. In: Singer R (ed) Effects of acid precipitation on benthos. Proc. Symp. Acidic Precipitation on Benthos, North American Benthological Society, Hamilton, New York, pp 67–76
Mitchell MJ, David MB, Morgan CR (1982) Importance of organic sulfur constituents of forest soils and the role of the soil macrofauna in affecting sulfur flux and transformation. In: Lebrun Ph, Andre HM, de Medts A, Gregoire-Wibo C, Wauthy G (eds) New trends in soil biology. Proc. VIII Int. Colloquium of Soil Zoology. Louvain-la-Neuve (Belgium). 30 August–2 September 1982
Neuhauser EF, Hartenstein R (1978) Phenolic content and palatibility of leaves and wood to soil isopods and diplopods. Pedobiologia 18:99–109
Nriagu JO (1978) Sulfur in the environment: II. Ecological impacts. Wiley, New York
Richter DD, Johnson DW (1983) Determination of inorganic sulfate in foliage with barium chloranilate. Soil Sci Soc Am J 47:522–524
Schindler SC, Mitchell MJ, Scott TJ, Fuller RD, Driscoll CT (1986) Incorporation of 35S-sulfate in inorganic and organic constituents of two forest soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 50:457–462
Strick JE, Nakas JP (1984) Calibration of microbial sulfur technique for use in forest soils. Soil Biol Biochem 16:289–291
Strick JE, Schindler SC, David MB, Mitchell MJ, Nakas JP (1982) Importance of organic sulfur constituents and microbial activity to sulfur transformations in an Adirondack forest soil. Northeastern Environ Sci 1:161–169
Sutton S (1980) Woodlice. Pergamon, New York
Turner J, Lambert MJ (1980) Sulfur nutrition of forests. In: DS Shriner, Richmond CR, Lindberg SE (eds) Atmospheric sulfur deposition: environmental impact and health. Ann Arbor Scienc, pp 3221–331
Waugh J, Mitchell MJ (1981) Effect of the earthworm, Eisenia foetida, on sulfur speciation and decomposition is sewage sludge. Pedobiologia 22:205–223
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to the late Prof. Dr. M.S. Ghilarov
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morgan, C.R., Mitchell, M.J. The effects of feeding by Oniscus asellus on leaf litter sulfur constituents. Biol Fert Soils 3, 107–111 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00260589
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00260589