Summary
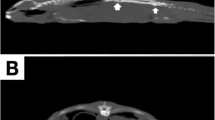
In a 3 year old female domestic cat a suppurative, granulomatous lesion of the tail and sacral area penetrated into the epidural space, causing paraplegia. A. viscosus was isolated from the inflammatory tissues. A comparative light and electron-microscopic study of the bacterial elements and the architecture of the granules (Drusen) show that the latter are in-vivo microcolonies of the agent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brion, A.: L'actinomycose du chien et du chat. Rev. de Méd. Vét.3, 121–159 (1939)
Bulkacz, J.: Actinomyces viscosus. The biology of the Actinomycetes and related organisms11, 93–97 (1976)
Cedervall, A.: Über Streptothrikose bei Karnivoren. Nord. Vet. Med.6, 159–172 (1954)
Davenport, A. A., Carter, G. R., Schirmer, R. G.: Canine Actinomycosis due to Actinomyces viscosus. Vet. Med./Small Anim. Clin.69, 1442–1447 (1974)
Davenport, A. A., Carter, G. R., Patterson, M. J.: Identification of Actinomyces viscosus from canine infections. J. Clin. Microbiol.1, 75–78 (1975a)
Davenport, A. A., Carter, G. R., Beneke, E. S.: Actinomyces viscosus in relation to the other Actinomycetes and Actinomycosis. Vet. Bulletin45, 313–318 (1975b)
Davis, B. D., Dulbecco, R., Eisen, H. N., Ginsberg, H. S., Wood, Jr., W. B., McCarty, M.: Microbiology, 2. edit. New York: Harper & Row 1973
Duda, J. J., Slack, J. M.: Ultrastructural studies on the genus Actinomyces. J. gen. Microbiol.71, 63–68 (1972)
Fey, H.: Personal communication (1977)
Georg, L. K., Brown, J. M., Baker, H. J., Cassell, G. H.: Actinomyces viscosus as an agent of Actinomycosis in the dog. Am. J. Vet. Res.33, 1457–1470 (1972)
Girard, A. E., Jacius, B. H.: Ultrastructure of Actinomyces viscosus and Actinomyces naeslundii. Archs oral Biol.19, 71–79 (1974)
Gygax, M.: Experimentelle Farmerlunge in Meerschweinchen. Immunhistologischer Nachweis von Micropolyspora faeni im Gewebe kranker Tiere. Lizentiatsarbeit, Bern (1973)
Kitamura, T.: Brain involvement in Whipple's disease. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)33, 275–278 (1975)
Pelczar, Jr., M. J., Reid, R. D.: Microbiology, 2. edit. New York: McGraw-Hill 1965
Pine, L., Overman, J. R.: Determination of the structure and composition of the “sulphur granules” of Actinomyces bovis. J. Gen. Microbiol.32, 209–223 (1963)
Schochet, Jr., S. S., Lampert, P. W.: Granulomatous encephalitis in Whipple's disease. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)13, 1–11 (1969)
Silbert, S. W., Parker, E., Horenstein, S.: Whipple's disease of the central nervous system. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)36, 31–38 (1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation under grant No. 3.459.75
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bestetti, G., Bühlmann, V., Nicolet, J. et al. Paraplegia due to actinomyces viscosus infection in a cat. Acta Neuropathol 39, 231–235 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00691702
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00691702