Summary
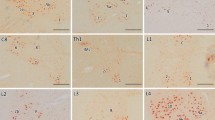
Neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) occur in neurons of human central nervous system (CNS) both in aged subjects and patients with several degenerative diseases, with a certain topographical predilection. In surveying the NFT distribution in nervous tissue of patients with progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), we found silver-positive fibrillary tangles in the neurons of dorsal root ganglia (DRG) in two of five patients. By immunohistochemistry, these tangles were stained with antibodies to human tau protein, paired helical filaments (PHFs) and ubiquitin. Electron microscopy revealed that they were mainly composed of PHFs that were morphologically indistinguishable from PHFs in the NFTs of CNS typically seen in Alzheimer's disease brains. Our data demonstrate for the first time that the neurons of DRG produce NFTs in PSP and suggest that the pathological process(es) leading to tangle formation can occur in the neurons of the peripheral nervous system in this disease condition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bancher C, Lassmann H, Budka H, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Wiche G, Seitelberger F, Wisniewski HM (1987) Neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease and progressive supranuclear palsy: antigenic similarities and differences. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 74:39–46
Bugiani O, Mancardi GL, Brusa A, Ederli A (1979) The fine structure of subcortical neurofibrillary tangles in progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 45:147–152
Dickson DW, Kress Y, Crowe A, Yen S-E (1985) Monoclonal antibodies to Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. 2. Demonstration of a common antigenic determinant between ANT and neurofibrillary degeneration in progressive supranuclear palsy. Am J Pathol 120:292–303
Flament S, Delacourte A, Verny M, Hauw J-J, Javoy-Agid F (1991) Abnormal Tau protein in progressive supranuclear palsy. Similarities and differences with the neurofibrillary degeneration of the Alzheimer type. Acta Neuropathol 81:591–596
Galloway PG (1988) Antigenic characteristics of neurofibrillary tangles in progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurosci Lett 91:148–153
Ghatak NR, Nochlin D, Hadfield MG (1980) Neurofibrillary pathology in progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 52:73–76
Hirano A, Zimmerman HM (1962) Alzheimer's neurofibrillary changes: a topographic study. Arch Neurol 7:73–88
Ihara Y (1988) Massive somatodendritic sprouting of cortical neurons in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res 459:138–144
Ihara Y, Abraham C, Selkoe DJ (1983) Antibodies to paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease do not recognize normal brain proteins. Nature 304:727–730
Ishino H, Ikeda Otsuki S (1975) Contribution to clinical pathology of progressive supranuclear palsy (subcortical argyrophilic dysrophy): on the distribution of neurofibrillary tangles in the basal ganglia and brain-stem and its clinical significance. J Neurol Sci 471–481
Jellinger K, Riederer P, Tomonaga M (1980) Progressive supranuclear palsy: clinicopathological and biochemical studies. J Neural Transm 16 [Suppl]:111–128
Kawasaki H, Murayama S, Tomonaga M, Izumiyama N, Shimada H (1987) Neurofibrillary tangles in human upper cervical ganglia: morphological study with immunohistochemistry and electron microscopy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 75:156–159
Kosik KS, Joachim CL, Selkoe DJ (1986) Microtubulé-associated protein tau (τ) is a major antigenic component of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:4044–4048
Nagashima K, Oota K (1974) A histopathological study of the human spinal ganglia. 1. normal variations in aging. Acta Pathol Jpn 24:333–344
Nishimura M, Namba Y, Ikeda K, Oda M (1992) Glial fibrillary tangles with straight tubules in the brains of patients with progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurosci Lett 143:35–38
Powell HC, London GW, Lampert PW (1974) Neurofibrillary tangles in progressive supranuclear palsy. Electron microscopic observations. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 33:98–106
Roy S, Datta CK, Hirano A, Ghatak NR, Zimmermann HM (1974) Electron microscopic study of neurofibrillary tangles in Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 29:175–179
Shibayama H, Kitoh J (1978) Electron microscopic structure of the Alzheimer's neurofibrillary changes in case of atypical senile dementia. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 41:229–234
Steele JC, Richardson JC, Olszewski J (1964) Progressive supranuclear palsy. Arch Neurol 10:333–359
Tellez-Nagel I, Wisneiwski HM (1973) Ultrastructure of neurofibrillary tangles in Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome. Arch Neurol 29:324–327
Tomonaga M (1977) Ultrastructure of neurofibrillary tangles in progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 37:177–181
van den Bosch de Aguilar Ph, Goemaere-Vanneste J (1984) Paired helical filaments in spinal ganglion neurons of elderly rats. Virchows Arch [B] 47:217–222
Wischik CM, Novak M, Thogersen HC, Edwards PC, Runswick MJ, Jakes R, Walker JE, Klug A (1988) Isolation of a fragment of tau derived from the core of the paired helical filament of Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:4506–4510
Wisniewski H, Terry RD, Hirano A (1970) Neurofibrillary pathology. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 24:163–176
Wood JG, Mirra SS, Pollock NJ, Binder LI (1986) Neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer disease share antigenic determinants with the axonal microtubule-associated protein tau (τ). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:4040–4043
Yagishita S, Itoh Y, Amano N, Nakano T, Saitoh A (1979) Ultrastructure of neurofibrillary tangles in progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 48:27–30
Yamada T, McGeer PL, McGeer EG (1992) Appearance of paired nucleated, Tau-positive glia on patients with progressive supranuclear palsy brain tissues. Neurosci. Lett. 135:99–102
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research of the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture of Japan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nishimura, M., Namba, Y., Ikeda, K. et al. Neurofibrillary tangles in the neurons of spinal dorsal root ganglia of patients with progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol 85, 453–457 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230481
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230481