Abstract
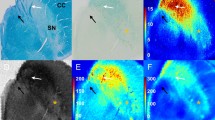
In the basal ganglia of three autopsy cases of pallidonigroluysian degeneration, we found marked iron deposition, a finding which has not been mentioned previously in the literature. Besides severe astrogliosis and neuronal loss in the pallidum, Luysian body and nigra, granular deposits of brown pigments were found in the neuropil, microglias, oligodendrocytes and astrocytes in three such the nuclei and the striatum. These brown pigments proved histochemically to be iron. Our histochemical semiquantitative study showed a significantly stronger reation for iron in the degenerated nuclei in these three cases than in control cases comprising non-degenerative and the other degenerative diseases. Quantitative study with inductively coupled emission spectrometry also demonstrated a markedly higher iron content in the globus pallidus and the striatum in comparison with the control cases. The possibility is discussed that iron deposition plays a role in generating the lesions of pallidonigroluysian degeneration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chan PH, Schmidley JW, Fishman RA, Longer SM (1984) Brain injury, edema and vascular permeability changes induced by oxygen-derived free radicals. Neurology 34:315–320
Contamin F, Escourolle R, Nick J, Mignot R (1971) Atrophie pallido-nigro-luysienne syndrome akinetique palielie, rigiditie oppositionelle et catatonie. Rev Neurol (Paris) 124:107–120
Dexter DT, Wells FR, Agid F, Agid Y, Lees AJ, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1987) Increased nigral iron content in postmortem parkinsonian brain. Lancet II:1219–1220
Dexter DT, Wells FR, Lees AJ, Agid F, Agid Y, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1989) Increased nigral iron content and alteration on other metal ions occurring in brain in Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem 52:1830–1836
Gomori G (1936) Microtechnical demonstration of iron, a criticism of its methods. Am J Pathol 12:655–663
Gray F, De Baecque C, Serdaru M, Escourolle R (1981) Pallidoluysionigral atrophy and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol [Suppl] VIII:348–351
Gray F, Eizenbaum JF, Gherardi R, Degos JD, Poirier J (1985) Luysio-pallido-nigral atrophy and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 66:78–82
Gutteridge JM, Westermarck T and Santavuori P (1983) Iron and oxygen radicals in tissue damage: implications for the neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. Acta Neurol Scand 68:365–370
Halliwell B (1978) Superoxide-dependent formation of hydroxyl radicals in the presence of iron chelates. FEBS Lett 92:231–326
Jellinger K (1986) Pallidal, pallidonigral and pallidoluysionigral degeneration including association with thalamic and dentate degeneration. Handb Clin 49:445–464
Jellinger K, Kienzl E, Paulus W, Riederer W, Rumpelmaier G, Youdim M (1992) Increase of iron in the substantia nigra of Parkinson's disease. Clin Neuropathol 11:227
Kosaka K, Matsushita M, Oyanagi S, Uchiyama S, Iwase S (1981) Pallido-nigro-luysial atrophy with massive appearance of corpora amylacea in the CNS. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 53:169–172
McCord JM, Day ED Jr (1978) Superoxide-dependent production of hydroxyl radical catalyzed by iron-EDTA complex. FEBS Lett 86:139–142
Minotti G, Aust SD (1987) The requirement for iron (III) in the initiation of lipid peroxidation by iron (II) and hydrogen peroxide. J Biol Chem 262:1098–1104
Perry TL, Norman MG, Yong VW, Whiting S, Crichton JU, Hansen S, Kish S (1985) Hallervorden-Spatz disease: cysteine accumulation and cysteine dioxygenese deficiency in the globus pallidus. Ann Neurol 18:482–489
Riederer P, Sofic E, Rausch WD, Schmidt B, Reynolds GP, Jellinger K, Youdim BH (1989) Transition metals, ferritin, glutathione, and ascorbic acid in parkinsonian brains. J Neurochem 52:515–520
Schmelzer W (1933) Der mikrochemische Nachweis von Eisen in Gewebselementen Rhodanwasserstoffsaure und die Konservierung der Reactionin Paraffinol. Z Wiss Mikrosk Mikrosk Tech 50:99–102
Sofic E, Riederer P, Heisen H, Beckmann H, Reynolds GP, Hebenstreit G, Youdim MBH (1988) Increased iron (III) and total iron content in post mortem substantia nigra of parkinsonian brain. J Neural Trnsm 74:199–205
Takahashi K, Nakashima R, Takao T, Nakamura H (1977) Pallido-nigro-luysial atrophy associated with degeneration o the centrum medianum. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 37:81–85
Uchida H, Nojiri Y, Haraguch H, Fuwa K (1981) Simultaneous multi-element analysis by inductively-coupled plasma emission spectrometry utilizing micro-sampling techniques with internal standard. Anal Chim Acta 123:57–63
Uchida H, Hisada S, Toyoda H, Takahashi J, Tomita H, Ohmori H (1985) Simultaneous multielement analysis of trace metals in hair and serum by inductively coupled emission spectrometry. Biryou Kinzoku Taisya 13:173–180 (in Japanese)
Youdim MBH, Ben-Shachar D, Riederer P (1989) Is Parkinson's disease a progressive siderosis of substantia nigra resulting in iron- and melanin-induced neurodegeneration? Acta Neurol Scand 127:36–541
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawai, J., Sasahara, M., Hazama, F. et al. Pallidonigroluysian degeneration with iron deposition: a study of three autopsy cases. Acta Neuropathol 86, 609–616 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00294300
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00294300