Abstract
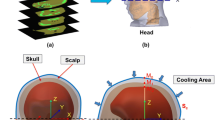
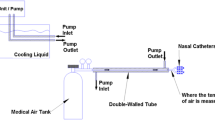
We describe a method of focal cooling of the head and its effects on hypoxic-ischemic cerebral damage in neonatal rat. Focal cooling of the head was obtained by positioning a catheter under the scalp ipsilateral to the ligated common carotid artery and by running cold water through the catheter during 2 h of systemic hypoxia. Hypoxia was produced in neonatal rats by breathing 8% oxygen for 2 h in a 37°C chamber. Animals underwent focal cooling with ipsilateral scalp temperatures ranging from 22°C to 35°C. Temperature recordings from the ipsilateral scalp, cerebral hemisphere (dorsal hippocampus) and core (rectal) were obtained. The results suggest that the method is effective in cooling of brain and also to a lesser extent in lowering of the core temperature. At a mean scalp temperature of 28°C, mean hippocampal temperature in hypoxic rat was 29.5°C and mean core temperature in hypoxic rat was 32.8°C. At a lower scalp temperature of 22°C, mean hippocampal temperature in hypoxic rat was 24.7°C and mean core temperature was 31.3°C. Neuropathologic examination 3–4 days following hypoxia-ischemia showed that focal cooling with a scalp temperature of lower than 28°C completely protected from brain damage, and that there was a trend towards greater damage with higher scalp temperatures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Busto R, Dietrich WD, Globus MY-T, Valdés I, Scheinberg P, Ginsberg MD (1987) Small differences in intraischemic brain temperature critically determine the extent of ischemic neuronal injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 7: 729–738
Busto R, Dietrich WD, Globus MY-T, Ginsberg MD (1989) Postischemic moderate hypothermia inhibits CA1 hippocampal ischemic neuronal injury. Neurosci Lett 101: 299–304
Busto R, Dietrich WD, Globus MY-T, Ginsberg MD (1989) The importance of brain temperature in cerebral ischemic injury. Stroke 20: 1113–1114
Chopp M, Chen H, Dereski MO, Garcia JH (1991) Mild hypothermic intervention after graded ischemic stress in rats. Stroke 22: 37–43
Connolly JE, Boyd RJ, Calvin JW (1962) The protective effect of hypothermia in cerebral ischemia: experimental and clinical application by selective brain coolings in the human. Surgery 52: 15–24
Hirsch H, Müller HA (1962) Funktionelle und histologische Veränderungen des Kaninchengehirns nach kompletter Gehirnischämie. Pflügers Arch 275: 277–291
Horn M, Schlote W, Henrich HA (1991) Global cerebral ischemia and subsequent selective hypothermia. A neuropathological and morphometrical study on ischemic neuronal damage in cat. Acta Neuropathol 81: 443–449
Kopf GS, Mirvis DM, Myers RE (1975) Central nervous system tolerance to cardiac arrest during profound hypothermia. J Surg Res 18: 29–34
Levine S (1960) Anoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in rats. Am J Pathol 36: 1–17
Little DM (1959) Hypothermia. Anesthesiology 20: 842–877
Marshall SB, Owens JC, Swan H (1956) Temporary circulatory occlusion to the brain of the hypothermic dog. Arch Surg 72: 98–106
Minamisawa H, Nordström C-H, Smith M-L, Siesjö BK (1990) The influence of mild body and brain hypothermia on ischemic brain damage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 10: 365–374
Miyake T, Kinoshita K, Ishii N, Endo M (1982) First report of an experimental study in dogs of cerebrocardiopulmonary resuscitation (CCPR). Resuscitation 10: 105–120
Miyake T, Endo M, Ishii N, Fukuda Y, Kinoshita K, Masuda K (1984) Second report of an experimental study of cerebrocardiopulmonary resuscitation (CCPR) in dogs with reference to a new continuous brain cooling method, using a resusci pump TM-1. Resuscitation 12: 9–24
Morikawa E, Ginsberg MD, Dietrich WD, Duncan RC, Kraydieh S, Globus MY-T, Busto R (1992) The significance of brain temperature in focal cerebral ischemia: histological consequences of middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 12: 380–389
Mujsce DJ, Towfighi J, Vannucci RC (1990) Physiologic and neuropathologic aspects of hypothermic circulatory arrest in newborn dogs. Pediatr Res 28: 354–360
O'Connor JV, Wilding T, Farmer P, Sher J, Ergin MA, Griepp RB (1986) the protective effect of profound hypothermia on the canine central nervous system during one hour of circulatory arrest. Ann Thorac Surg 41: 255–259
Onesti ST, Baker CJ, Sun PP, Solomon RA (1991) Transient hypothermia reduces focal ischemic brain injury in the rat. Neurosurgery 29: 369–373
Pulsinelli WA, Brierley JB (1979) A new model of bilateral hemispheric ischemia in the unanesthetized rat. Stroke 10: 267–272
Rice JE, Vannucci RC, Brierley JB (1981) The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann Neurol 9: 131–141
Sherwood NM, Timiras PS (1970) A stereotaxic atlas of the developing rat brain. University of California Press, Berkley
Steen PA, Soule EH, Michenfelder JD (1979) Detrimental effect of prolonged hypothermia in cats and monkeys with and without regional cerebral ischemia. Stroke 10: 522–529
Steen PA, Milde JH, Michenfelder JD (1980) The detrimental effects of prolonged hypothermia and rewarming in the dog. Anesthesiology 52: 224–230
Towfighi J, Yager JY, Housman C, Vannucci RC (1991) Neuropathology of remote hypoxic-ischemic damage in the immature rat. Acta Neuropathol 81: 578–587
Welsh FA, Sims RE, Harris VA (1990) Mild hypothermia prevents ischemic injury in gerbil hippocampus. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 10: 557–563
White RJ, Austin PE Jr, Austin JC, Taslitz N, Takoaka Y (1973) Recovery of the subhuman primate after deep cerebral hypothermia and prolonged ischaemia. Resuscitation 2: 117–122
White RJ, Brown HW, Albin MS, Verdura J (1983) Rapid selective brain-cooling using head immersion and naso-oral perfusion in dogs. Resuscitation 10: 189–191
Yager J, Towfighi J, Vannucci RC (1993) Influence of mild hypothermia on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the immature rat. Pediatr Res 34: 525–529
Young RSK, Olenginski TP, Yagel SK, Towfighi J (1983) The effect of graded hypothermia on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage: a neuropathologic study in the neonatal rat. Stroke 14: 929–934
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was supported in part by Grant No. HD19913 from the National Institutes of Health
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Towfighi, J., Housman, C., Heitjan, D.F. et al. The effect of focal cerebral cooling on perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Acta Neuropathol 87, 598–604 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00293321
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00293321