Summary
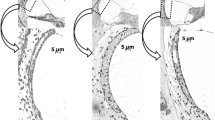
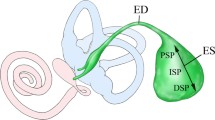
The ultrastructure of the basement membrane of the murine endolymphatic sac was studied under various experimental conditions in labyrinthectomized and ethacrynic acid-treated animals and was compared with normal anatomy. The basement membrane was clearly visualized after staining with ruthenium red or dialyzed iron. The basement membrane of the murine sac consists of two different layers: the lamina rara and the lamina densa. It demarcates the border between the epithelial cells and the subepithelial connective tissue. Our findings suggest that the basement membrane acts as a physical support to the epithelium in the endolymphatic sac. The basement membrane also shows a dynamic capacity to form a new basement membrane, with the result that the lateral intercellular space between contiguous epithelial cells may be integrated with the subepithelial space. This system is believed to act as a macromolecular and bulk water transport system. In the subepithelial space, collagen, reticular and elastic fibrils are found having a close relationship to the basement membrane. The elastic fibres are presumed to play a role in the pressure-regulating mechanism in the endolymphatic sac.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagger-Sjöbäck D, Friberg U, Rask-Andersen H (1986) The human endolymphatic sac: an ultrastructural study. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 112:398–409
Barbara M, Bagger-Sjöbäck D, Rask-Andersen H (1987) Ultrastructure of the endolymphatic sac in the mongolian gerbil. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 244:284–287
Erwall C, Friberg U, Bagger-Sjöbäck D, Rask-Andersen H (1988) Effect of ototoxic diuretics (loop diuretics) on the endolymphatic sac. ORL 50:42–53
Friberg U, Bagger-Sjöbäck D, Rask-Andersen H (1985) The lateral intercellular space in the endolymphatic sac. A pathway for fluid transport? Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) [Suppl] 426:1–17
Kefalides NA, Alper R, Clark CC (1979) Biochemistry and metabolism of basement membranes. Int Rev Cytol 61:167–228
Kimura RS, Schuknecht HF (1965) Membraneous hydrops of the inner ear of the guinea pig after obliteration of the endolymphatic sac. Pract Otorhinolaryngol 27:343–354
Luft JH (1971) Ruthenium red and violet. II. Fine structural localization in animal tissues. Anat Rec 171:369–415
Lundquist PG (1965) The endolymphatic duct and sac in the guinea pig: an electron microscopic and experimental investigation. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) [Suppl] 201:1–108
Martinez-Hernandez A, Amenta PS (1983) The basement membrane in pathology. Lab Invest 48:656–677
Mynderse LA, Hassel J, Kleinman HK, Martin GR, Martinez-Hernandez A (1983) Loss of heparan sulfate proteoglycan from glomerular basement membrane of nephrotic rats. Lab Invest 48:292–302
Rask-Andersen H, Erwall C, Steel KP, Friberg U (1987) The endolymphatic sac in a mouse mutant with cochleosaccular degeneration: electrophysiological and ultrastructural correlations. Hear Res 26:177–190
Rennke HG, Cotran RS, Venkatachalam MA (1975) Role of molecular charge in glomerular permeability: tracer studies with cationized ferritin. J Cell Biol 67:638–646
Takumida M, Bagger-Sjöbäck D, Rask-Andersen H (1988) Ruthenium red staining of the endolymphatic sac. J Laryngol Otol (in press)
Welling LW, Grantham JJ (1972) Physical properties of isolated perfused renal tubules and tubular basement membranes. J Clin Invest 51:1063–1075
Wetzel MG, Wetzel BK, Spicer SS (1966) Ultrastructural localization of acidic mucosubstances in the mouse colon with ion-containing stains. J Cell Biol 30:299–315
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takumida, M., Bagger-Sjöbäck, D. & Rask-Andersen, H. The basement membrane and associated structures in the murine endolymphatic sac. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 245, 266–272 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00464628
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00464628