Abstract
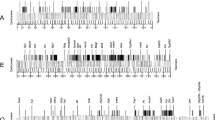
We present a strategy for assembling a physical map of the genome of Drosophila melanogaster based on yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs). In this paper we report 500 YACs containing inserts of Drosophila DNA averaging 200 kb that have been assigned positions on the physical map by means of in situ hybridization with salivary gland chromosomes. The cloned DNA fragments have randomly sheared ends (DY clones) or ends generated by partial digestion with either NotI (N clones) or EcoRI (E clones). Relative to the euchromatic portion of the genome, the size distribution and genomic positions of the clones reveal no significant bias in the completeness or randomness of genome coverage. The 500 mapped euchromatic clones contain an aggregate of approximately 100 million base pairs of DNA, which is approximately one genome equivalent of Drosophila euchromatin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashburner, M (1989) Drosophila: A laboratory handbook. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Bender, W, Spierer, P, Hogness, DS (1983) Chromosome walking and jumping to isolate DNA from the Ace and rosy loci and the Bithorax complex in Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol 168: 17–33
Bingham, PM, Levis, R, Rubin, GM (1981) Cloning of DNA sequences from the white locus of Drosophila melanogaster by a novel and general method. Cell 25: 693–704
Bingham, PM, Kidwell, MG, Rubin, GM (1982) The molecular basis of P-M hybrid dysgenesis: the role of the P element, a P-strain specific transposon family. Cell 29: 995–1004
Bridges, CM (1935) Salivary chromosome maps with a key to the banding of the chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. J Hered 26: 60–64
Burke, DT, Carle, GF, Olson, MV (1987) Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors. Science 236: 806–812
Capecchi, M (1990) How efficient can you get? Nature 348: 109
Carle, GF, Olson, MV (1984) Separation of chromosomal DNA molecules from yeast by orthogonal-field-alternation gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res 12: 5647–5663
Clayton, FE, Guest, WC (1986) Overview of chromosomal evolution in the family Drosophilidae. In: Ashburner, M, Carson, HL, Thompson, JNJ (eds) Genetics and biology of Drosophila. Academic Press, New York, pp 1–38
Cooley, L, Kelley, R, Spradling, A (1988) Insertional mutagenesis of the Drosophila genome with single P elements. Science 239: 1121–1128
Coulson, A, Sulston, J, Brenner, S, Karn, J (1986) Toward a physical map of the genome of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 7821–7825
Coulson, A, Waterston, R, Kiff, J, Sulston, J, Kohara, Y (1988) Genome linking with yeast artificial chromosomes. Nature 335: 184–186
Craig, AG, Nizetic, D, Hoheisel, JD, Zehetner, G, Lehrach, H (1990) Ordering of cosmid clones covering Herpes simplex virus type I (HSV-I) genome: a test case for fingerprinting by hybridization. Nucleic Acids Res 18: 2653–2660
Danilevskaya, ON, Kurenova, EV, Pavlova, MN, Link, AJ, Koga, A, Vellek, A, Hartl, DL (1991) He-T family DNA sequences in the Y chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster share homology with the X-linked Stellate genes. Chromosoma 100: 118–124
Feinberg, AP, Vogelstein, B (1984) A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity: Addendum. Anal Biochem 137: 266–267
Feller, W (1950) An introduction to probability theory and its applications. John Wiley, New York
Garza, D, Ajioka, JW, Burke, DT, Hartl, DL (1989a) Mapping the Drosophila genome with yeast artificial chromosomes. Science 246: 641–646
Garza, D, Ajioka, JW, Carulli, JP, Jones, RW, Johnson, DH, Hartl, DL (1989b) Physical mapping of complex genomes. Nature 340: 577–578
Green, ED, Olson, MV (1990) Systematic screening of yeast artificial-chromosome libraries by use of the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 1213–1217
Healy, MJ, Russell, RJ, Miklos, GLG (1988) Molecular studies on interspersed repetitive and unique sequences in the region of the complementation group uncoordinated on the X chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Gen Genet 213: 63–71
Johnson, DH (1990) Molecular cloning of DNA from specific chromosomal regions by microdissection and sequence-independent amplification of DNA. Genomics 6: 243–251
Kohara, Y, Akiyama, K, Isono, K (1987) The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: Application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell 50: 495–508
Langer-Safer, PR, Levine, M, Ward, DC (1982) Immunological method for mapping genes on Drosophila polytene chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79: 4381–4385
Lefevre, GJr (1976) A photographic representation and interpretation of the polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster savary glands. In: Ashburner, M, Novitski, E (eds) The genetics and biology of Drosophila. Academic Press, New York, pp 31–66
Lindsley, DL, Zimm, G (1985) The genome of Drosophila melanogaster. Part 1: Genes A-K. Dros Inf Serv 62: 1–227
Lindsley, DL, Zimm, G (1986) The genome of Drosophila melanogaster. Part 2: lethals; maps. Dros Inf Serv 64: 1–158
Lindsley, DL, Zimm, G (1987) The genome of Drosophila melanogaster. Part 3: rearrangements. Dros Inf Serv 65: 1–224
Lindsley, DL, Zimm, G (1990) The genome of Drosophila melanogaster. Part 4: Genes L-Z. Dros Inf Sery 68: 1–382
Ochman, H, Gerber, AS, Hartl, DL (1988) Genetic applications of an inverse polymerase chain reaction. Genetics 120: 621–623
Ochman, H, Medhora, MM, Garza, D, Hartl, DL (1990) Amplification of flanking sequences by inverse PCR. In: Innis, M, Gelfand, D, Sninsky, J, White, T (eds) PCR protocols: A guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, New York, pp 219–227
Olson, MV, Dutchik, JE, Graham, MY, Brodeur, GM, Helms, C, Frank, M, MacCollin, M, Scheinman, R, Frank, T (1986) Random-clone strategy for genomic restriction mapping in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 7826–7830
Olson, MV, Hood, L, Cantor, C, Botstein, D (1989) A common language for physical mapping of the human genome. Science 245: 1434–1440
Painter, TS (1933) A new method for the study of chromosome rearrangements and the plotting of chromosome maps. Science 78: 585–586
Palazzolo, MJ, Hyde, DR, VijayRaghavan, K, Mecklenberg, K, Benzer, S, Meyerowitz, E (1989) Use of a new strategy to isolate and characterize 436 Drosophila cDNA clones corresponding to RNAs detected in adult heads but not early embryos. Neuron 3: 527–539
Pfeifer, GP, Steigerwald, SD, Mueller, PR, Wold, B, Riggs, AD (1989) Genomic sequencing and methylation analysis by ligation mediated PCR. Science 246: 810–813
Riethman, HC, Moyzis, RK, Meyne, J, Burke, DT, Olson, MV (1989) Cloning human telomeric DNA fragments into Saccharomyces cerevisiae using a yeast-artificial-chromosome vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 6240–6244
Riley, J, Butler, R, Ogilvie, D, Finniear, R, Jenner, D, Powell, S, Anand, R, Smith, JC, Markham, AF (1990) A novel, rapid method for the isolation of terminal sequences from yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) clones. Nucleic Acids Res 18: 2887–2890
Rubin, GM, Spradling, AC (1982) Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science 218: 348–353
Rudkin, GT (1969) Non replicating DNA in Drosophila. Genetics 61 [Suppl 1]: 227–238
Saunders, RDC, Glover, DM, Ashburner, M, Siden-Kiamos, I, Louis, C, Monastirioti, M, Savakis, C, Kafatos, F (1989) PCR amplification of DNA microdissected from a single polytene chromosome band: a comparison with conventional microcloning. Nucleic Acids Res 17: 9027–9037
Scott, MP, Weiner, AJ, Polisky, BA, Hazelrigg, TI, Pirrotta, V, Scalenghe, F, Kaufman, TC (1983) The molecular organization of an Antennapedia locus of Drosophila. Cell 35: 763–776
Siden-Kiamos, I, Saunders, RDC, Spanos, L, Majerus, T, Treanear, J, Savakis, C, Louis, C, Glover, DM, Ashburner, M, Kafatos, FC (1990) Towards a physical map of the Drosophila melanogaster genome: Mapping of cosmid clones within defined genomic divisions. Nucleic Acids Res 18: 6261–6270
Smoller, D, Petrov, D, Hartl, DL (1991) Characterization of bacteriophage P1 library containing inserts of Drosophila DNA of 75–100 kilobase pairs. Chromosoma 100: 487–494
Sorsa, V (1988a) Chromosome maps of Drosophila, vol I. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida
Sorsa, V (1988b) Chromosoma maps of Drosophila, vol II. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida
Southern, EM (1975) Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98: 503–517
Steller, H, Pirrotta, V (1985) A transposable P vector that confers selectable G418 resistance to Drosophila larvae. EMBO J 4: 167–171
Sternberg, N (1990) Bacteriophage P1 cloning system for the isolation, amplification, and recovery of DNA fragments as large as 100 kilobase pairs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 103–107
Sturtevant, AH (1913) The linear arrangement of six sex-linked genes in Drosophila, as shown by their mode of association. J Exp Zool 14: 43–59
Vogelstein, B, Gillespie, D (1979) Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76: 615–619
Vollrath, D, Davis, RW (1987) Resolution of DNA molecules greater than 5 megabases by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Nucleic Acids Res 15: 7865–7876
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
by W. Hennig
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ajioka, J.W., Smoller, D.A., Jones, R.W. et al. Drosophila genome project: One-hit coverage in yeast artificial chromosomes. Chromosoma 100, 495–509 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00352200
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00352200