Abstract
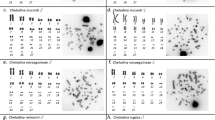
Chromosome analyses of common Indian Krait, B. caeuleus from three geographical regions of India have revealed variable diploid numbers of 43, 44 and 45 in different female individuals but a constant diploid number of 44 in the males. C-banding and in situ hybridization studies, using radio labelled W sex chromosome specific satellite DNA as a probe, have shown that C-banding and sex chromosome associated satellite DNA's are exclusively localised in the W chromosome. The W chromosome is involved in reciprocal translocations either with a medium sized macroautosome or with a microchromosome resulting in a multiple sex chromosome constitution of Z1Z1Z2Z2♂/Z1Z2W♀ type. In some female individuals dissociation of the W has resulted in multiple W chromosomes, W1 and W2. These polymorphisms are uniquely confined to the female sex only. A predominance of polymorphic females, involving particularly the translocation of a medium sized macrochromosome, in all three geeographical regions and the restriction of the females having the original chromosome constitution (ZW) to one geographical region suggests that polymorphic individuals have adaptive flexibility and higher fecundity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, R.J., Bull, J.J., Mengden, G.A.: Chromosomes of Elaphe subocularis (Reptilia: Serpentes), with the description of an in vivo technique for preparation of snake chromosomes. Experientia (Basel) 27, 1228–1229 (1971)
Capanna, E., Cristaldi, M., Perticone, P., Rizzoni, M.: Identification of chromosomes involved in the nine Robertsonian fusions of the Apennine mouse with a 22-chromosome karyotype. Experientia (Basel) 31, 294–296 (1975)
Capanna, E., Gropp, A., Winking, H., Noack, G., Civitelli, M.V.: Robertsonian metacentrics in the mouse. Chromosoma (Berl.) 58, 341–353 (1976)
Dallapiccola, B., Mastroiacovo, P., Gandini, E.: Centric fission of chromosome No. 4 in the mother of two patients with trisomy 4p. Hum. Genet. 31, 121–125 (1976)
Egozcue, J.: A possible case of centric fission in a primate. Experientia (Basel) 27, 969–970 (1971)
Fredga, K., Bergström, U.: Chromosome polymorphism in the root vole (Microtus oeconomus). Hereditas (Lund) 66, 145–152 (1970)
Gropp, A., Winking, H., Zech, L., Müller, H.J.: Robertsonian chromosomal variation and identification of metacentric chromosomes in feral mice. Chromosoma (Berl.) 39, 265–288 (1972)
Hansen, S.: A case of centric fission in man. Humangenetik 26, 257–259 (1975)
Jones, K.W.: In situ hybridization. In: New technique in biophysics and cell biology (R.H. Pain and B.J. Smith, eds.), pp. 29–66. London: J. Wiley and Sons 1973
Marmur, J.: A procedure for the isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid from microorganisms. J. molec. Biol. 3, 208–218 (1961)
Matthey, R.: Polymorphisme chromosomique intraspécifique et intraindividuel, chez Acomys minous Bate (Mammalia-Rodentia-Muridae). Chromosoma (Berl.) 14, 468–497 (1963)
Matthey, R.: Evolution chromosomique et speciation chez les Mus du sous-genre Leggada Gray 1837. Experientia (Basel) 20, 657–665 (1964)
Matthey, R.: Le polymorphisme chromosomique des Mus africains du sous-genre Leggada. Révision generale portant sur E'analyse de 213 individuals. Rev. Suisse Zool. 42, 585–607 (1966)
Matthey, R.: Nouvelles donnés sur la cytogénétique et la speciation des Leggada (Mammalia-Rodentia-Muridae). Experientia (Basel) 26, 102–103 (1970)
Nevers, P., Saedler, H.: Transposable genetic elements as agents of gene instability and chromosomal rearrangements. Nature (Lond.) 268, 109–115 (1977)
Rigby, P.W.J., Dieckmann, M., Rhodes, C., Berg, P.: Labelling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase 1. J. molec. Biol. 113, 237–251 (1977)
Sharman, G.B.: Chromosomes of the common shrew. Nature (Eond.) 177, 941–942 (1956)
Singh, L.: Evolution of karyotypes in snakes. Chromosoma (Berl.) 38, 185–236 (1972a)
Singh, L.: Multiple W chromosome in a sea snake, Enhydrina schistosa Daudin. Experientia (Basel) 28, 95–97 (1972b)
Singh, L., Ray-Chaudhuri, S.P.: Localization of C-band in the W sex chromosome of the common Indian Krait Bungarus caeruleus Schneider. Nucleus (Calcutta) 18, 163–166 (1975)
Singh, L., Purdom, I.F., Jones, K.W.: Satellite DNA and evolution of sex chromosomes. Chromosoma (Berl.) 59, 43–62 (1976)
Singh, L., Purdom, I.F., Jones, K.W.: Effect of different denaturing agents on the detectability of specific DNA sequences of various base compositions by in situ hybridization. Chromosoma (Berl.) 60, 377–389 (1977)
Singh, L., Purdom, I.F., Jones, K.W.: Behaviour of sex chromosome associated satellite DNAs in somatic and germ cells in snakes. Chromosoma (Berl.) 71, 167–181 (1979)
Singh, L., Sharma, T., Ray-Chaudhuri, S.P.: Multiple sex-chromosomes in the common Indian Krait, Bungarus caeruleus Schneider. Chromosoma (Berl.) 31, 386–391 (1970)
Sinha, A.K., Pathak, S., Nora, J.J.: A human family suggesting evidence for centric fission and stability of a telocentric chromosome. Hum. Hered. 22, 423–429 (1972)
Sumner, A.T.: A simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Exp. Cell Res. 75, 304–306 (1972)
Thorgaard, G.H.: Robertsonian polymorphism and constitutive heterochromatin distribution in chromosomes of the rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 17, 174–184 (1976)
Wahrman, J., Zahavi, A.: Intra-generic difference in chromosome numbers of spiny mice (Rodentia, Murinae). Bull. Res. Council Israel 3, 265 (1953)
White, M.J.D.: Chromosomal rearrangements in mammalian population=polymorphism and speciation. In: Cytotaxonomy and vertebrate evolution (A.B. Chiarelli and E. Capanna, eds.), pp. 95–128. London, New York: Academic Press 1973
Zahavi, A., Wahrman, J.: Chromosome races in the genus Acomys (Rodentia, Murinae). Bull. Res. Council Israel B, 350E (1956)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, L., Ray-Chaudhuri, S.P., Majumdar, K. et al. Sex specific chromosome polymorphisms in the common Indian Krait, Bungarus caeruleus Schneider (Ophidia, Elapidae). Chromosoma 73, 93–108 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00294849
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00294849