Summary
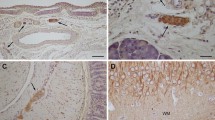
A biotinylated P 0 glycoprotein cDNA was hybridized in situ to aldehyde-fixed vibratome sections and to aldehyde-fixed thin sections of Lowicryl-embedded trigeminal ganglia of 15 day old rats. Alkaline phosphatase and peroxidase detectors were used for light microscopic (LM) studies and peroxidase or colloidal gold were employed for electron microscopic (EM) detection. In both LM and EM sections, probe was found in cytoplasmic areas of myelinforming Schwann cells that were enriched in granular endoplasmic reticulum, demonstrating that these regions contain P 0 mRNA. Interestingly, P 0 mRNA tended to cluster in regions close to the developing myelin sheath. Relatively simple methods are here described for EM detection of mRNA with reasonable tissue preservation and high resolution. These methods may be useful for developmental and disease-related studies of specific mRNAs in mammalian tissues.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Binder M, Tourmente S, Roth J, Renaud M, Gehring WJ (1986) In situ hybridization at the electron microscope level: Localization of transcripts on ultrathin sections of Lowicryl K4M-embedded tissue using biotinylated probes and protein A-gold complexes. J Cell Biol 102:1646–1653
Jamrich MKA, Mahon KA, Gavis ER, Gall JG (1984) Histone RNA in amphibian oocytes visualized by in situ hybridization to methacrylate-embedded tissue sections. EMBO J 3:1939–1943
Kristensson K, Zeller NK, DuBois-Dalcq ME, Lazzarini RA (1986) Expression of myelin basic protein gene in the developing rat brain as revealed by in situ hybridization. J Histochem Cytochem 34:467–473
Langer-Safer PR, Levine M, Ward DC (1982) Immunological method for mapping genes on Drosophila polytene chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:4381–4385
Lawrence JB, Singer RH (1986) Intracellular localization of messenger RNAs for cytoskeletal proteins. Cell 45:407–415
Lemke G, Axel R (1985) Isolation and sequence of a cDNA encoding the major structural protein of peripheral myclin. Cell 40:501–508
Manuelidis L (1984) Different central nervous system cell types display distinct and nonrandom arrangements of satellite DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:3123–3127
Manuelidis L (1985a) Indications of centromere movement during interphase and differentiation. Ann NY Acad Sci 450:205–221
Manuelidis L (1985b) In situ detection of DNA sequences using biotinylated probes. Focus 7:4–8
Manuelidis L, Ward DC (1984) Chromosomal and nuclear distribution of the hindIII 1.9-kb human DNA repeat segment. Chromosoma 91:28–38
Manuelidis L, Langer-Safer PR, Ward DC (1982) High resolution mapping of satellite DNA using biotin-labeled DNA probes. J Cell Biol 95:619–625
Trapp BD, Itovama Y, Sternberger NH, Quarles RH, Webster HdeF (1981) Immunocytochemical localization of P 0 protein in Golgi complex membranes and myelin of developing rat Schwann cells. J Cell Biol 90:1–6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Webster, H.F., Lamperth, L., Favilla, J.T. et al. Use of a biotinylated probe and in situ hybridization for light and electron microscopic localization of P 0 mRNA in myelin-forming Schwann cells. Histochemistry 86, 441–444 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500614
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500614