Abstract
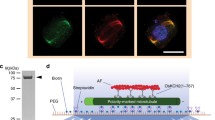
In plant cells, microtubule-based motor proteins have not been characterized to the same degree as in animal cells; therefore, it is not yet clear whether the movement of organelles and vesicles is also dependent on the microtubular cytoskeleton. In this work the kinesinimmunoreactive homologue from pollen tubes of Nicotiana tabacum L. has been purified and biochemically characterized. The protein preparation mainly contained a polypeptide with a relative molecular weight of approx. 100 kDa. This polypeptide bound to animal microtubules in an ATP-dependent manner and it further copurified with an ATPase activity fourfold-stimulated by the presence of microtubules. In addition, the sedimentation coefficient (approx. 9S) was similar to those previously shown for other kinesins. Immunofluorescence analyses revealed a partial co-distribution of the protein with microtubules in the pollen tube. These data clearly indicate that several properties of the kinesin-immunoreactive homologue are similar to those of kinesin proteins, and suggest that molecular mechanisms analogous to those of animal cells may drive the microtubule-based motility of organelles and vesicles in plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AE-LPLC:
-
anion-exchange low-pressure liquid chromatography
- AMPPNP:
-
5′-adenylylimidodiphosphate
- PKH:
-
pollen kinesin homologue
- SDS-PAGE:
-
sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
References
Amos, L.A. (1987) Kinesin from pig brain studied by electron microscopy. J. Cell Sci. 87, 105–111
Asada, T., Sonobe, S., Shibaoka, H. (1991) Microtubule translocation in the cytokinetic apparatus of cultured tobacco cells. Nature 350, 238–241
Baxter-Gabbard, K.L. (1972) A simple method for the large-scale preparation of sucrose gradients. FEBS Lett. 20, 117–119
Bloom, G.S. (1992) Motor proteins for cytoplasmic microtubules. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 4, 66–73
Bloom, G.S., Wagner, M.C., Pfister, K.K., Brady, S.T. (1988) Native structure and physical properties of bovine brain kinesin and identification of the ATP-binding subunit polypeptide. Biochemistry 27, 3409–3416
Bradford, M.M. (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein using the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254
Brady, S.T., Pfister, K.K., Bloom, G.S. (1990) A monoclonal antibody to the heavy chain of kinesin inhibits anterograde and retrograde axonal transport in isolated squid axoplasm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 1061–1065
Brewbaker, J.L., Kwack, B.H. (1963) The essential role of calcium ions in pollen germination and pollen tube growth. Am. J. Bot. 50, 859–865
Buster, D., Scholey, J.M. (1991) Purification and assay of kinesin from sea urchin eggs and early embryos. J. Cell Sci. 14, 109–115
Cohn, S.A., Ingold, A.I., Scholey, J.M. (1987) Correlation between the ATPase and microtubule translocating activities of sea urchin egg kinesin. Nature 328, 160–163
Cole, D.G., Cande, W.Z., Baskin, R.J., Skoufias, D.A., Hogan, C.J., Scholey, J.M. (1992) Isolation of sea urchin egg kinesin-related protein using peptide antibodies. J. Cell Sci. 101, 291–301
Dabora, S.L., Sheetz, M.P. (1988) The microtubule-dependent formation of a tubulovesicular network with characteristics of the ER from cultured cell extracts. Cell 54, 27–35
De Cuevas, M., Tao, T, Goldstein, L.S.B. (1992) Evidence that the stalk of Drosophila kinesin heavy chain is an α-helical coiled coil. J. Cell Biol. 116, 957–965
Emons, A.M.C., Pierson, E.S., Derksen, J. (1991) Cytoskeleton and intracellular movement in plant cells. In: Biotechnology — current progress, pp. 311–335, Cheremisimoff, P.N., Ferrante, L.M., eds. Technomic Publishing Co, Lancaster, Basel
Epstein, H., Scholey, J.M. (1992) Kinesins in the spindle: an update. Trends Cell Biol. 2, 315–318
Fellous, A., Francon, J., Lennon, A.M., Nunez, J. (1977) Microtubule assembly in vitro. Eur. J. Biochem. 78, 167–174
Fosket, D.E., Morejohn, L.C. (1992) Structural and functional organization of tubulin. In: Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 43, 201–240
Gonzalez-Romo, P., Sanchez-Nito, S., Gavilanes-Ruiz, M. (1992) A modified colorimetric method for the determination of orthophosphate in the presence of high ATP concentrations. Anal. Biochem. 200, 235–238
Hepler, P.K., Palevitz, B.A., Lancelle, S.A., McCauley, M.M., Lichtscheidl, I. (1990) Cortical endoplasmic reticulum in plants. J. Cell Sci. 96, 355–373
Hirokawa, N.N., Pfister, K.K., Yorufuji, H., Wagner, M.C., Brady, S.T., Bloom, G.S. (1989) Submolecular domains of bovine brain kinesin identified by electron microscopy and monoclonal antibody decoration. Cell 56, 867–878
Hirokawa, N., Sato-Yoshitake, R., Kobayashi, N., Pfister, K.K., Bloom, G.S., Brady, S.T. (1991) Kinesin associates with anterogradely transported membranous organelles in vivo. J. Cell Biol. 114, 295–302
Hollenbeck, P.J. (1989) The distribution, abundance and subcellular localization of kinesin. J. Cell Biol. 108, 2335–2342
Hollenbeck, P.J., Swanson, J.A. (1990) Radial extension of the macrophage tubular lysosomes supported by kinesin. Nature 346, 864–866
Houliston, E., Elinson, R.P. (1991) Evidence for the involvement of microtubules, ER, and kinesin in the cortical rotation of fertilized frog eggs. J. Cell Biol. 114, 1017–1028
Ingold, A.L., Cohn, S.A., Scholey, J.M. (1988) Inhibition of kinesindriven microtubule motility by monoclonal antibodies to kinesin heavy chains. J. Cell Biol. 107, 2657–2667
Kachar, B., Albanesi, J.P., Fujisaki, M., Korn, E.D. (1987) Extensive purification from Acanthamoeba castellanii of a microtubule-dependent translocator with microtubule-activated Mg2+-ATPase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 262, 16180–16185
Khono, T., Ishikawa, R., Negata, T., Kohama, K., Shimmen, T. (1992) Partial purification of myosin from lily pollen tubes by monitoring with in vitro motility assay. Protoplasma 170, 77–85
Kuznetsov, S.A., Vaisberg, Y.A., Shanina, N.A., Magretova, N.N., Chernyak, V.Y., Gelfand, V.I. (1988) The quaternary structure of bovine brain kinesin. EMBO J. 7, 353–356
Kuznetsov, S.A., Vaisberg, Y.A., Rothwell, S.W., Murphy, D.B., Gelfand, V.I. (1989) Isolation of a 45-kDa fragment from the kinesin heavy chain with enhanced ATPase and microtubulebinding activities. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 589–595
Laemmli, U.K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227, 680–685
Leslie, R.J., Hird, R.B., Wilson, L., McIntosh, J.R., Scholey, J.M. (1987) Kinesin is associated with a nonmicrotubule component of sea urchin mitotic spindle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 2771–2774
Leopold, P.L., McDowall, A.W., Pfister, K.K., Bloom, G.S., Brady, S.T. (1992) Association of kinesin with characterized membrane-bounded organelles. Cell Motil. Cytoskel. 23, 19–33
Martin, R.G., Ames, B.N. (1961) A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J. Biol. Chem. 236, 1372–1379
McCaffrey, G., Vale, R.D. (1989) Identification of a kinesin-like microtubule-based motor protein in Dyctiostelium discoideum. EMBO J. 8, 3229–3234
Murofushi, H., Ikai, A., Okuhara, K., Kotani, S., Aizawa, H., Kumakura, K., Sakai, H. (1988) Purification and characterization of kinesin from adrenal medulla. J. Biol. Chem. 263, 12744–12750
Neighbors, B.W., Williams, R.C.Jr., McIntosh, J.R. (1988) Localization of kinesin in cultured cells. J. Cell Biol. 106, 1193–1204
Pfister, K.K., Wagner, M.C., Stenoien, D.L., Brady, S.T., Bloom, G.S. (1989) Monoclonal antibodies to kinesin heavy chains stain vesicle-like structures, but not microtubules in cultured cells. J. Cell Biol. 108, 1453–1463
Pierson, E.S., Cresti, M. (1992) Cytoskeleton and cytoplasmic organization of pollen and pollen tube. Int. Rev. Cytol. 140, 73–125
Rodionov, V.I., Gyoeva, F.K., Gelfand, V.I. (1991) Kinesin is responsible for centrifugal movement of pigment granules in melanophores. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 4956–4960
Saxton, W.M., Porter, M.A., Cohn, S.A., Scholey, J.M., Raff, E.M., McIntosh, J.R. (1988) Drosophila kinesin: characterization of microtubule motility and ATPase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 1109–1113
Saxton, W.M., Hicks, J., Goldstein, L.S.B., Raff, E.C. (1991) Kinesin heavy chain is essential for viability and neuromuscular functions in Drosophila, but mutants show no defects in mitosis. Cell 64, 1093–1102
Scholey, J.M., Porter, M.E., Grissom, P.M., McIntosh, J.R. (1985) Identification of kinesin in sea urchin eggs and evidence for its localization in the mitotic spindle. Nature 318, 483–486
Scholey, J.M., Heuser, J., Yang, J.T., Goldstein, L.S.B. (1989) Identification of the globular mechanochemical heads of kinesin. Nature 338, 355–357
Schroer, T.A., Schnapp, B.J., Reese, T.S., Sheetz, M.P. (1988) The role of kinesin and other soluble factors in organelle movement along microtubules. J. Cell Biol. 107, 1785–1792
Tiezzi, A. (1991) The pollen tube Cytoskeleton. Electron Microsc. Rev. 4, 205–219
Tiezzi, A., Moscatelli, A., Milanesi, C., Ciampolini, F., Cresti, M. (1987) Taxol-induced structures derived from cytoskeletal elements of Nicotiana tabacum pollen tube. J. Cell Sci. 88, 657–661
Tiezzi, A., Moscatelli, A., Cai, G., Bartalesi, A., Cresti, M. (1992) An immunoreactive homologue of mammalian kinesin in Nicotiana tabacum pollen tube. Cell Motil. Cytoskel. 21, 132–137
Towbin, H., Staehelin, T., Gordon, J. (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets. Procedure and some applications. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 76, 4350–4354
Vale, R.D., Reese, T.S., Sheetz, M.P. (1985) Identification of a novel force-generating protein, kinesin, involved in microtubule-based motility. Cell 42, 39–50
Vallee, R.B., Shpetner, H.S. (1990) Motor proteins of cytoplasmic microtubules. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 59, 909–932
Wright, B.D., Wedaman, K.P., Willy, P.J., Morand, J.N., Scholey, J.M. (1991) Subcellular localization and sequence of sea urchin kinesin heavy chain: evidence for its association with membranes in the mitotic apparatus and interphase cytoplasm. J. Cell Biol. 113, 817–833
Wagner, M.C., Pfister, K.K., Bloom, G.S., Brady, S.T. (1989) Copurification of kinesin polypeptides with microtubule-stimulated Mg-ATPase activity and kinetic analysis of enzymatic properties. Cell Motil. Cytoskel. 12, 195–215
Yang, J.T., Saxton, W.M., Stewart, R.J., Raff, E.C., Golstein, L.S.B. (1990) Evidence that the head of kinesin is sufficient for force generation and motility in vitro. Science 249, 42–47
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, G., Bartalesi, A., Del Casino, C. et al. The kinesin-immunoreactive homologue from Nicotiana tabacum pollen tubes: Biochemical properties and subcellular localization. Planta 191, 496–506 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00195751
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00195751