Summary
Short time incorporation of 32P was carried out with synchronised algae (young cells) depleted of phosphate. For the separation and determination of the acid-insoluble phosphate fractions of the cells an improved fractionation procedure was applied. In order to exclude competition by carbon dioxide all experiments were done in the absence of CO2.
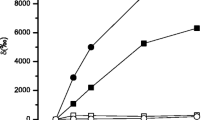
Compared with nitrogen, CO2-free air produces an increase in the labelling of phosphorylated compounds in the light. In strong white light, at high pH, air effects a remarkable increase of 32P in the acid-insoluble phosphate (P u), mainly in inorganic polyphosphates (P ul), whereas the total phosphate uptake remains almost unchanged. The increase in labelling of acid-insoluble phosphate is, therefore, accompanied by a substantial decrease in the labelling of acid-soluble compounds (P l). In weak white light or in far-red light, at low pH even in strong white or red light, an increase of phosphate uptake and an increased labelling of the acid-stable organic acid-soluble fraction (P os) is observed instead. The effect of oxygen increases somewhat with increasing light intensity up to light saturation, and it increases markedly with increasing oxygen concentration.
An essential contribution by oxidative phosphorylation to this oxygen effect can be ruled out on account of its much higher sensitivity to oxygen. Pseudocyclic photophosphorylation is also not regarded as the main force because of its higher oxygen affinity. Occurrence of photorespiration has not been clearly established so far in related algae (Chlorella), and its use for phosphorylation is unknown. A better, although not complete explanation is given by comparing the oxygen effect with the well-known inhibition of photosynthesis by oxygen (Warburg effect), which leads to an increase in glycolate formation and a simultaneous decrease in the pool sizes of carbon reduction cycle intermediates, even in the absence of CO2. Since the photophosphorylation process, as well as the photosynthetic electron flow, seem unaffected by high oxygen concentrations whereas the formation of organic phosphate compounds is partially inhibited, excess ATP may be available for polyphosphate synthesis. This explanation would be consistent with the assumption that polyphosphate-ADP kinase mediates an equilibrium between ATP and polyphosphates, mainly at higher pH. At low pH and in other cases the excess ATP might be available for an increased phosphate uptake and for phosphorylation of endogenous carbohydrates.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Bassham, J. A., Kirk, M.: The effect of oxygen on the reduction of CO2 to glycolic acid and other products during photosynthesis by Chlorella. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 9, 376–380 (1962).
Björkman, O.: The effect of oxygen concentration on photosynthesis in higher plants. Physiol. Plantarum (Copenh.) 19, 618–633 (1966).
Brown, D. L., Tregunna, E. B.: Inhibition of respiration during photosynthesis by some algae. Canad. J. Bot. 45, 1135–1143 (1967).
Coombs, J., Whittingham, C. P.: The mechanism of inhibition of photosynthesis by high partial pressures of oxygen in Chlorella. Proc. roy. Soc. B 164, 511–520 (1966).
Ellyard, P. W., Gibbs, M.: Inhibition of photosynthesis by oxygen in isolated spinach chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 44, 1115–1121 (1969).
Essl, A.: Vergleichende Untersuchungen über die Wirkungsspektren der Photophosphorylierungsprozesse und der photosynthetischen Sauerstoffproduktion bei der Blaualge Anacystis nidulans. Diss. Würzburg 1969.
Fock, H., Egle, K.: Über die Lichtatmung bei grünen Pflanzen. I. Die Wirkung von Sauerstoff und Kohlendioxyd auf den CO2-Gaswechsel während der Lichtund Dunkelphase. Beitr. Biol. Pflanzen 42, 213–239 (1966).
Gimmler, H., Ullrich, W., Domanski-Kaden, J., Urbach, W.: Excretion of glycolate during synchronous culture of Ankistrodesmus braunii in the presence of disalicylidenepropanediamine or hydroxypyridinemethanesulfonate. Plant and Cell Physiol. 10, 103–112 (1969).
Heber, U.: Conformational changes of chloroplasts induced by illumination of leaves in vivo. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 180, 302–319 (1969).
—, French, C. S.: Effects of oxygen on the electron transport chain of photosynthesis. Planta (Berl.) 79, 99–112 (1968).
Hess, J. L., Tolbert, N. E., Pike, L. M.: Glycolate biosynthesis by Scenedesmus and Chlorella in the presence or absence of NaHCO3. Planta (Berl.) 74, 278–285 (1967).
Hoch, G., Owens, O. V. H., Kok, B.: Oxygen metabolism in Anacystis nidulans. Coll. Intern. du CNRS 119, 261–272 (1963).
Iwamura, T., Kuwashima, M.: Formation of adenosine 5′-triphosphate from polyphosphate by a cell-free extract from Chlorella. J. gen. appl. Microbiol. 10, 83–86 (1964).
Jeschke, W. D.: Die cyclische und die nichtcyclische Photophosphorylierung als Energiequellen der lichtabhängigen Chloridionenaufnahme bei Elodea. Planta (Berl.) 73, 161–174 (1967).
—, Simonis, W.: Effect of CO2 on photophosphorylation in vivo as revealed by the light-dependent Cl- uptake in Elodea densa. Z. Naturforsch. 22b, 873–876 (1967).
Kanai, R., Aoki, S., Miyachi, S.: Quantitative separation of inorganic polyphosphates in Chlorella cells. Plant and Cell Physiol. 6, 467–473 (1965).
—, Simonis, W.: Eimbau von 32P in verschiedene Phosphatfraktionen, besonders Polyphosphate, bei einzelligen Grünalgen (Ankistrodesmus braunii) im Licht und im Dunkeln. Arch. Mikrobiol. 62, 56–71 (1965).
Kessler, E.: Der Einfluß von Sauerstoff auf die Photosynthese. In: Handbuch der Pflanzenphysiologie, Bd. V/1, S. 935–950. Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: Springer 1960.
Kowallik, U., Kowallik, W.: Eine wellenlängenabhängige Atmungssteigerung während der Photosynthese von Chlorella. Planta (Berl.) 84, 141–157 (1969).
Kulaev, I. S., Vagabov, B. M.: The effect of the cultivation conditions on the metabolism of inorganic polyphosphates and other phosphoric compounds in Scenedesmus obliquus. Biochimija 32, 253–260 (1967) [Russicsch].
Miyachi, S., Kanai, R., Mihara, S., Miyachi, S., Aoki, S.: Metabolic roles of inorganic polyphosphates in Chlorella cells. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 93, 625–634 (1964).
—, Tamiya, H.: Distribution and turnover of phosphate compounds in growing Chlorella cells. Plant and Cell Physiol. 2, 405–414 (1961).
Muller-Felter, S., Ebel, J. P.: Séparation des acides ribonucléiques et des polyphosphates inorganiques. II. Mise au point d'une technique de séparation par adsorption différentielle sur charbon. Bull. Soc. Chimie biol. (Paris) 44, 1175–1184 (1962).
Nobel, P. S.: A rapid technique for isolating chloroplasts with high rates of endogenous photophosphorylation. Plant Physiol. 42, 1389–1394 (1967).
Orth, G. M., Tolbert, N. E., Jimenez, E.: Rate of glycolate formation during photosynthesis at high pH. Plant Physiol. 41, 143–147 (1966).
Poskuta, J.: Photosynthesis, respiration and post-ilumination fixation of CO2 by corn leaves as influenced by light and oxygen. Physiol. Plantarum (Copenh.) 22, 76–85 (1969).
Ried, A.: Über die Wirkung blauen Lichtes auf den photosynthetischen O2-Austausch von Chlorella. Planta (Berl.) 87, 333–346 (1969).
Tanner, W., Dächsel, L., Kandler, O.: Effects of DCMU and antimycin A on photoassimilation of glucose in Chlorella. Plant Physiol. 40, 1151–1156 (1965).
—, Löffler, M., Kandler, O.: Cyclic photophosphorylation in vivo and its relation to photosynthetic CO2-fixation. Plant Physiol. 44, 422–428 (1969).
Ullrich, W., Simonis, W.: Die Bildung von Polyphosphaten bei Ankistrodesmus braunii durch Photophosphorylierung im Rotlicht von 683 und 712 nm unter Stickstoffatmosphäre. Planta (Berl.) 84, 358–367 (1969).
—, Urbach, W., Santarius, K. A., Heber, U.: Die Verteilung des Orthophosphates auf Plastiden, Cytoplasma und Vacuole in der Blattzelle und ihre Veränderung im Licht-Dunkel-Wechsel. Z. Naturforsch. 20b, 905–910 (1965).
Urbach, W., Simonis, W.: Further evidence for the existence of cyclic and noncyclic photophosphorylation in vivo by means of desaspidin and DCMU. Z. Naturforsch. 22b, 537–540 (1967).
Warburg, O., Krippahl, G.: Glykolsäurebildung in Chlorella. Z. Naturforsch. 15b, 197–199 (1960).
Whittingham, C. P.: Respiration of algae. In: Handbuch der Pflanzenphysiologie, Bd. XII/2, S. 447–454. Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: Springer 1960.
Wintermans, J. F. G. M.: On the formation of polyphosphates in Chlorella in relation to conditions for photosynthesis. Proc. kon. ned. Akad. Wet. 57C, 574–583 (1954).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Herrn Prof. Dr. W. Simonis zum 60. Geburtstag gewidmet.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ullrich, W.R. Zur Wirkung von Sauerstoff auf die 32P-Markierung von Polyphosphaten und organischen Phosphaten bei Ankistrodesmus braunii im Licht. Planta 90, 272–285 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00387179
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00387179