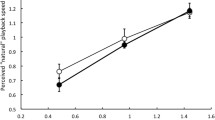
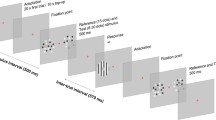
Summary
-
1.
The method of selective (differential) adaptation was applied to the parameters direction of movement and velocity in the perception of moving patterns.
-
2.
Adaptation was determined by measuring changes in the minimum duration of tachistoscopic presentations needed for the perception of translational movements as a function of the applied stimuli (including variations in direction of movement and velocity).
-
3.
This approach enabled the selective stimulus processing systems for direction of movement and velocity to be separated, and may ultimately allow the structure of human afferent movement perception to be analyzed.
-
4.
The results are discussed in connection with the neurophysiology of movement perception.
Zusammenfassung
-
l.
Die Methode der selektiven Adaptation wurde auf die Parameter „Bewegungsrichtung“ und „Geschwindigkeit“ bei der Wahrnehmung von bewegten Mustern angewendet.
-
2.
Adaptation war dabei definiert als die Veränderung in der minimalen Entdeckungszeit für Translationsbewegungen (tachistoskopische Darbietung) in Abhängigkeit von den Adaptationsreizen (bei Variation von Bewegungsrichtung und Geschwindigkeit).
-
3.
Mit dieser Methode konnten für die Wahrnehmungsanalyse von Eigenschaften bewegter optischer Muster informationsselektive Verarbeitungssysteme ausgegliedert werden, die bewegungsrichtungs- und geschwindigkeitsempfindlich sind. Dadurch sind Möglichkeiten aufgezeigt, die Struktur der afferenten Bewegungswahrnehmung des Menschen zu analysieren.
-
4.
Die Ergebnisse konnten zu den vorliegenden Daten der Neurophysiologie des Bewegungssehens in Beziehung gesetzt werden.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Barlow, H. B., Hill, R. M.: Evidence for a physiological explanation of the water-fall phenomenon and figural aftereffects. Nature (Lond.) 200, 1345–1347 (1963)
Barlow, H. B., Levick, W. R.: The mechanisms of directionally selective units in rabbit's retina. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 178, 477–504 (1965)
Blakemore, C., Campbell, F. W.: On the existence of neurones in the human visual system selectively sensitive to the orientation and size of retinal images. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 203, 471–197 (1969)
Blakemore, C., Julesz, B.: Stereoscopic depth aftereffect produced without monocular cues. Science 171, 286–288 (1971)
Blakemore, C., Nachmias, J.: The orientation specificity of two visual aftereffects. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 213, 157–174 (1971)
Blakemore, C., Nachmias, J., Sutton, P.: The perceived spatial frequency shift: evidence for frequency selective neurones in the human brain. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 210, 727–750 (1970)
Brown, J. F.: The visual perception of velocity. Psych. Forsch. 14, 199–232 (1931)
Campbell, F. W., Cleland, B. G., Cooper, G. F., Enroth-Cugell, Ch.: The angular selectivity of visual cortical cells to moving gratings. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 198, 237–250 (1968)
Campbell, F. W., Kulikowski, J. J.: Orientational selectivity of the human visual system. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 187, 437–445 (1966)
Campbell, F. W., Kulinowski, J. J., Levinson, J.: The effect of orientation on the visual resolution of gratings. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 187, 427–436 (1966)
Campbell, F. W., Maffei, L.: Electrophysiological evidence for the existance of orientation and size detectors in the human visual system. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 207, 635–652 (1970)
Dichgans, J., Körner, F., Voigt, K.: Vergleichende Skalierung des afferenten und efferenten Bewegungssehens beim Menschen: Lineare Funktion mit verschiedener Anstiegssteilheit. Psychol. Forsch. 32, 277–295 (1969)
Erke, H., Gräser, H.: Reversibility of perceived motion: selective adaptation of the human visual system to speed, size and orientation. Vision Res. 12, 69–87 (1972)
Eysel, U. Th., Grüsser, O. J.: Neurophysiological basis of pattern recognition in the cat's visual system. In: Zeichenerkennung durch biologische und technische Systeme, S. 60–80. Grüsser, O. J., Klinke, R.: Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1971
Gilinsky, A. S.: Orientation specific effects of patterns of adapting light on visual acuity. J. opt. Soc. Amer. 58, 13–18 (1968)
Gilinsky, A. D., Cohen, H. H.: Reaction time to change in visual orientation. Perception and Psychophysics 11, 129–134 (1972)
Gilinsky, A. S., Doherty, R. S.: Interocular transfer of orientational effects. Science 164, 454–455 (1969)
Gilinsky, A. S., Mayo, Th. H.: Inhibitory effects of orientational adaptation. J. opt. Soc. Amer. 61, 1710–1714 (1971)
Gleser, W. D.: Zur Untersuchung der Mechanismen der Bilderkennung. Z. Psychol. 171, 80–91 (1965)
Graham, C. H.: Perception of motion. In: Vision and visual perception, S. 575–588. (Graham, C. H. Ed.): New York-London-Sydney: John Wiley and Sons, Inc. 1965
Gregory, R. L.: Auge und Gehirn. Zur Psychophysiologie des Sehens. München: Kindler Verlag 1966
Grüsser, O. J., Grüsser-Cornehls, U.: Neurophysiologie des Bewegungssehens. Bewegungsempfindliche und richtungsspezifische Neurone im visuellen System. Ergebn. Physiol. 61, 178–265 (1969)
Hajos, A.: Psychophysiologische Probleme bei „Farbkonturen“ und „Konturfarben“. Berichte des Instituts für Psychol. Marburg, 1967, Nr. 13
Hajos, A.: Verlauf formspezifischer Farbadaptation im visuellen System des Menschen. Berichte des Instituts für Psychol. Marburg 1969, Nr. 18
Hajos, A.: Verlauf formenspezifischer Farbadaptation. Psychol. Beitr. 11, 95–114 (1969)
Hajos, A.: Adaptationsprozesse bei Konturfarben und Farbkonturen. Habilitationsschrift Marburg 1969
Hajos, A.: Sinnespsychologische Untersuchungen zur Invarianzbildung im visuellen System des Menschen. In: Zeichenerkennung durch biologische- und technische Systeme, S. 97–113. Grüsser, O. J., Klinke, R.: Berlin-Heidelberg-NewYork: Springer 1971
Hajos, A., Maul, U.: Subjektive Geometrie bei Streifennachbildern. Berichte des Instituts für Psychol. Marburg 1969, Nr. 16
Hajos, A., Ritter, M.: Experiments to the problem of interocular transfer. Acta Psychol. (Amst.) 24, 81–90 (1965)
Hubel, D. H., Wiesel, T. N.: Receptive fields and functional architecture in two nonstriate visual areas (18 and 19) of the cat. J. Neurophysiol. 28, 228–289 (1965)
Hubel, D. H., Wiesel, T. N.: Receptive and functional architecture of monkey striate cortex. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 195, 215–243 (1968)
Johansson, G.: Geschehenswahrnehmung. In: Handbuch der Psychologie; Allgemeine Psychologie I/1, S. 745–775. Göttingen: Verlag für Psychologie, Dr. C. J. Hogrefe 1966
Jung, R.: Neuronal mechanisms of pattern vision and motion detection. In: Sensory processes at neuronal and behavioral levels, p. 1–17. Gersuni, G. U. (Ed.): New York-London: Academic Press 1971
Kahneman, D.: Method, findings and theory in the studies of visual masking. Psychol. Bull. 70, 404–425 (1968)
Kohler, I.: de: über Aufbau und Wandlungen der Wahrnehmungswelt, insbesondere über „bedingte Empfindungen“. Sitz. Ber. Österr. Akad. d. Wiss.: phil. hist. Kl. 227/1, 1–181, 1951
Kohler, I.: Der Brillenversuch in der Wahrnehmungspsychologie mit Bemerkungen zur Lehre der Adaptation. Z. exp. angew. Psychol. 3, 381–417 (1956)
Lücke, G.: Untersuchungen über die Adaptation von Konturdetektoren des menschlichen visuellen Systems durch die Analyse der Nachbilder alternierender Reizmuster. Referat auf der 10. Tagung exp. arb. Psychol. Marburg 1968
McCollough, C.: Color adaptation of edge-detectors in the human visual system. Science 149, 1115–1116 (1965)
Pantle, A., Sekuler, R. W.: Velocity-sensitive elements in human vision: Initial psychophysical evidence. Vision Res. 8, 445–450 (1968)
Pantle, A., Sekuler, R. W.: Contrast response of human visual mechanisms sensitive to orientation and direction of motion. Vision Res. 9, 297–406 (1969)
Redslob, O.: Über Sättigung gesehener Bewegungsrichtung. Psychol. Forsch. 22, 211–237 (1938)
Sekuler, R. W., Ganz, L.: After-effect of seen motion with a stabilized retinal image. Science 139, 419–420 (1963)
Sekuler, R. W., Rubin, E. L., Cushman, W. H.: Selectivities of human visual mechanisms for direction of movement and contour orientation. J. opt. Soc. Amer. 58, 1146–1150 (1968)
Spigel, I. M.: Readings in the study of perceived movement. New York: Harper and Row 1965
Wallach, H.: Über visuell wahrgenommene Bewegungsrichtung. Psychol. Forsch. 20, 325–380 (1935)
Weisstein, N.: What the frog's eye tells the human brain: single cell analysers in the human visual system. Psychol. Bull. 72, 157–176 (1969)
Woll, St., Erikson, Ch. W., Hake, H. W.: A forced-choice study of edge detectors in the human visual system. Perception and Psychophysics 9, 247–252 (1970)
Wurtz, R. H.: Visual receptive fields of striate cortex neurons in the awake monkey. J. Neurophysiol. 32, 727–742 (1969)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dem Fonds zur Förderung der wissenschaftlichen Forschung, Wien, danken wir für die Bereitstellung der finanziellen Mittel.
Jetzt Fachbereich Psychologie, Philipps-Universität Marburg.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ritter, M., Lücke, G. & Zihl, J. Selektive Analyse von Bewegungsrichtung und Geschwindigkeit in der visuellen Wahrnehmung des Menschen. Psychol. Forsch. 36, 267–296 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00424480
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00424480