Summary
The existence of both adrenergic and cholinergic innervation of the atrial myocardium of the adult human heart was demonstrated by means of fluorescence induced by formaldehyde or glyoxylic acid and by electron microscopy.
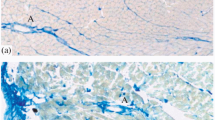
The adrenergic fluorescing axons (1) followed the course of blood vessels as typical perivascular nerve plexuses, and (2) formed a three-dimensional fairly dense nerve net obviously not related to the blood vessels. The varicosities frequently came into close apposition on myocardial cells.
Several types of nerve terminals were differentiated at electron microscopy: (1) an “adrenergic” type containing small (diameter 450–700 Å) dense-cored vesicles and usually (in various proportions) small “empty” and/or large (900–1500 Å) dense-cored vesicles, (2) a “cholinergic” type containing small (ca. 500 Å) “empty” vesicles and occasionally also some large (mean diameter ca. 1200 Å) dense-cored vesicles, (3) a “pale” type containing only a few or no vesicles, (4) a “disintegrated” type containing degenerated mitochondria, autophagic vacuoles, and occasional normal-looking mitochondria, (5) nerve terminals containing a large number of mitochondria in addition to varying vesicle populations, and (6) a (possibly baroreceptive type of) nerve terminal containing myelinlike lamellated structures. The “disintegrated” and the “pale” types of nerve terminals possibly represent different stages of axonal degeneration, or may correspond to diminution in the transmitter substance concentration under certain pathophysiologic conditions, respectively. Nerve terminals crowded with mitochondria may be sensory and involved in mechano-or chemoreceptive functions.
In preliminary experiments convincing evidence was obtained that the glyoxylic acid-induced fluorescence histochemical method will be suitable for comparative studies on (human) clinical specimens, e.g., for analyzing the degree of the functional activity of the intrinsic adrenergic innervation of the myocardium under various pathophysiologic conditions. The modification which appeared most appropriate for such studies is described in detail, and is proposed for use as a standard method in other similar or related studies on human clinical series. The essential criteria for analyzing the specimens at fluorescence microscopy are suggested as well.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angelakos, E. T., Fuxe, K., Torchiana, M. L.: Chemical and histochemical evaluation of the distribution of catecholamines in the rabbit and guinea-pig hearts. Acta physiol. scand. 59, 184–192 (1963)
Baumgarten, H. G.: Über die Verteilung von Catecholaminen im Darm des Menschen. Z. Zellforsch. 83, 133–146 (1967)
Burnstock, G., Iwayama, T.: Fine-structural identification of autonomic nerves and their relation to smooth muscle. Progr. Brain Res. 34, 389–404 (1971)
Chiba, T.: Fine structure of the baroreceptor nerve terminals in the carotid sinus of the dog. J. Electron Microscopy 21, 139–148 (1972)
Chiba, T., Yamauchi, A.: On the fine structure of the nerve terminals in the human myocardium. Z. Zellforsch. 108, 324–338 (1970)
Chidsey, C. A., Braunwald, E., Morrow, A. G., Mason, D. T.: Myocardial norepinephrine concentration in man. Effects of reserpine and of congestive heart failure. New Engl. J. Med. 269, 653–658 (1963)
Corrodi, H., Hillarp, N.- Å., Jonsson, G.: fluorescence methods for the histochemical demonstration of monoamines. 3. Sodium borohydride reduction of the fluorescent compounds as a specificity test. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 12, 582–586 (1964)
Dail, W. G., Jr., Palmer, G. C.: Localization and correlation of catecholamine-containing cells with adenyl cyclase and phosphodiesterase in the human fetal heart. Anat. Rec. 177, 265–288 (1973)
Ehinger, B., Falck, B., Persson, H., Sporrong, B.: Adrenergic and cholinesterase-containing neurons of the heart. Histochemie 16, 197–205 (1968)
Eränkö, O.: Distribution of fluorescing islets, adrenaline and noradrenaline in the adrenal medulla of the hamster. Acta endocr. (Kbh.) 18, 174–179 (1955)
Eränkö, O.: The practical histochemical demonstration of catecholamines by formaldehyde induced fluorescence. J. roy micr. Soc. 87, 259–276 (1967)
Falck, B.: Observations on the possibilities of the cellular localization of monoamines by a fluorescence method. Acta physiol. scand. 56, Suppl. 197 (1962)
Falck, B., Hillarp, N.- Å., Thieme, G., Torp, A.: Fluorescence of catecholamines and related compounds condensed with formaldehyde. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 10, 348–354 (1962)
Hirsch, E. F., Borghard-Erdle, A. M.: The innervation of the human heart. I. The coronary arteries and the myocardium. Arch. Path. 71, 384–407 (1961)
Hirsch, E. F., Borghard-Erdle, A. M.: The innervation of the human heart. II. The papillary muscles. Arch. Path. 73, 100–117 (1962)
Jacobowitz, D.: Histochemical studies on the relationship of chromaffin cells and adrenergic nerve fibres to the cardiac ganglia of several species. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 158, 227–240 (1967)
Jonsson, G.: The formaldehyde fluorescence method for the histochemical demonstration of biogenic monoamines. M. D. Thesis, Stockholm 1967
Jonsson, G.: Microfluorimetric studies on the formaldehyde-induced fluorescence of noradrenaline in adrenergic nerves of the rat iris. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 17, 714–723 (1969)
Lidbrink, P., Jonsson, G.: Semiquantitative estimation of formaldehyde-induced fluorescence of noradrenaline in central noradrenaline nerve terminals. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 19, 747–757 (1971)
Lindvall, O., Björklund, A.: The glyoxylic acid fluorescence histochemical method: a detailed account of the methodology for the visualization of central catecholamine neurons. Histochemistry 39, 97–127 (1974)
Lindvall, O., Björklund, A., Svensson, L.- Å.: Fluorophore formation from catecholamines and related compounds in the glyoxylic acid fluorescence histochemical method. Histochemistry 39, 197–227 (1974)
McLean, J. R.: An improved technique for the demonstration of sympathetic nerves in human cardiac muscle. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 16, 590–591 (1968)
Nilsson, E., Sporrong, B.: Electron microscopic investigation of adrenergic and nonadrenergic axons in the rabbit SA-node. Z. Zellforsch. 111, 404–412 (1970)
Partanen, S., Korkala, O.: Catecholamines in human fetal heart. Experientia (Basel) 30, 798–799 (1974)
Pearse, A. G. E.: In: Cardiomyopathies, Ciba Foundation Symposium (eds. G. E. W. Wolstenholme and M. O'Connor), pp. 132–171. London: J. & A. Churchill Ltd. 1964
Penttilä, O., Merikallio, E., Sutanen, P., Klinge, E.: Auricular catecholamine content in ischaemic heart disease. Abstract in VI International Congress of Pharmagology, July 1975, Helsinki
Ploem, J. S.: The microscopic differentiation of the colours of formaldehyde-induced fluorescence. Progr. Brain Res. 34, 27–37 (1971)
Reynolds, E. S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17, 208–212 (1963)
Ritzén, M.: Cytochemical identification and quantitation of biogenic monoamines. M. D. Thesis, Stockholm 1967
Sachs, C.: Uptake and accumulation in vitro of 3H-noradrenaline in adrenergic nerves of human atrium. Histochemie 19, 189–198 (1969)
Schiebler, T. H., Winckler, J.: On the vegetative cardiac innervation. Progr. Brain Res. 34, 405–413 (1971)
Stöhr, Ph., Jr.: Mikroskopische Anatomie des vegetativen Nervensystems. In: Handbuch der mikroskopischen Anatomie des Menschen. Erg.-Bd. zu VII/4. und IX/1. Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: Springer 1957
Tranum-Jensen, J.: Ultrastructure of baroreceptors (BR) in the atrial endocardium of young pigs. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 50, 385 (1975)
Vogel, H. K., Jacobowitz, D., Chidsey, C. A.: Distribution of norepinephrine in the failing bovine heart. Correlation of chemical analysis and fluorescence microscopy. Circulat. Res. 24, 71–84 (1969)
Waris, T., Partanen, S.: Demonstration of catecholamines in peripheral adrenergic nerves in stretch preparations with fluorescence induced by aqueous solution of glyoxylic acid. Histochemistry 41, 369–372 (1975)
Watson, M. L.: Staining of tissue sections for electron microscopy with heavy metals. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 4, 475–478 (1958)
Winckler, J.: Über die adrenergen Herznerven bei Ratte und Meerschweinchen. Entwicklung und Innervationsmuster. Z. Zellforsch. 98, 106–121 (1969)
Yamauchi, A., Chiba, T.: Adrenergic and cholinergic innervation of the turtle heart ventricle. Z. Zellforsch. 143, 485–493 (1973)
Zypen, E. van der: Über die Ausbreitung des vegetativen Nervensystemes in den Vorhöfen des Herzens. Acta anat. (Basel) 88, 363–384 (1974)
Zypen, E. van der, Hasselhorst, G., Merz, R., Fillinger, H.: Histochemische und elektronen-mikroskopische Untersuchungen an den intramuralen Ganglien des Herzens bei Mensch und Ratte. Acta anat. (Basel) 88, 161–187 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kyösola, K., Partanen, S., Korkala, O. et al. Fluorescence histochemical and electron-microscopical observations on the innervation of the atrial myocardium of the adult human heart. Virchows Arch. A Path. Anat. and Histol. 371, 101–119 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00444927
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00444927