Summary
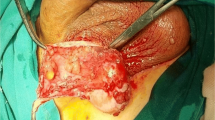
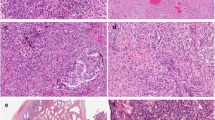
Ultrastructural features of a papillary mesothelioma arising in a hydrocele-sack are reported. The tumour cells presented numerous microvilli, desmosomes, basement membranes and abundant bundles of microfilaments, which all are hallmarks of mesotheliomas. The predominant cell type was the “clear epithelial cell”, but transitional cells and degenerative forms (foamy cells) were also found. The morphology and differential diagnosis of mesothelial tumours arising in the tunica vaginalis propria testis are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abell MR, Holtz F (1968) Testicular and paratesticular neoplasms in patients 60 years of age and older. Cancer 21:852–870
Echevarria RA, Arean VM (1968) Ultrastructural evidence of secretory differentiation in a malignant pleural mesothelioma. Cancer 22:323–332
Eimoto T, Inoue I (1977) Malignant fibrous mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis. Cancer 39:2059–2066
Ferenczy A, Fenoglio J, Richart RM (1972) Observations on benign mesothelioma of the genital tract (adenomatoid tumour). A comparative ultrastructural study. Cancer 30:244–260
Holland JM (1962) Multiple mesothelial cysts of the parietal tunica vaginalis testis — case report. J Urol 87:903–905
Jaugitz H (1977) Vergleichende elektronenoptische Untersuchungen an Mesotheliomzellen. Arch Geschwulstforsch 47:204–209
Kasdon EJ (1969) Malignant mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis propria testis. Report of two cases. Cancer 23:1144–1150
Kay S, Silverberg SG (1971) Ultrastructural studies of a malignant fibrous mesothelioma of the pleura. Arch Pathol 92:449–455
Klima M, Gyorkey F (1977) Benign pleural lesions and malignant mesothelioma. Virchows Arch [Pathol Anat] 376/181–193
Mouchel J (1971) Etude en microscopie électronique de deux mésothélioma pleuraux diffus. J Microsc 7:81–82
Mostofi FK, Price EB (1973) Tumors of the male genital system. AFIP, Washington DC
Nistal M, Contreras F, Paniagua R (1978) Adenomatoid tumour of the epididymis: Histochemical and ultrastructural study of 2 cases. Br J Urol 50:121–125
Osamura RY (1977) Ultrastructure of localized fibrous mesothelioma of the pleura. Cancer 39:139–142
Pugh RCB (1976) Pathology of the testis. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford London Edinburgh Melbourne
Stoebner P, Miech G, Sengel A, Witz JP (1970) Notions d'ultrastructure pleurale. II. Les mésothéliomes. Presse Med 24:1403–1408
Suzuki Y, Churg J, Kannerstein M (1976) Ultrastructure of human malignant diffuse mesothelioma. Am J Pathol 85:241–262
Taxy JB, Battifora H, Oyasu R (1974) Adenomatoid tumours: a light microscopic, histochemical and ultrastructural study. Cancer 34:306–316
Willis RA (1967) Pathology of tumors. 4th eds, Butterworth London
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mikuz, G., Höpfel-Kreiner, I. Papillary mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis propria testis. Virchows Arch. A Path. Anat. and Histol. 396, 231–238 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00431244
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00431244