Summary
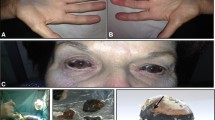
This paper reports three cases of membranous lipodystrophy (Nasu-Hakola disease) in two families and studies the carbohydrate components of membranocystic lesions in all three cases, using twelve kinds of lectins labelled by horseradish peroxidase (HRP).Maclura pomifera agglutinin (MPA), which specifically binds α-D-galactose residues, strongly stained typical membranocystic lesions, whereas the other lectins did not. However,Helix pomatia agglutinin (HPA), which specifically binds to N-acetyl-D-galactosamine (GalNAc), stained the membranes of degenerated adipose cells. These were thought to appear during the initial or early stage of the membranocystic lesions. This suggests that a change of carbohydrate residues occurs during the formation of the membranocystic lesions. We also investigated the lectin binding sites at the ultrastructural level using MPA-HRP colloidal gold (CG) conjugate. In the well developed membrane, CG particles were arranged regularly along the minute tubular structures. On the other hand, there were a few irregularly spaced CG particles on the thinner membranes and also on the membranes of the degenerating adipose cells. No CG particles labelled the cell membranes of normal adipose cells. The presence of α-D-galactose residues in the membranocystic lesions is demonstrated for the first time at the electron microscopic level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akai M, Tateishi A, Cheng CH, Morii K, Abe M, Ohno T, Ben M (1977) Membranous lipodystrophy - a clinicopathological study of six cases. J Bone Joint Surg 59-A:802–809
Bausch JN, Poretz RD (1977) Purification and properties of the hemagglutinin fromMaclura pomifera seeds. Biochemistry 16:5790–5794
Bird TD, Koerker RM, Leaird BJ, Vluk BW, Thorning DR (1983) Lipomembranous polycystic osteodysplasia (brain, bone and fat disease): A genetic cause of presenile dementia. Neurology 33:81–86
Carlemalm E, Garavito RM, Villiger W (1982) Resin development for electron microscopy and an analysis of embedding at low temperature. J Microsc 126:123–143
Frens G (1973) Controlled nucleation for the regulation of the particle size in monodisperse gold solutions. Nature Phys Sci 241:20–22
Fujiwara M (1979) Histopathological and histochemical studies of membranocystic lesion (Nasu). Shinshu Med J (Jpn) 27:78–100
Graham RC, Karnovsky MJ (1966) The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney. Ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem 14:291–302
Hakola HPA (1972) Neuropsychiatric and genetic aspects of a new hereditary disease characterized by progressive dementia and lipomembranous polycystic osteodysplasia. Acta Psychiat Scand Suppl 232:1–172
Hakola HPA, Partanen VSJ (1983) Neurophysiological findings in the hereditary presenile dementia characterised by polycystic lipomembranous osteodysplasia and sclerosing leukoencephalopathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 46:515–520
Hammerström S, Kabat EA (1969) Purification and characterization of a blood group A reactive hemagglutinin from the snailHelix pomatia and a study of its combinding site. Biochemistry 8:2696–2705
Harada K (1975) Ein Fall von “Membranoser Lipodystrophie (Nasu)”, unter besonderer Berücksichtigung des psychiatrischen und neuropathologisches Befundes. Folia Psychiatr Neurol Jpn 29:169–177
Inoue K, Funayama M, Suda A, Higuchi I (1975) Intraosseous lipomatosis. Report of a case. J Jpn Orthop Ass 49:223–230
Kitajima I, Igata A, Senba I, Nagamatsu K (1987) Histological studies on the hard tissue in membranous lipodystrophy (Nasu). J Bone Mineral Metabolism 4:199–205
Laasonen von EM (1975) Das Syndrom der Polyzystischen Osteodysplasie mit progressiver Demenz. Fortschr Rontgenstr 122:313–316
Machinami R (1983) Membranous lipodystrophy-like changes in ischemic necrosis of the legs. Virchows Arch [A] 399:191–205
Machinami R (1984) Incidence of membranous lipodystrophy-like change patients with limb necrosis caused by chronic arterial obstruction. Arch Pathol Lab Med 108:823–826
Maxwell MH (1978) Two rapid and simple methods used the removal of resins from 1.0 µm thick epoxy sections. J Microsc 112:253–255
Nasu T (1978) Pathology of membranous lipodystrophy. Trans Soc Pathol Jpn 67:57–98
Nasu T, Fujiwara M, Suganuma T, Tanaka R (1977) An autopsy case of dermatomyositis accompanied by a membranocystic lesions (Nasu) in subcutaneous tissue. Connect Tissue (Jpn) 9:25–31
Nasu T, Tsukahara Y, Terayama K (1973) A lipid metabolic disease - membranous lipodystrophy - an autopsy case demonstrating numerous peculiar membrane-structures composed of compound lipid in bone and bone marrow and various adipose tissues. Acta Pathol Jpn 23:539–558
Ohtani Y, Miura S, Yamai Y, Kojima H, Kashima H (1979) Neutral lipid and sphingolipid composition of the brain of a patient with membranous lipodystrophy. J Neurol 220:77–82
Roth J (1983) Application of lectin-gold complexes for electron microscopic localization of glycoconjugates on thin sections. J Histochem Cytochem 31:987–999
Slot JW, Geuze HJ (1981) Sizing of protein A-colloidal gold probes for immunoelectron microscopy. J Cell Biol 90:533–536
Sourander P (1970) A new entity of phacomatosis: B. brain lesions (sclerosing leukoencephalopathy). Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Suppl 215:44
Suganuma T (1978) Experimental study on membranous lipodystrophy (Nasu). Shinshu Med J (Jpn) 26:460–489
Suganuma T, Ihida K, Matsunaga S, Tsuyama S, Sakou T, Murata F (1987) Glycoconjugate histochemistry and ultrastructural study of membranous lipodystrophy. Acta Histochem Cytochem 20:21–30
Tanaka J (1980) Leukoencephalopathic alteration in membranous lipodystrophy. Acta Neuropathol 50:193–197
Tokunaga M, Wakamatsu E, Sato M, Namiki O, Yokosawa A, Motomiya M (1981) Lipid composition of adipose tissue from “membranous lipodystrophy”. Tohoku J Exp Med 133:451–456
Wood C (1978) Membranous lipodystrophy of bone. Arch Pathol Lab Med 102:22–27
Yagishita S, Ito Y, Ikezaki R (1976) Lipomembranous polycystic osteodysplasia. Virchows Arch [A] 372:245–251
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kitajima, I., Suganuma, T., Murata, F. et al. Ultrastructural demonstration ofMaclura pomifera agglutinin binding sites in the membranocystic lesions of membranous lipodystrophy (Nasu-Hakola disease). Vichows Archiv A Pathol Anat 413, 475–483 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00750387
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00750387