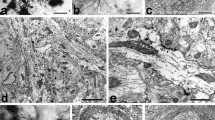
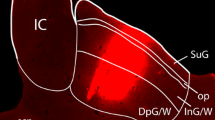
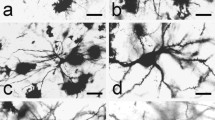
Summary
The retrograde fluorescent tracers Fast Blue (FB) and Diamidino Yellow (DY) have been used to study subcortical afferents of the claustrum. DY or FB was injected into the claustrum. The greatest amount of labeled cell bodies were observed in the posterior thalamic nuclear complex. They were especially abundant in its caudal part, lying between the medial geniculate body and the pretectal area. In comparison to the numerous labeled cells near the diencephalic-mesencephalic junction, the number of fluorescing neurons in the brain stem was considerably lower. These neurons were mostly concentrated in the monoaminergic cell groups. The results indicate the presence of a substantial projection from the posterior thalamic and anterior pretectal region to the calustrum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen DL (1968) Some striatal connections to the claustrum. Exp Neurol 20:261–267
Bentivoglio M, Kuypers HGJM, Catsman-Berrevoets CE (1980a) Retrograde neuronal labeling by, means of bisbenzimide and nuclear yellow (Hoechst S 769121). Measures to prevent diffusion of the tracers out of retrogradely labeled neurons. Neurosci Lett 18:19–24
Bentivoglio M, Kuypers HGJM, Catsman-Berrevoets CE, Loewe H, Dann O (1980b) Two new fluorescent retrograde neuronal tracers which are transported over long distances. Neurosci Lett 18:25–30
Bentivoglio M, Molinari M, Minciacchi D, Macchi G (1983) Organization of the cortical projections of the posterior complex and intralaminar nuclei of the thalamus as studied by means of retrograde tracers. In: Macchi G, Rustioni A, Spreafico R (eds) Somatosensory integration in the thalamus. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 337–363
Berkley KJ (1973) Response properties of cells in ventrobasal and posterior group nuclei of the cat. J Neurophysiol 36:940–952
Berkley KJ (1980) Spatial relationships between the terminations of somatic sensory and motor pathways in the rostral brainstem of cats and monkeys. I. Ascending somatic sensory inputs to lateral diencephalon. J Comp Neurol 193:283–317
Bharos TB, Kuypers HGJM, Lemon RN, Muir RB (1981) Divergent collaterals from deep cerebellar neurons to thalamus and tectum, and to medulla oblongata and spinal cord: Retrograde fluorescent and electrophysiological studies. Exp Brain Res 42:399–410
Boivie J (1971) The termination of the spinothalamic tract in the cat. An experimental study with silver impregnation methods. Exp Brain Res 19:331–353
Boivie J (1979) An anatomical re-investigation of the termination of the spinothalamic tract in the monkey. J Comp Neurol 186:343–370
Bonvallet MP, Dell P, Higelin A (1952) Projections olfactives, gustatives, viscérales, vagales, visuelles et auditives au niveau des formations grises antérieures du chat. J Physiol (Paris) 44:222–224
Bowsher D (1983) Pain pathways and mechanisms. In: Swerdlow M (ed) Relief of intractable pain. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1–23
Burton H, Craig AF (1983) Spinothalamic projections in cat, raccoon and monkey: A study based on anterograde transport of horseradish peroxidase. In: Macchi G, Rustioni A, Spreafico R (eds) Somatosensory integration in the thalamus. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 17–41
Carey RG, Bear MF (1981) Reciprocal, connections between the claustrum and the thalamus in the tree shrew (Tupaia glis). Anat Rec 199:44A
Carey RG, Bear MF, Diamond IT (1980) The laminar organization between the claustrum and striate cortex in the tree shrew, Tupaia glis. Brain Res 184:193–198
Carman JB, Cowan WM, Powell TPS (1964) The cortical projection upon the claustrum. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiat 27:46–51
Carpenter MB (1984) Interconnections between the corpus striatum and brain stem nuclei. In: McKenzie JS, Kemm RE, Wilcock LN (eds) The basal ganglia. Structure and function. Plenum, New York, London, pp 1–68
Cavada C, Huisman AM, Kuypers HGJM (1984) Retrograde double labeling of neurons: the combined use of horseradish peroxidase and diamidino yellow dihydrochloride (DY.2HC1) compared with true blue and DY.2HC1 in rat descending brainstem pathways. Brain Res 308:123–136
Chorazyna H, Stepien L, Sychowa B (1965) Changes in auditory conditioning in dogs after lesion of the claustrum. XXIII Int Congr Physiol Sci Tokyo, pp 456–457
Craig AD, Burton H (1985) The distribution and topographical organization in the thalamus of anterogradely-transported horseradish peroxidase after spinal injections in cat and raccoon. Exp Brain Res 58:227–254
Dray A (1980) The physiology and pharmacology of mammalian basal ganlia. Progr Neurobiol 14:221–335
Druga R (1966) Cortico-claustral connections. I. Fronto-claustral connections. Folia Morphol (Prague) 14:391–399
Druga R (1968) Cortico-claustral connections. II. Connections from the parietal, temporal, and occipital cortex to the claustrum. Folia Morphol (Prague) 16:143–149
Druga R (1984) Reciprocal connections between the claustrum and the gyrus sigmoideus posterior in the cat. An experimental study using the anterograde degeneration methods and the HRP retrograde axonal transport. Anat Anz 156:109–118
Fallon JH (1981) Collateralization of monoamine neurons: mesotelencephalic dopamine projections to caudate, septum, and frontal cortex. J Neurosci 1:1361–1368
Fallon JH, Loughlin SE (1982) Monoamine innervation of the forebrain: Collateralization. Brain Res Bull 9:295–307
Follon JH, Moore RY (1978) Catecholamine innervation of the basal forebrain. IV. Topography of dopamine cell projections to the basal forebrain and neostriatum. J Comp Neurol 180:545–580
Fallon JH, Koziell DA, Moore RY (1978) Catecholamine innervation of the basal forebrain. II. Amygdala, suprarhinal cortex and entorhinal cortex. J Comp Neurol 180:509–532
Getz B (1952) The termination of spinothalamic fibers in the cat as studied by the method of terminal degeneration. Acta Anat 16:271–290
Graybiel AM (1972a) Some ascending connections of the pulvinar and nucleus lateralis posterior of the thalamus in the cat. Brain Res 44:99–125
Graybiel AM (1972b) Some fiber pathways related to the posterior thalamic region in the cat. Brain Behav Evol 6:363–393
Graybiel AM (1973) The thalamo-cortical projection of the socalled posterior nuclear group: A study with anterograde degeneration methods in the cat. Brain Res 49:229–244
Graybiel AM, Ragsdale CW Jr (1979) Fiber connections of the basal ganglia. In: Cuénod M, Kreutzberg GW, Bloom FE (eds) Development and chemical specifity of neurons. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 239–283
Grofová I (1979) Extrinsic connections of the neostriatum. In: Divac I, Öberg RGE (eds) The neostriatum. Pergamon, Oxford, pp 37–51
Guldin WO, Markowitsch HJ (1983) Cortical and thalamic afferent connections of the insular and adjacent cortex of the rat. J Comp Neurol 215:135–153
Guldin WO, Markowitsch HJ (1984) Cortical and thalamic afferent connections of the insular and adjacent cortex of the cat. J Comp Neurol 229:393–418
Guldin WO, Pritzel M, Markowitsch HJ (1981) Prefrontal cortex of the mouse defined as cortical projection area of the thalamic mediodorsal nucleus. Brain Behav Evol 19:93–107
Hassler R (1960) Die zentralen Systeme des Schmerzes. Acta Neurochir 8:353–423
Hassler R (1970) Dichotomy of facial pain conduction in the diencephalon In: Hasser R, Walker AE (eds) Trigeminal neuralgia, Thieme, Stuttgart pp 123–138
Hassler R (1972) Hexapartition of inputs as a primary role of the thalamus. In: Frigyesi T, Rinvik E, Yahr MD (eds) Corticothalamic projections and sensorimotor activities. Raven, New York, pp 551–579
Hassler R (1978) Striatal control of locomotion intentional actions, and of integrating and percetive activity. J Neurol Sci 36:187–224
Herkenham M (1978) The connections of the nucleus reuniens, thalami: Evidence for a direct thalamo-hippocampal pathway in the rat. J Comp Neurol 177:589–610
Hinova-Palova DV, Paloff AM, Usunoff KG (1980a) Identification of three types of degenerated boutons in claustrum dorsale of the cat after lesion of the temporal cortex. C R Acad Bulg Sci 33:125–128
Hinova-Palova DV, Paloff AM, Usunoff KG (1980b) Identifiaction of three types of degenerated boutons in claustrum dorsale of the cat after lesion of the frontal cortex? C R Acad Bulg Sci 33:129–132
Hinova-Palova DV, Paloff AM, Usunoff KG (1984) Electron microscopic identification of thalamoclaustral axon terminals in the cat. Second Symposium on Peripheral and CentralSynapses, Varna, 1984
Infantellina F, Rapisarda C, Rizzo R, Urbano A (1965) Activités évoquées dans le claustrum par stimulation de nerfs somatiques chez le chat. Arch Sci Biol (Bologna) 49:275–290
Jastreboff P, Sikora M, Frydrychowski A, Sloniewski P (1983) Claustral single cell reactions to tooth pulp stimulation in cats. Acta Neurobiol Exp 43:291–298
Jayaraman A (1984) Thalamostriate projections — an overview. In: McKenzie JS, Kemm RE, Wilcock LN (eds) The basal ganglia. Structure and function. Plenum, New York, London, pp 69–86
Jayaraman A, Updyke BV (1979) Organization of visual cortical projections to the, claustrum in the cat. Brain Res 178:107–115
Jones EG, Burton H (1974) Cytoarchitecture and somatic sensory connectivity of thalamic nuclei other than the ventrobasal complex in the cat. J Comp Neurol 154:395–432
Jones EG, Leavitt RY (1974) Retrograde axonal transport and the demonstration of non-specific projections to the cerebral cortex and striatum from thalamic intralaminar nuclei in the rat, cat, and monkey, J Comp Neurol 154:349–378
Juraniec J, Narkiewicz O, Wrzolkova T (1971) Axon terminals in the claustrum of the cat: an electron microscope study. Brain Res 35:277–282
Kaufman EFS, Rosenquist AC (1985) Efferent projections of the thalamic intralaminar nuclei in the cat. Brain Res 335:257–279
Keizer K, Kuypers HGJM, Huisman AM, Dann O (1983) Diamidino yellow dihydrochloride (DY.2HC1); a new fluorescent retrograde neuronal tracer, which migrates only very slowly out of the cell. Exp Brain Res 51:179–191
Kevetter GA, Willis WD (1984) Collateralization in the spinothalamic tract: New methodology to support or deny phylogenetic theories. Brain Res Rev 7:1–14
Krettek JE, Price LJ (1977) The cortical projections of the mediodorsal nucleus and adjacent thalamic nuclei in the rat J Comp Neurol 171:157–192
Künzle H (1975) Bilateral projections from precentral motor cortex to the putamen and other parts of the basal ganglia. An autoradiographic study in Macaca fascicularis. Brain Res 88:195–209
Künzle H (1978) An autoradiographic analysis of the efferent connections from premotor and adjacent prefrontal regions (area 6 and 9) in Macaca fascicularis. Brain Behav Evol 15:185–234
Künzle H, Akert K (1977) Efferent connections of cortical area 8 (frontal eye field) in Macaca fascicularis. A reinvestigation using the autoradiographic technique. J Comp Neurol 173:147–164
Kuypers HGJM, Bentivolgio M, Catsman-Berrevoets CE, Bhros AT (1980) Double retrograde neuronal labeling through divergent axon collaterals, using two fluorescent tracers with the same excitation wavelength which label different features of the cell. Exp Brain Res 40:383–392
LeVay S, Sherk H (1981a) The visual claustrum of the cat. I. Structure and connections. J Neurosci 1:956–980
LeVay S, Sherk H (1981b) The visual claustrum of the cat. II. The visual field map. J Neurosci 1:981–992
Loughlin SE, Fallon JH (1984) Substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area projections to cortex: Topography and collateralization. Neuroscience 11:425–435
Macchi G, Bentivoglio M, Minciacchi D, Molinari M (1981) The organization of claustroneocortical projections in the cat studied by means of the HRP retrograde axonal transport. J Comp Neurol 195:681–695
Macchi G, Bentivoglio M, Minciacchi D, Molinari M (1983) Claustroneocortical projections studied in the cat by means of multiple retrograde fluorescent tracing. J Comp Neurol 215:121–134
Macchi G, Bentivoglio M, Molinari M, Minciacchi D (1984) The thalamo-caudate versus thalamo-cortical projections as studied in the cat with fluorescent retrograde double lebeling. Exp Brain Res 54:225–239
Mantyh PW, Mehler WR (1980) Unpublished data Quoted from Mehler WR (1980) Subcortical afferent connections of the amygdala in the monkey. J Comp Neurol 190:733–762 (see p 751)
Markowitsch HJ, Pritzel M (1978) The insular region. Part of the prefrontal cortex? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2:271–276
Markowitsch HJ, Pritzel M (1979) The prefrontal cortex: Projection area of the thalamic mediodorsal nucleus? Physiol Psychol 7:1–6
Markowitsch HJ, Pritzel M (1981) Prefrontal cortex of the guinea pig (Cavia porcellus) defined as cortical projection area of the thalamic mediodorsal nucleus. Brain Behav Evol 18:80–95
Mehler WR (1966) Some observations on secondary ascending afferent systems in the central nervous system. In: Knighton RS, Dumke PR (eds) pain. Little, Brown & Co., Boston, pp 11–32
Mehler WR (1969) Some neurological species differences — a posteriori. Ann NY Acad Sci 167:424–468
Mehler WR (1974) Central pain and the spinothalamic tract. In: Bonica JJ (ed) Int. Symp. on Pain, Adv. in Neurology, Vol. 4, Raven Press, New York, pp 127–146
Mehler WR, Fefferman ME, Nauta WJH (1960) Ascending axon degeneration following anterolateral cordotomy. An experimental study in the monkey. Brain 83:718–750
Mesulam M-M (1982) Tracing neural connections with horseradish peroxidase. John Wiley, New York
Narkiewicz O (1964) Degenerations in the claustrum after regional neocortical ablations in the cat. J Comp Neurol 123:335–356
Narkiewicz O, Sloniewski P (1981) Claustral afferents from the pretectum in the cat. Acta Anat 111:104
Narkiewicz O, Sloniewski P, Morys J (1983) Pretectal projections to the claustrum in the cat. Verh Anat Ges 77:685–687
Narkiewicz O. Morys J, Sloniewski P (in press) Neurons of the lamina medullaris pretectothalamica and their projections to the insuloclaustral area in the cat. Verh Anat Ges 79
Nauta WJH (1961) Fiber degeneration following lesions of the amygdaloid complex in the monkey. J Anat (London) 95:515–531
Nauta WJH, Domesick VB (1984) Afferent and effrent relationships of the basal ganglia. In: Evered D, O'Connor M (eds) Functions of the basal ganglia, CIBA foundation symposia, Vol. 107, Pitman Publ. Ltd., London, pp 3–29
Nauta WJH, Whitlock DG (1954) An anatomical analysis of the non-specific thalamic projection system. In: Delafrasnaye JF (ed) Brain mechanisms and consciousness. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 81–116
Nauta WJH, Pritz MB, Lasek RJ (1974) Afferents to the rat caudato putamen studied with horseradish peroxidase. An evaluation of a retrograde neuroanatomical research method. Brain Res 67:219–238
Nobin A, Björklund A (1973) Topography of the monoamine neuron system in the human brain as revealed in fetuses. Acta Physiol Scand 88 (Suppl 388) 1–40
Norita M (1977) Demonstration of bilateral claustro-cortical connections in the cat with the method of retrograde axonal transport of horseradish peroxidase. Arch Histol Jpn 40:1–10
Olson CR, Graybiel AM (1980) Sensory maps in the claustrum of the cat. Nature 288:479–481
Paxinos G, Watson C (1982) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, Australia, North Ryde, NSW
Pearson JC, Haines DE (1980) Somatosensory thalamus of a prosimian primate (Galago senegalensis). I. Configuration of nuclei and termination of spinothalamic fibers. J Comp Neurol 190:533–558
Pickel VM, Segal M, Bloom FE (1974) A radioautographic study of the efferent pathways of the nucleus locus coeruleus. J Comp Neurol 155:15–42
Rapisarda C, Azzaroni A, Infantellina F (1969) An electrophysiological analysis of the visual projections to the claustrum in unanesthetized cats. Arch Sci Biol (Bologna) 53:130–148
Riche D, Lanoir J (1978) Some claustro-cortical connections in the cat and baboon as studied by retrograde horseradish peroxidase tranpsort. J Comp Neurol 177:435–444
Rockel AJ, Heath CJ, Jones EG (1972) Afferent connections to the diencephalon in the marsupial phalanger and the question of sensory convergence in the “posterior group” of the thalamus. J Comp Neurol 145:105–130
Royce GJ, Bromley S (1984) Fluorescent double labeling studies of thalamostriatal and corticostriatal neurons. In: McKenzie JS, Kemm RE, Wilcock LN (eds) The basal ganglia. Structure and function. Plenum Press, New York, London, pp 131–146
Sanides D, Buchholtz CS (1979) Identification of the projection from the visual cortex to the claustrum by retrograde axonal transport in the cat. Exp Brain Res 34:197–200
Segundo JP, Machne X (1956) Unitary responses to afferent volleys in lenticular nucleus and claustrum. J Neurophysiol 19:325–339
Sherk H, LeVay S (1981a) Visual claustrum: Topography and receptive field properties in the cat. Science 212:87–89
Sherk H, LeVay S (1981b) The visual claustrum of the cat. III. Receptive field properties. J Neurosci 1:993–1002
Sloniewski P (1983) Pretectal connections to the claustrum: An HRP retrograde transport study in cats. Acta Neurobiol Exp 43:165–182
Sloniewski P, Pilgrim Ch (1984) Claustro-neocortical connections in the rat as demonstrated by retrograde tracing with lucifer yellow. Neurosci Lett 49:29–32
Sloniewski P, Pilgrim Ch (in press) Stimulation des Glukoseverbrauchs im Claustrum der Ratte durch Schmerz. Verh Anat Ges 80
Sloniewski P, Usunoff KG, Pilgrim Ch (submitted) Retrograde transport of fluorescent tracers reveals extensive ipsi- and contralateral claustrocortical connections in the rat.
Spector I (1974) Sensory properties of single neurons of cat's clausstrum. Brain Res 66:39–65
Spector I, Hassmannova J, Albe-Fessard D (1970) A macrophysiological study of functional organization of the claustrum. Exp Neurol 29:31–51
Squatrito S, Bataglini PP, Galetti C, Riva Sanseverino E (1980) Projections from the visual cortex to the contralateral claustrum of the cat revealed by an anterograde axonal transport method. Neurosci Lett 19:271–275
Steinbusch HWM (1981) Distribution of serotonin-immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the rat. Cell bodies and terminals. Neurocience 6:557–618
Symonds LL, Rosenquist AC, Edwards SB, Palmer LA (1981) Projections of the pulvinar-lateral posterior complex to visual cortical areas in the cat. Neuroscience 6:1995–2020
Updyke BV (1983) A reevaluation of the functional organization and cytoarchitecture of the feline lateral posterior complex, with observations on adjoining cell groups. J Comp Neurol 219:143–181
Urbano A, Rapisarda C, Infantellina F (1966) Etude microphysiologique des afférences somatiques au claustrum chez le chat. Arch Sci Biol (Bologna) 50:41–54
Van der Kooy D (1979) The organization of the thalamic, nigral, and raphe cells projecting to the medial vs lateral caudateputamen in rat. A fluorescent retrograde double labeling study. Brain Res 169:381–387
Veening JG, Cornelissen FM, Lieven PAJM (1980) The topical organization of the afferents to the caudatoputamen of the rat. A horseradish peroxidase study. Neuroscience 5:1253–1268
Warr WB, De Olmos JS, Heimer L (1981) Horseradish peroxidase: The basic procedure. In: Heimer L. RoBards MJ (eds) Neuroanatomical tract-tracing methods. Plenum Press, New York, London, pp 207–262
Zemlan FP, Leonard CM, Kow L-M, Pfaff DW (1978) Ascending tracts of the lateral columns of the rat spinal cord: A study using the silver impregnation and horseradish peroxidase techniques. Exp Neurol 62:298–334
Zilles K, Zilles B, Schleicher A (1980) A quantitative approach to cytoarchitectonics. VI. The areal pattern of the cortex of the albino rat. Anat Embryol 159:335–360
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
P.S. was a fellow of the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation, on leave from the Department of Anatomy, Medical Academy, Debinki 1, 80-211 Gdansk, Poland
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sloníewski, P., Usunoff, K.G. & Pilgrim, C. Diencephalic and mesencephalic afferents of the rat claustrum. Anat Embryol 173, 401–411 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00318925
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00318925