Abstract
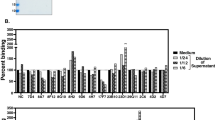
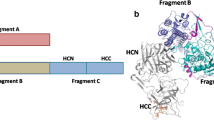
Monoclonal antibodies against tetanus toxin and its toxoid were produced by immunizing mice with toxoid or toxin. They were measured by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), by a toxin neutralization test in mice (in vivo prevention test), and by their ability to prevent binding of125I-toxin to brain membranes or gangliosides (in vitro prevention test). Six monoclonal antibodies obtained by immunization with toxoid (anti-toxoid 1–6) were investigated in more detail. They belonged to IgG class 1. Three of them (anti-toxoid 1, 2 and 3) recognized both toxoid and toxin as well as fragment B and the light chain of toxin, but not fragment C. Two other antibodies (anti-toxoid 4 and 5) were directed against toxoid only. Neither of them prevented toxin action in vitro or in vivo. Anti-toxoid 6 recognized toxin, toxoid and fragment C, but not light chain, and prevented toxin action in vitro and in vivo. Immunization against toxin was initiated with a toxin-antitoxin complex and boosted with toxin. We studied six antibodies in more detail, all of IgG type 2. Their KD against125I-tetanus toxin varied from 10−9 to 10−10 M. Anti-toxin 2 recognized toxin, toxoid, light chain and fragment B, but not fragment C. The others reacted with toxin, toxoid and fragment C, but not with light chain or fragment B. All of them prevented toxin action in vitro and in vivo. As calculated from the maximal extinction achieved in the ELISA, tetanus toxin combined with a maximum of two different antibody molecules from our set. Gel filtration data indicate that tetanus toxin reacts with monoclonal antibodies one by one. Compared with polyclonal antiserum, monoclonal antibodies yield flatter slopes in both in vitro and in vivo prevention tests. Thus, they cannot substitute for the polyclonal antibodies in clinical situations, and cannot be calibrated in international units.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bizzini B (1974) Immunochimie et mécanisme d'action de la toxine tétanique. Bull Inst Pasteur 72:177–219
Bolton AE, Hunter WM (1973) The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J 133:529–539
Gigliotti F, Insel RA (1982) Protective human hybridoma antibody to tetanus toxin. J Clin Invest 70:1306–1309
Habermann E (1978) Tetanus, In: Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW (eds) Infections of the nervous system, part I. Handbook of clinical neurology, vol. 33 North Holland, Amsterdam pp 491–547
Hawkes R, Niday E, Gordon J (1982) A dot-immuno binding assay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Anal Biochem 119:142–147
Kozbor D, Lagarde AE, Roder JC (1982) Human hybridomas constructed with antigenspecific Epstein-Barr virus-transformed cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:6651–6655
Kryzhanovskyi GN (1981) Pathophysiology. In: Veronesi R (ed) Tetanus. Important new concepts. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, pp 109–206
Layton GT (1980) A micro enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and radio-immunosorbent technique (RIST) for the detection of immunity to clinical tetanus. Med Lab Sci 37:323–329
Matsuda M, Yoneda M (1977) Antigenic substructure of tetanus neurotoxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 77:268–274
Mizuguchi J, Yoshida T, Sato Y, Nagaoka F, Kondo S, Matuhasi T (1982) Requirement of at least two distinct antibodies for efficient neutralization of tetanus toxin in vivo. Naturwissenschaften 69:597–598
Moore GE, Gerner RE, Franklin HA (1967) Culture of normal human leukocytes. J Am Med Assoc 199:519–524
Nagel J, Cohen H (1973) Studies on tetanus antitoxins. II. Demonstration of at least four antitoxins of different specificity in antitoxic sera. J Immunol 110:1388–1393
Neubauer V, Helting T (1981) Structure of tetanus toxin. The arrangement of papain digestion products within the heavy chain — light chain framework of extracellular toxin. Biochim Biophys Acta 668:141–148
Ngo TT, Lennhoff HM (1980) A sensitive and versatile chromogenic assay for peroxidase and peroxidase-coupled reactions. Anal Biochem 105:389–397
Rathjen FG, Schachner M (1983) Immunocytological and biochemical characterization of a neuronal cell surface component (L1 antigen) which is involved in cell adhesion. EMBO J, in press
Wellhöner HH (1981) Immunology of tetanus: basic and clinical aspects. In: Veronesi, R (ed) Tetanus. Important new concepts. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, pp 40–108
Wellhöner HH (1982) Tetanus neurotoxin. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 93:1–68
Zurawski VR, Haber E, Black PH (1978) Production of antibody to tetanus toxoid by continuous human lymphoblastoid cell lines. Science 199:1439–1441
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This communication contains parts of the M.D. thesis of K.G. and C.V.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahnert-Hilger, G., Bizzini, B., Goretzki, K. et al. Monoclonal antibodies against tetanus toxin and toxoid. Med Microbiol Immunol 172, 123–135 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02124513
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02124513