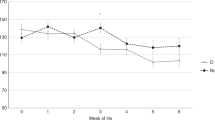
Abstract
Low antithrombin III (AT III) levels in shock are usually ascribed to disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). However, decreased activities of clotting factors and their inhibitors could reflect a generalised fall in plasma proteins rather than DIC. AT III and albumin were compared in 48 asphyxiated and non-asphyxiated newborn rabbits (pH6.70–7.30). Both AT III and albumin were markedly decreased in the sickest animals and there was a direct linear relationship between the two proteins (P<0.001). Similar results were obtained in ten newborn infants suffering from shock and haemorrhagic diathesis. In all cases AT III and albumin were decreased below the normal range and significantly correlated (P<0.01). Our findings suggest that AT III is not a useful diagnostic marker of DIC. Further, a similar fall of clottable and non-clottable proteins in shock questions the general assumption that the ensuing coagulopathy is due to intravascular coagulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AT III:
-
antithrombin III
- DIC:
-
disseminated intravascular coagulation
- PT:
-
prothrombin time
- PTT:
-
partial prothrombin time
- FDP:
-
fibrin-fibrinogen degradation products
References
Abel FL, Wolf MB (1973) Increased capillary permeability to125I-labeled albumin during experimental hemorrhagic shock. Trans NY Acad Sci 35:243–252
Bick RL, Dukes ML, Wilson WL, Fekete LF (1977) Antithrombin III (AT-III) as a diagnostic aid in disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb Res 10:721–729
Bick R (1981) Disseminated intravascular coagulation A clinical/laboratory study of 48 patients. Ann NY Acad Sci 370:843–850
Deysine M, Lieblich N, Aufses AH (1973) Albumin changes during clinical septic shock. Surg Gynecol Obstet 137:475–478
Deysine M, Lieblich N, Saunders S, Shannon R Rothschild M, Aufses AH (1975) Albumin compartmental changes secondary to sepsis. In: Grayson J, Zingg W (eds) Microcirculation 2, Transport Mechanisms Disease States. Plenum Press, New York London, p 241
Faxelius G, Raye J, Gutberlet R, Swanstrom S, Tsiantos A, Dolanski E, Dehan M, Dyer N, Lindstrom D, Brill AB, Stahlman M (1977) Red cell volume measurements and acute blood loss in high-risk newborn infants. J Pediatr 90:273–281
Göbel U, von Voss H, Jürgens H, Petrich C, Pothmann R, Sprock J, Lemburg P (1980) Efficiency of heparin in the treatment of newborn infants with respiratory distress syndrome and disseminated intravascular coagulation. Eur J Pediatr 133:47–49
Gross S, Melhom DK (1971) Exchange transfusion with citrated whole blood for disseminated intravascular coagulation. J Pediatr 78:415–419
Hardie G, Harrison VC, Kench JE (1968) Further observations on serum proteins in respiratory distress syndrome of the newborn. Arch Dis Child 43:471–474
Hathaway WE, Neumann LL, Borden CA, Jacobson LY (1978) Immunologic studies of antithrombin III heparin cofactor in the newborn. Thromb Haemost 39:624–630
Hutter JJ, Hathaway WE, Wayne ER (1976) Hematologic abnormalities in severe neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr 88:1026–1031
Mahasandana C, Hathaway WE (1973) Circulating anticoagulants in the newborn: relation to hypercoagulability and the idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatr Res 7:670–673
McGovern VJ, Tiller DJ (1980) Shock A clinicopathologic correlation. Masson Publishing, USA
Mehta P, Vasa R, Neumann L, Karpatkin M (1980) Thrombocytopenia in the high-risk infant. J Pediatr 97:791–794
Müller-Berghaus G, Niepoth M, Rabens-Alles B, Rump E, Murano G (1983) Antithrombin III concentration and antithrombin III substitution in experimental disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb Haemost 50:323, (Abstract)
Peters M, ten Cate JW, Breederveld C, de Leeuw R, Emeis J, Koppe J (1984) Low antithrombin III levels in neonates with idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome: poor prognosis. Pediatr Res 18:273–276
Peters M, ten Cate JW, Koo LH, Breederveld C (1984) Persistent antithrombin III deficiency: risk factor for thromboembolic complications in neonates small for gestational age. J Pediatr 105:310–314
Rüegg R, Straub PW (1980) Exchange between intravascularly and extravascularly injected radioiodinated fibrinogen and its in vivo derivatives. J Lab Clin Med 95:842
Schipper HG, Kahlé LH, Jenkins CSP, ten Cate JW (1978) Anti-thrombin III transfusion in disseminated intravascular coagulation. Lancet 1:854–856
Schmidt B, Wais U, Pringsheim W, Künzer W (1984) Plasma elimination of antithrombin III (heparin cofactor activity) is accelerated in term newborn infants. Eur J Pediatr 141:225–227
Spero JA, Lewis JH, Hasiba U (1980) Disseminated intravascular coagulation. Findings in 346 patients. Thromb Haemost 43:28–33
von Kaulla E, von Kaulla K (1967) Antithrombin III and diseases. Am J Clin Pathol 48:69–80
Weissbach G, Domula M, Lenk H, Schneider P (1974) The progressive antithrombin activity and its relations to other factors of the coagulation system in newborns. Acta Paediatr Scand 63:555–561
Zipursky A, DeSa D, Hsu E, Johnston M, Milner R (1979) Clinical and laboratory diagnosis of hemostatic disorders in newborn infants. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 1:217–226
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, B.K., Muraji, T. & Zipursky, A. Low antithrombin III in neonatal shock: DIC or non-specific protein depletion?. Eur J Pediatr 145, 500–503 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02429051
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02429051