Abstract
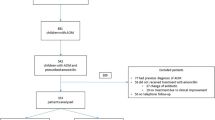
A total of 110 children with acute otitis media were assigned randomly to treatment with 60mg/kg per day amoxicillin in a twice-daily (group A) or a thrice-daily (group B) regimen for 10 days. Patients were scheduled for follow-up examinations at mid-treatment, 5 days after the end of therapy and 30, 60, 90 days after starting therapy. At 15 days 6 out of 55 patients (10.9%) treated with amoxicillin twice daily were considered treatment failures compared to 4 children (7.2%) in the thrice daily group. Rates of cure, recurrent otitis media and persistent middle ear effusion were comparable in the two groups of patients at later time intervals. By 90 days the total cure rate was 42.3% (22/52) in children treated twice daily and 41.5% (22/53) in those who had received amoxicillin thrice daily. At the same time persistence of bilateral and unilateral effusion was noted in 12/52 (23.1%) and in 8/52 (15.3%) children in group A and in 16/53 (30.1%) and in 10/53 (18.9%) in group B respectively.
No significant difference was noted in the two treatment regimens with regard to adverse side effects.
Because reduction in division of the amoxicillin dose caused no significant difference in the efficacy of antibiotic treatment of acute otitis media in infants and children, we think that this simplified scheme of therapy can routinely be used in clinical practice and thus improve compliance to antibiotic administration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AOM:
-
acute otitis media
- WBC:
-
white blood cell count
- ESR:
-
erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- CRP:
-
C-reactive protein
- OME:
-
otitis media with effusion
References
Bluestone CD (1981) Recent advances in the pathogenesis, diagnosis and management of otitis media. Pediatr Clin North Am 28:727–755
Bluestone CD (1982) Chronic otitis media with effusion. Pediatr Infect Dis 1:180–187
Casselbrant ML, Brostoff LM, Cantekin E, Flaherty MR, Doyle WJ, Bluestone CD, Fria TJ (1985) Otitis media with effusion in preschool children. Laryngoscope 95:428–436
Chaput de Saintonge DM, Levine DF, Temple Savage I, Burgess GWS, Sharp J, Mayhew SR, Sadler MG, Moody R, Griffiths R, Griffiths S, Meadows G (1982) Trial of three-day and ten-day courses of amoxicillin in otitis media. Br Med J 284:1078–1081
Finney JW, Friman PC, Rapoff MA, Christophersen ER (1985) Improving compliance with antibiotic regimens for otitis media. Am J Dis Child 139:89–95
Ginsburg CM, McCracken GH Jr, Nelson JD (1981) Pharmacology of oral antibiotics used for treatment of otitis media and tonsillopharyngitis in infants and children. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 5:37–43
Howie VM, Ploussard JH (1972) Efficacy of fixed combination antibiotics versus separate components in otitis media. Clin Pediatr 11:205–214
Klein JO, Bluestone CD (1982) Acute otitis media. Pediatr Infect Dis 1:66–73
Lahikainen EA (1953) Clinico-bacteriologic studies on acute otitis media: aspiration of tympanum as diagnostic and therapeutic method. Acta Otolaryngol [Suppl] (Stockh) 107:1–82
Lous J, Fiellau-Nikolajsen M (1981) Epidemiology of middle ear effusion and tubal dysfunction: a one-year prospective study comprising monthly tympanometry in 387 non-selected seven-year-old children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 3:303–317
Marchant CD, Shurin PA (1983) Therapy of otitis media. Pediatr Clin North Am 30:281–296
Marchant CD, Shurin PA, Turczyk VA, Feinstein JC, Johson CE, Wasikowski DE, Knapp LJ, Tutihasi MA (1984) A randomized controlled trial of cefaclor compared with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for treatment of acute otitis media. J Pediatr 105:633–638
Marchant CD, Shurin PA, Turczyk VA, Wasikowski DE, Tutihasi MA, Kinney SE (1984) Course and outcome of otitis media in early infancy: a prospective study. J Pediatr 104:826–831
Marchisio P, D'Urbino G, Barbi Guidotti M, Bigalli L, Principi N (1986) Eziologia dell'otite media acuta in età pediatrica. Giorn Mal Infett Parass 38:110–115
McCracken GH Jr (1984) Antimicrobial therapy for acute otitis media. Pediatr Infect Dis 3:383–386
Meistrup-Larsen KI, Sorensen H, Johnsen NJ, Thomsen J, Mygind N, Sederberg-Olsen J (1983) Two versus seven days penicillin treatment for acute otitis media. A placebo controlled trial in children. Acta Otolaryngol 96:99–104
Odio CM, Kusmiesz H, Shelton S, Nelson JD (1985) Comparative treatment trial of augmentin versus cefaclor for acute otitis media with effusion. Pediatrics 75:819–826
Paradise JL (1980) Otitis media in infants and children. Pediatrics 65:917–943
Peltola H, Laipio M-L, Siimes MA (1984) Quantitative C-reactive protein (CRP) determined by an immunoturbidimetric method in rapid differential diagnosis of acute bacterial and viral diseases of children. Acta Paediatr Scand 73:273–274
Portoian-Shuhaiber S, Cullinan TR (1984) Middle ear disease assessed by impedance in primary school children in south London. Lancet 1:1111–1113
Riding KH, Bluestone CD, Michaels RH, Cantekin E, Doyle WJ, Poziviak CS (1978) Microbiology of recurrent and chronic otitis media with effusion. J Pediatr 93:739–743
Sarkkinen H, Ruuskanen O, Meurman O, Puhakka H, Virolainen E, Eskola J (1985) Identification of respiratory virus antigens in middle ear fluids of children with acute otitis media. J Infect Dis 151:444–448
Schwartz RH, Rodriguez WJ, Grundfast KM (1984) Duration of middle ear effusion after acute otitis media. Pediatr Infect Dis 3:204–207
Shurin PA, Pelton SI, Donner A, Klein JO (1979) Persistence of middle ear effusion after acute otitis media in children. N Engl J Med 300:1121–1123
Stool SE (1984) Medical relevancy of immittance measurements. Ear Hear 5:309–313
Tarpay M, Marks MI, Hopkins C, Ngo K, San Joaquin VH (1982) Cefaclor therapy twice daily for acute otitis media. Am J Dis Child 136:33–35
Thomsen J, Meistrup-Larsen KI, Sorensen H, Larsen PK, Mygind N (1980) Penicillin and acute otitis media: short and long-term results. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 89[Suppl 68]:271–274
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Principi, N., Marchisio, P., Bigalli, L. et al. Amoxicillin twice daily in the treatment of acute otitis media in infants and children. Eur J Pediatr 145, 522–525 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02429056
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02429056