Abstract
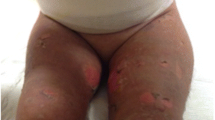
Severe exfoliative dermatitis and liver dysfunction developed in a 5-year-old girl 3 weeks after initiation of phenobarbital therapy. Liver function improved gradually after discontinuation of phenobarbital. During the convalescent stage an initially mild renal dysfunction was exacerbated by episodes of post-transfusion haemolysis. Liver biopsy revealed moderate parenchymal damage with subacute cellular infiltration. Renal biopsy demonstrated the cardinal findings of interstitial nephritis, excluding the possibility of acute tubular necrosis caused by haemolysis. Serial lymphocyte transformation studies and skin patch tests gave positive results for phenobarbital, supporting the view that these were unusual complications of phenobarbital hypersensitivity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldwin DS, Levine BB, McCluskey RT, Gallo GR (1968) Renal failure and interstitial nephritis due to penicillin and methicillin. N Engl J Med 279: 1245–1252
Faarup P, Christensen E (1974) IgE-containing plasma cells in acute tubulointerstitial nephropathy. Lancet II: 718
Hogg RJ, Sawyer M, Hecox K, Eigenbrodt E (1981) Carbamazepine-induced acute tubulointerstitial nephritis. J Pediatr 98: 830–832
Houwerzijl J, DeGast GC, Nater JP, Esselink MT, Nieweg HO (1977) Lymphocyte-stimulating test and patch tests in carbamazepine hypersensitivity. Clin Exp Immunol 29: 272–277
Hyman LR, Ballow M, Knieser MR (1978) Diphenylhydantoin interstitial nephritis. Roles of cellular and humoral immunologic injury. J Pediatr 92: 915–920
Lane T, Peterson EA (1980) Hepatitis is a manifestation of phenobarbital hypersensitivity. South Med J 77: 94
Linton AL, Clark WF, Driedger AA, Turnbull DI, Lindsay RM (1980) Acute interstitial nephritis due to drugs. Review of the literature with a report of nine cases. Ann Intern Med 93: 735–741
McGeachy TE, Bloomer WE (1953) The phenobarbital sensitivity syndrome. Am J Med 14: 600–604
Menninger WC (1928) Skin eruptions with phenobarbital. JAMA 91: 14–18
Nicholls DP, Yasin M (1972) Acute renal failure from carbamazepine. BmJ IV: 490
Sexton DL, Pike GM, Neilson A (1941) Exfoliative dermatitis and death due to phenobarbital. JAMA 116: 700
Shapiro PA, Antonioli DA, Peppercorn MA (1980) Barbiturate-induced submassive hepatic necrosis: Report of a case and review of the literature. Am J Gastroenterol 74: 270–273
Sheth KJ, Casper JT Good TA (1977) Interstitial nephritis due to phenytoin hypersensitivity. J Pediatr 91: 438–441
Tisher CC, Brenner BM (1989) Renal pathology with clinical and functional correlations. JB Lippincott Company, Philadelphia
Tomita H, Konno M, Ishikawa N, Kajii N (1987) A case of hepatic failure with exfoliative dermatitis due to phenobarbital hypersensitivity (abstract) Nippon Shonika Gakkai Zasshi 91: 1465–1471
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sawaishi, Y., Komatsu, K., Takeda, O. et al. A case of tubulo-interstitial nephritis with exfoliative dermatitis and hepatitis due to phenobarbital hypersensitivity. Eur J Pediatr 151, 69–72 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02073898
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02073898