Abstract
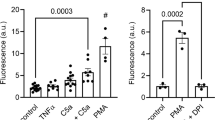
To study the role of cytosolic free calcium, [Ca2+]i, in cell activation, in particular during adhesion and movement on a surface in response to chemotactic peptide stimulation and during phagocytosis, we monitored [Ca2+]i in single human neutrophils. The neutrophils were loaded with fura-2 and allowed to adhere to albumin-coated glass coverslips. [Ca2+]i was monitored with a dual excitation microfluorimeter. Half of the cells showed spontaneous [Ca2+]i transients that lasted up to 15 min with an amplitude averaging 77±10 nM above basal levels (mean basal value of 110±20 nM) and a mean duration of 28±5 s. These repetitive [Ca2+]i elevations depended on the continuous presence of extracellular Ca2+ and could be dissociated from those triggered by the chemotactic peptide N-formyl-methionyl-leucylphenylalanine (fMLP). Cell morphology was monitored in parallel by recording fluorescent images with a high sensitivity charge coupled device (CCD) camera. The majority of the cells studied showed visible changes in shape which started either before or at the same time as the onset of the [Ca2+]i transients. Removal of extracellular Ca2+ abolished [Ca2+]i transients without impairing cell movement and spreading. Blockade of adherence and cell movement with cytochalasin B markedly inhibited [Ca2+]i transients. Monoclonal antibodies directed against the leucocyte integrin CR3 (CD11b/CD18 αmβ2) blocked adherence, spreading and most of the [Ca2+]i activity. Total [Ca2+]i activity was assessed during phagocytosis of C3bi-opsonized yeast particles and correlated with fusion of secondary granules with the phagosomal membrane (P-L fusion). In Ca2+-containing medium, upon contact with a yeast particle, a rapid rise in [Ca2+]i was observed, followed by one or more Ca2+ peaks. P-L fusion was detected in 80% of the cells after 5–10 min. Increasing the cytosolic Ca2+ buffering capacity by loading the cells with MAPT/AM led to a dose-dependent inhibition both of [Ca2+]i elevations and P-L fusion. Under conditions where basal [Ca2+]i was reduced to <20 nM and intracellular Ca2+ stores were depleted, P-L fusion was drastically inhibited while the cells ingested yeast particles normally. Taken together these results indicate that: 1. The action of leucocyte integrins is necessary for the generation of the multiple [Ca2+]i transient observed in surface adherent human neutrophils. These [Ca2+]i transients do not preclude and can be dissociated from the response to fMLP and they prime the cell to subsequent stimulation. 2. Although the ingestion step of phagocytosis is a Ca2+-independent event, [Ca2+]i transients triggered upon contact with opsonized particles are necessary to control the subsequent fusion of granules with the phagosomal membrane. 3. Studies at a single cell level will be necessary to detect subtle deficiencies in intracellular mediators during human diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- [Ca2+]i :
-
cytosolic free calcium concentration
- [Ca2+]o :
-
extracellular free calcium concentration
- fMLP:
-
N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine
- MAPT/AM:
-
1,2-bis-bis-5-methylaminophenoxylethane-N,N,n′-tetra-acetoxymethyl acetate
- P-L:
-
phagosome-lysosome
- TNFα:
-
tumor necrosis factor α
References
Ali SM, Geisow MJ, Burgoyne RD (1989) A role for calpactin in calcium-dependent exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature 340:313–315
Anderson DC, Miller LJ, Schmalstieg FC, Rothlein R, Springer TA (1986) Contributions of the Mac-1 glycoprotein family to adherence-dependent granulocyte functions: structure-function assessments employing subunit-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol 137:15–27
Andersson T, Dahlgren C, Pozzan T, Stendahl O, Lew PD (1986) Characterization of fMet-Leu-Phe receptor-mediated Ca2+ influx across the plasma membrane of human neutrophils. Mol Pharmacol 30:437–443
Arndt-Jovin DJ, Robert-Nicoud M, Kaufman SJ, Jovin TM (1985) Fluorescence digital imaging microscopy in cell biology. Science 230:247–256
Barrowman MM, Cockcroft S, Gomperts BD (1987) Differential control of azurophilic and specific granule exocytosis in sendai-virus-permeabilized rabbit neutrophils. J Physiol 383: 115–124
Berridge MJ, Cobbold PH, Cuthbertson KS (1988) Spatial and temporal aspects of cell signalling. Philos Trans R Soc Lond (Biol) 320:325–343
Bridges RB, Fu MC, Rehm SR (1985) Increased neutrophil myeloperoxidase activity associated with cigarette smoking. Eur J Respir Dis 67:84–93
Detmers PA, Olsen E, Cohn ZA (1988) Cytochalasin D inhibits the binding activity of complement receptors on human neutrophils. FASEB J 2:A1450–6703 (Abstr.)
Di Virgilio F, Lew PD, Pozzan T (1984) Protein kinase C activation of physiological processes in human neutrophils at vanishingly small cytosolic Ca2+ levels. Nature 310:691–693
Di Virgilio F, Milani D, Leon A, Meldolesi J, Pozzan T (1987) Voltage-dependent activation and inactivation of calcium channels in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem 262:9189–9195
Fällman M, Lew PD, Stendahl O, Andersson T (1989) Receptor-mediated phagocytosisin human neutrophils is associated with increased formation of inositol phosphates and diacylglycerol. Regulation and importance for the engulfment process. J Clin Invest 84:886–891
Jaconi MEE, Rivest RW, Schlegel W, Wollheim CB, Pittet D, Lew PD (1988) Spontaneous and chemoattractant-induced oscillations of cytosolic free calcium in single adherent human neutrophils. J Biol Chem 263:10557–10560
Jaconi MEE, Lew PD, Carpentier JL, Magnusson KE, Sjögren M, Stendahl O (1990) Cytosolic free calcium elevation mediates the phagosome-lysosome fusion during phagocytosis in human neutrophils. J Cell Biol 110:1555–1564
Jaconi MEE, Theler J-M, Schlegel W, Appel RD, Wright SD, Lew PD (1991) Multiple elevations of cytosolic free Ca2+ in human neutrophils: initiation by adherence receptors of the integrin family. J Cell Biol 112:1249–1257
Korchak HM, Rutherford LE, Weissmann G (1984) Stimulus response coupling in the human neutrophil. Kinetic analysis of changes in calcium permeability. J Biol Chem 259:4070–4075
Kruskal BA, Maxfield FR (1987) Cytosolic free calcium increases before and oscillates during frustrated phagocytosis in macrophages. J Cell Biol 105:2685–2693
Kruskal BA, Shak S, Maxfield FR (1986) Spreading of human neutrophils is immediately preceded by a large increase in cytoplasmic free calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:2919–2923
Lad PM, Olson CV, Grewal IS (1986) A step sensitive to pertussis toxin and phorbol ester in human neutrophils regulates chemotaxis and capping but not phagocytosis. FEBS Lett 200: 91–96
Levitz SM, Lyman CA, Murata T, Sullivan JA, Mandell GL (1987) Cytosolic calcium changes in individual neutrophils stimulated by opsonized and unopsonizedCandida albicans hyphae. Infect Immun 55:2783–2788
Lew PD, Andersson T, Hed J, Di Virgilio F, Pozzan T, Stendahl O (1985) Ca2+-dependent and Ca2+-independent phagocytosis in human neutrophils. Nature 315:509–511
Lew PD, Wollheim CB, Waldvogel FA, Pozzan T (1984) Modulation of cytosolic-free calcium transients by changes in intracellular calcium-buffering capacity: correlation with exocytosis and O2-production in human neutrophils. J Cell Biol 99:1212–1220
Deleted
Lew PD, Monod A, Waldvogel FA, Dewald B, Baggiolini M, Pozzan T (1986) Quantitative analysis of the cytosolic free calcium dependency of exocytosis from three subcellular compartments in intact human neutrophils. J Cell Biol 102:2197–2204
Lew PD, Monod A, Waldvogel FA, Pozzan T (1987) Role of cytosolic free calcim and phospholipase C in leukotriene-B4-stimulated secretion in human neutrophils. Comparisonwith the chemotactic peptide formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine. Eur J Biochem 162:161–168
Malgaroli A, Milani D, Meldolesi J, Pozzan T (1987) Fura-2 measurement of cytosolic free Ca2+ in monolayers and suspensions of various types of animal cells. J Cell Biol 105:1245–2155
Marks PW, Maxfield FR (1990) Transient increases in cytosolic free calcium appear to be required for the migration of adherent human neutrophils. J Cell Biol 110:43–52
Marks PW, Maxfield FR (1990) Local and global changes in cytosolic free calcium in neutrophils during chemotaxis and phagocytosis. Cell Calcium 11:181–190
Meers P, Ernst JD, Duzgunes N, Hong KL, Fedor J, Goldstein IM, Papahadjopoulos D (1987) Synexin-like proteins from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes Identification and characterization of granule-aggregating and membrane-fusing activities. J Biol Chem 262:7850–7858
Murata T, Sullivan JA, Sawyer DW, Mandell GL (1987) Influence of type and opsonization of ingested particle on intracellular free calcium distribution and superoxide production by human neutrophils. Infect Immun 55:1784–1791
Nathan CF, Srimal S, Farber C, Sanchez E, Kabbash L, Asch A, Gailit J, Wright SD (1989) Cytokine-induced respiratory burst of human neutrophils: dependence of extracellular matrix proteins and CD11/CD18 integrins. J Cell Biol 109:1341–1349
Neher E, Almers W (1986) Fast calcium transients in rat peritoneal mast cells are not sufficient to trigger exocytosis. EMBO J 5:51–53
Omann GM, Allen RA, Bokoch GM, Painter RG, Traynor AE (1987) Signal transduction and cytoskeletal activation in the neutrophil. Physiol Rev 67:285–322
Perez HD, Marder S, Elfman F, Ives HE (1987) Human neutrophils contain subpopulations of specific granules exhibiting different sensitivities to changes in cytosolic free calcium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 145(2):976–981
Pryzwansky KB, MacRae EK, Spitznagel JK, Cooney MH (1979) Early degranulation of human neutrophils: Immunochemical studies of surface and intracellular phagocytic events. Cell 18:1025–1033
Putney JW Jr (1986) A model for receptor-regulated calcium entry. Cell Calcium 7:1–12
Richter J, Andersson T, Olsson I (1989) Effect of tumor necrosis factor and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor on neutrophil degranulation. J Immunol 142:3199–3205
Sawyer DW, Sullivan JA, Mandell GL (1985) Intracellular free calcium localization in neutrophils during phagocytosis. Science 230:663–666
Schlegel W, Winiger BP, Mollard P, Vacher P, Wuarin F, Zahnd GR, Wollheim CB, Dufy B (1987) Oscillations of cytosolic Ca2+ in pituitary cells due to action potentials. Nature 329:719–721
Schlegel W, Winiger BP, Wuarin F, Zahnd GR, Wollheim CB (1988) Monitoring receptor mediated regulation of cytosolic calcium in single pituitary cells by dual excitation microfluorimetry. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 50:1745–1750
Segal AW (1989) The electron transport chain of the microbicidal oxidase of phagocytic cells and its involvement in the molecular pathology of CGD. J Clin Invest 83:1785–1793
Seligmann B, Chused TM, Gallin JI (1984) Differential binding of chemoattractant peptide to subpopulations of human neutrophils. J Immunol 133:2641–2646
Southwick FS, Dabiri GA, Paschetto M, Zigmond SH (1989) Polymorphonuclear leukocyte adherence induces actin polymerization by a transduction pathway which differs from that used by chemoattractants. J Cell Biol 109:1561–1569
Sperling RI, Lewis RA, Austen KF (1986) Regulation of 5-lipoxygenase pathway product generation in human neutrophils by n-3 fatty acids. Prog Lipid Res 25:101–104
Stossel TP (1989) From signal to pseudopod. How cell control actin assembly. J Biol Chem 264:18261–18264
Theler J-M, Wollheim CB, Schlegel W (1991) Rapid ‘on-line’ image processing as a tool in the evaluation of kinetic and morphological aspects of receptor-induced cell activation. J Recept Res II:627–639
Tscharner V von, Prod'hom B, Baggiolini M, Reuter H (1986) Ion channels in human neutrophils activated by a rise in free cytosolic calcium concentration. Nature 324:369–372
Tsien RY, Rink TJ, Poenie M (1985) Measurement of cytosolic free Ca2+ in individual small cells using fluorescence microscopy with dual excitation wavelength. Cell Calcium 6: 145–157
Wright SD, Detmers PA (1988) Adhesion-promoting receptors on phagocytes. J Cell Sci 9:99–120
Wright SD, Weitz JI, Huang AJ, Levin SM, Silverstein SC, Loike JD (1988) Complement receptor type three (CD11b/CD18) of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes recognizes fibrinogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:7734–7738
Wright SD, Detmers PA, Aida Y, Adamowski R, Anderson DC, Chad Z, Kabbash LG, Pabst MJ (1990) CD18-deficient cells respond to lipopolysaccharide in vitro. J Immunol 144: 2566–2571
Zigmond SH, Slonczewski JL, Wilde MW, Carson M (1988) Polymorphonuclear leukocyte locomotion in insensitive to lowered cytoplasmic calcium levels. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 9:184–189
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaconi, M.E.E., Theler, J.M., Schlegel, W. et al. Cytosolic free Ca2+ signals in single adherent human neutrophils: Generation and functional role. Eur J Pediatr 152 (Suppl 1), 26–32 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02072084
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02072084