Abstract
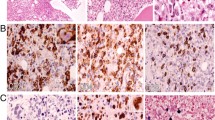
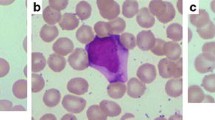
Virus-associated haemophagocytic syndrome (VAHS) is a non-neoplastic, generalized histiocytic proliferation disorder showing marked haemophagocytosis associated with systemic viral infection. We describe the case of a 1-year-old girl with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-related VAHS, in whom Southern blot analysis showed monoclonal proliferation of bone marrow cells with the EBV genome; detected with the Xho-1 fragment of the latent infection membrane protein genome. EBV serology showed anti-Epstein-Barr virus nuclear associated antigen (EBNA), anti-viral capsid antigen (VCA)-IgG, anti-VCA-IgA elevation and positive EBNA of Sheep red blood cells (SRBC)-rosette-forming bone marrow cells in the late period of her clinical course, indicative of EBV infection. DNA analysis of her bone marrow cells showed monoclonal rearrangement of the T-cell receptor-β and-ψ chain genes but not of the immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Those results suggest that EBV may infect T-cells, after which the cells proliferate monoclonally. Repeated administration of epipodophyllotoxin VP-16-213 induced remission, but adrenocortical steroid, vincristine, and cyclophosphamide had no effect on the patient's condition. Ours is a first case report of VAHS showing monoclonal proliferation of EBV-infected T-cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EBV :
-
Epstein-Barr virus
- VAHS :
-
virus-associated hemophagocytic syndrome
- EBNA :
-
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear-associated antigen
- VCA :
-
viral capsid antigenSRBC sheep red blood cells
- VP16 :
-
epipodophyllotoxin VP-16-213
- FACS :
-
fluorescence-activated cell sorter
References
Ambruso DR, Hays T, Zwartjes WJ, Tubergen DG, Favara BE (1980) Successful treatment of lymphohistiocytic reticulosis with phagocytosis with epipodophyllotoxin VP-16-213. Cancer 45: 2516–2520
Boyum A (1968) Separation of lymphocytes from blood and bone marrow. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 21: 31–35
Henle W, Henle G, Horwitz CA (1974) Epstein-Barr virus-specific diagnostic tests in infectious mononucleosis. Hum Pathol 5: 551–565
Ishihara S, Tawa A, Yumura-Yagi K, Murata M, Hara J, Yabuuchi H, Kawa-Ha KK (1989) Clonal T-cell lymphoproliferation containing Epstein-Barr (EB) virus in a patient with chronic active EB virus infection. Jpn J Cancer Res 80: 99–101
Jones JF, Shurin S, Abramowsky G, Tubbs RR, Sciotto GG, Wahl R, Sands J, Gottaman D, Katz ZB, Sklar J (1988) T-cell lymphomas containing Epstein-Barr viral DNA in patients with chronic Epstein-Barr virus infection. N Engl J Med 318: 733–741
Kawa-Ha K, Ishihara S, Ninomiya T, Yamura-Yagi K, Hara J, Murayama F, Tawa A, Hirai K (1989) CD3-negative lymphoproliferative disease of granular lymphocytes containing Epstein-Barr viral DNA. J Clin Invest 84: 51–55
Kikuta H, Taguchi Y, Tomizawa K, Kojima K, Kawamura N, Ishizaka A, Skaiyama Y, Matsumoto S, Imai S, Kinoshita T, Koizumi S, Osato T, Kobayashi I, Hamada I, Hirai K (1988) Epstein-Barr virus genome-positive T lymphocytes in a boy with chronic active EBV infection associated with Kawasaki-like disease. Nature 333: 455–457
Lefranc MP, Forster A, Rabbitts TH (1986) Genetic polymorphism and exon changes of the constant regions of the human T-cell rearranging gene ψ. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 9596–9600
Lock AT, Nagele RF, Callihan T, Herrod HG, Henle W (1981) Fatal Epstein-Barr virus infection in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in remission. Cancer Res 41: 4280–4283
McClain K (1986) Epstein-Barr Virus DNA in lymphocytes of patients with the virus-associated hemophagocytic syndrome. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 8: 121–127
Mckenna RW, Risdall RJ, Brunning RD (1981) Virus-associated hemophagocytic syndrome. Hum Pathol 12: 395–398
Mizutani S, Ford AM, Weideman LM, Chan LC, Furley AJ, Greaves MF, Molgaard HV (1986) Rearrangement of immunoglobulin heavy chain genes in human T leukaemic cells shows preferential utilization of the D segment (DQ52) nearest to the J region. EMBO J 5: 3457–3473
Nancy RT, Kathy F (1986) The structure of the termini of the Epstein-Barr virus as marker of clonal cellular proliferation. Cell 47: 883–889
Purtilo DT (1987) Epstein-Barr Virus: the spectrum of its manifestations in Human Beings. South Med J 80: 943–946
Purtilo DT, Tatsumi E, Manolov G, Manolov Y, Haracla S, Lipscomb H, Krueger G (1985) Epstein-Barr virus as an etiological agent in the pathogenesis of lymphoproliferative and aproliferative diseases in immune-deficient patients. Int Rev Exp Pathol 27: 113–183
Reedman BM, Klein G (1973) Cellular localization of an EBV-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer 11: 499–520
Reisman RP, Greco MA (1984) Virus-associated hemophagocytic syndrome due to Epstein-Barr virus. Hum Pathol 15: 290–293
Richel DJ, Lepouter Jos MM, Ooms CM, Boom WR, Boucher CAB, Kluin PM (1990) Epstein-Barr Virus in a CD8-positive T-cell Lymphoma. Am J Pathol 136: 1093–1099
Risdall RJ, Mckenna RW, Nebit ME, William K, Balfour HH, Simmons RL, Brunning RD (1979) Virus-associated hemophagocytic syndrome: a benign histiocytic proliferation distinet from malignant histiocytosis. Cancer 44: 993–1002
Rubin CM, Burke BA, Mckenna RW, McClain KL, White JG, Nesbit Jr ME, Filipovich AH (1985) The accelerated phase of Chediak-Higashi syndrome: an expression of the virus-associated hemophagocytic syndrome. Cancer 56: 524–530
Sullivan JL, Woda BA, Herrod HG, Koh G, Rivara FP, Mulder C (1985) Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic syndrome: virological and immunopathological studies. Blood 65: 1097–1104
Sumaya CV, Ench J (1985) Epstein-Barr virus infectious mononucleosis in children. II. Heterophil antibody and viral-specific responses. Pediatrics 75: 1011–1019
Wilson ER, Malluh A, Stagmo S, Crist WM (1981) Fatal Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic syndrome. J Pediatr 98: 260–262
Yata J, Desgraneges C, Tachibana T, De-The G (1973) Separation of human lymphocytes forming spontaneous rosettes with sheep erythrocytes. Biomedicine 19: 475–478
Yoneda N, Tatsumi E, Kawanishi M, Teshigawara K, Masuda S, Yamamura Y, Inui A, Yoshino G, Oimomi M, Baba S, Yamaguchi N (1990) Detection of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome in benign proliferative T cells of a young male patient. Blood 76: 172–177
Yoshikai Y, Anatoniou D, Clark SP, Yanagi Y, Sangster R, Von den Elsen R, Terhost C, Mak TW (1984) Sequence and expression of transcripts of the human T-cell receptor β-chain genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 312: 521–524
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noma, T., Kou, K., Yoshizawa, I. et al. Monoclonal proliferation of Epstein-Barr virus-infected T-cells in a patient with virus-associated haemophagocytic syndrome. Eur J Pediatr 153, 734–738 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01954490
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01954490