Abstract
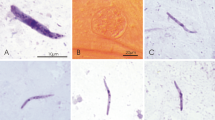
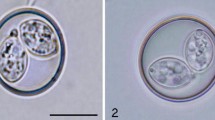
The life cycle ofHepatozoon sipedon sp. nov. was studied in two snake species, the Northern water snake and the Eastern garter snake, in its mosquito hostsCulex pipiens andC. territans, and in the Northern leopard frog. Gametogenesis, fertilization and sporogony occurred within fat body cells in the haemocoel of mosquitoes that had fed on infected water snakes. Mature oocysts averaging 263 μm in diameter and containing more than 500 sporocysts were observed in mosquitoes 28 days post-feeding. Each sporocyst enclosed eight sporozoites. Dizoic cysts were found in the liver of frogs that had been fed infected mosquitoes seven days previously. Two rounds of merogony in various internal organs and intraerythrocytic gamonts were observed in snakes that had been fed frogs which had been orally inoculated with infected mosquitoes. Developmental stages were not seen in snakes that were fed infected mosquitoes directly. A comparison of this life cycle with those described for otherHepatozoon species infecting snakes is presented with reference to the different modes of transmission featured by these parasites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison B, Desser SS (1981) Developmental stages ofHepatozoon lygosomarum (Doré, 1919) comb. n. (Protozoa: Haemogregarinidae), a parasite of a New Zealand skink,Leiolopisma nigriplantare. J Parasitol 67:852–858
Ayala SC (1970) Hemogregarine from sandfly infecting both lizards and snakes. J Parasitol 56:387–388
Ball GH (1958) A haemogregarine from a water snake,Natrix piscator taken in the vicinity of Bombay, India. J Protozool 5:274–281
Ball GH, Oda SN (1971) Sexual stages in the life history of the hemogregarineHepatozoon rarefaciens (Sambon and Seligman, 1907). J Protozool 18:697–700
Ball GH, Chao J, Telford SR (1967) The life history ofHepatozoon rarefaciens (Sambon and Seligman, 1907) fromDrymarchon corais (Colubridae), and its experimental transfer toConstrictor constrictor (Boidae). J Parasitol 53:897–909
Ball GH, Chao J, Telford SR (1969)Hepatozoon fusifex sp. n., a hemogregarine fromBoa constrictor producing marked morphological changes in infected erythrocytes. J Parasitol 55:800–813
Bashtar AR, Boulos R, Mehlhorn H (1984a)Hepatozoon aegypti nov. sp. 1. Life cycle. Z Parasitenkd 70:29–41
Bashtar AR, Ghaffar FA, Mehlhorn H (1984b)Hepatozoon aegypti nov. sp. 2. Electron microscopic studies on the erythrocytic stages and schizogony inside the snake,Spalerosophis diadema. Z Parasitenkd 70:43–52
Bashtar AR, Ghaffar FA, Mehlhorn H (1984c)Hepatozoon aegypti nov. sp. 3. Electron microscopic studies on the gamogony and sporogony inside the vectorCulex pipiens molestus. Z Parasitenkd 70:53–65
Bashtar AR, Abdel-Ghaffar FA, Shazly MA (1987) Developmental stages ofHepatozoon gracilis (Wenyon, 1909) comb. nov., a parasite of the Egyptian skink,Mabuya quiquetaeniata. Parasitol Res 73:507–514
Behler JL, King FW (1979) The Audubon Society field guide to North American reptiles and amphibians. Alfred A. Knopf, New York
Bennett GF, Earlé RA, Penzhorn BL (1992)Ornithodoros peringueyi (Argasidae) andXenopsylla trispinis (Siphonaptera), probable intermediate hosts ofHepatozoon atticorae of the South African cliff swallow,Hirundo spilodera. Can J Zool 70:188–190
Booden T, Chao J, Ball GH (1970) Transfer ofHepatozoon sp. fromBoa constrictor to a lizard,Anolis carolinensis, by mosquito vectors. J Parasitol 56:832–833
Bozzola JJ, Russell LD (1992) Electron microscopy: principles and techniques for biologists. Jones and Bartlett, Boston
Carpenter SJ, LaCasse WJ (1955) Mosquitoes of North America (north of Mexico). University of California Press, Los Angeles, California
Chao J, Ball GH (1969) Transfer ofHepatozoon rarefaciens (Sambon and Seligman, 1907) from the indigo snake to a gopher snake by a mosquito vector. J Parasitol 55:681–682
Clark GM (1958)Hepatozoon griseisciuri n. sp., a new species ofHepatozoon from the grey squirrel (Sciurus carolinensis Gmelin, 1788), with studies on the life cycle. J Parasitol 44:52–63
Clark KA, Robinson RM, Weishuhn LL, Galvin TJ, Hovarth K (1973)Hepatozoon procyonis infections in Texas. Parasitology 48:419–422
DeBiasi P, Pessôa SB, Belluomini HE (1972) Novas observaçoes sôbre transmissao congênita de hematozoários de serpentes peçonhentas vivíparas. Mem Inst Butantan Sao Paulo 36:245–249
Desser SS (1990) Tissue “cysts” ofHepatozoon griseisciuri in the grey squirrel,Sciurus carolinensis: the significance of these cysts in species ofHepatozoon. J Parasitol 76:257–259
Desser SS (1993) The Haemogregarinidae and Lankesterellidae. In: Levine N (ed) Parasitic Protozoa, vol 4. Academic Press, New York, pp 247–272
Furman DP (1966)Hepatozoon balfouri (Laveran, 1905): sporogonic cycle, pathogensis, and transmission by mites to jerboa hosts. J Parasitol 52:373–382
Göbel E, Krampitz HE (1982) Histologische Untersuchungen zur Gamogonie und Sporogonie vonHepatozoon erhardovae in experimentell infizierten Rattenflöhen (Xenopsylla cheopis). Z Parasitenkd 67:261–271
Hayes RO (1961) Host preferences ofCuliseta melanura and allied mosquitoes. Mosquito News 21:179–187
Hull RW, Camin JH (1960) Haemogregarines in snakes: the incidence of the erythrocytic stages. J Parasitol 46:515–523
Johnson B (1989) Familiar reptiles and amphibians of Ontario. Natural Heritage/Natural History, Toronto
Krampitz HE, Wongchari V (1980) The development ofHepatozoon erhardovae in experimental mammalian and arthropod hosts. I. The evaluation of suitable arthropod vectors. Proc Int Congr Fleas Rotterdam 1975: 349–358
Landau I (1973) A comparison of the life cycles ofToxoplasma andHepatozoon, with reference to the general phenomenon and the role of cyst formation in the Coccidia. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 67:403–407
Landau I, Michel JC, Chabaud AG, Brygoo ER (1972) Cycle biologique d'Hepatozoon domerguei; discussion sur les caractères fondamentaux d'un cycle de Coccidie. Z Parasitenkd 38:250–270
Langmann G (1899) On haemosporidia in American reptiles and batrachians. N Y Med J 69:1–6
Levine ND (1988) The protozoan phylum Apicomplexa. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, pp 115–134
Levine ND, Wacha RS (1983) Haemogregarines (Protozoa, Apicomplexa) in Iowa reptiles. J Parasitol 69:827
Lewis JE, Wagner ED (1964)Hepatozoon sauromali sp. n., a hemogregarine from the chuckwalla (Sauromalus spp.) with notes on the life history. J Parasitol 50:11–14
Lowichik A, Yaeger RG (1987) Ecological aspects of snake hemogregarine infections from two habitats in southeastern Louisiana. J Parasitol 73:1109–1115
Lowichik A, Lanners NL, Lowrie RC, Meiners NE (1993) Gametogenesis and sporogony ofHepatozoon mocassini (Apicomplexa: Adeleina: Hepatozoidae) in an experimental mosquito host. J Euk Microbiol 40:287–297
Mackerras MJ (1962) The life history of aHepatozoon (Sporozoa: Adeleidea) of varanid lizards in Australia. Aust J Zool 10:35–44
Marquardt WC (1966) Haemogregarines andHaemoproteus in some reptiles in southern Illinois. J Parasitol 52:823–824
McKinstry DM (1973) Blood parasites in snakes of northwestern Pennsylvania. J Parasitol 59:343
Michel JC (1973)Hepatozoon mauritanicum (Et. et Ed. Sergent, 1904) n. comb., parasite deTestudo graeca: redescription de la sporogonie chezHyalomma aegyptium et la schizogonie tissulaire d'après le matérial d'E. Brumpt. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp 48:11–21
Miller WW (1908)Hepatozoon perniciosum n. g., n. sp., a haemogregarine pathogenic for white rats; with a brief description of the sexual cycle in the intermediate host, a mite (Laelaps echidnius Berlese). Bull Hyg Lab Washington 46:51–123
Mohammed AHH, Mansour NS (1959) The haemogregarine complex (an analytical systematic review). Bull Fac Sci Cairo Univ 35:39–51
Murphey FJ, Burbutis PP, Bray DF (1967) Bionomics ofCulex salinarius Coquillett. II. Host acceptance and feeding by adult females ofC. salinarius and other mosquito species. Mosquito News 27:366–374
Nadler SA, Miller JH (1984) A redescription ofHepatozoon mocassini (Laveran, 1902) n. comb. fromAgkistrodon piscivorus leucostoma Troost, 1836. J Protozool 31:321–324
Oda SN, Chao J, Ball GH (1971) Additional instances of transfer of reptile hemogregarines to foreign hosts. J Parasitol 57:1377–1378
Pessôa SB (1970) Formas evolutivas doHepatozoon leptodactyli (LeSage, 1908) na sanguessugaHaementeria lutzi Pinto, 1920. Rev Goiana Med 16:35–39
Pessôa SB, Cavalheiro J (1969a) Notas sobre hemogregarinas de serpentes brasileiras. VIII. Sôbre a evoluçao daHaemogregarina miliaris na sanguessugaHaementeria lutzi. Rev Bras Biol 29:451–458
Pessôa SB, Cavalheiro J (1969b) Notas sobre hemogregarinas de serpentes brasileiras. IX. Sôbre a hemogregarina daHelicops carinicauda (Wied.). Rev Goiana Med 15:161–168
Pessôa SB, DeBiasi P (1973a) Consideraçoes taxonômicas sobre cistos esquizogônicos e sobre gametócitos deHepatozoon (Sporozoa, Haemogregarinidae), parasitas de serpentes brasileiras. Mem Inst Butantan Sao Paulo 37:291–298
Pessôa SB, DeBiasi P (1973b) Nota taxonômica sobre cistos esporogônicos de algumas espécies deHepatozoon (Sporozoa, Haemogregarinidae), parasitas de serpentes brasileiras. Mem Inst Butantan Sao Paulo 37:299–307
Redington BC, Jachowski LA (1971) Syngamy and sporogony ofHepatozoon griseisciuri Clark, 1958 (Sporozoa: Haemogregarinidae), in its natural vector,Haemogamasus reidi Ewing, 1925 (Acari: Mesostigmata). J Parasitol 57:953–960
Reichenow, E (1921) Die Hämococcidien der Eidechsen. Arch Protistenkd 42:179–291
Richie JP Jr, Mills BJ, Lang CA (1986) Dietary nordihydroguaiaretic acid increases the life-span of the mosquito. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 183:81–85
Robin LA (1936) Cycle évolutif d'unHepatozoon deGecko verticillatus. Ann Inst Pasteur 56:376–394
Spurr AR (1969) A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res 26:31
Stehbens WE, Johnston RL (1968) Cystic bodies and schizonts associated with a haemogregarine (Sporozoa) parasitic inGehyra variegata (Reptilia: Gekkonidae). J Parasitol 54:1151–1165
Telford SR (1984) Haemoparasites of reptiles. In: Hoff GL, Frye FL, Jacobson ER (eds) Diseases of amphibians and reptiles. Plenum Press, pp 408–434
Upton SJ, Current WL, Ernst JV, Barnard SM (1984) Extraintestinal development ofCaryospora simplex (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae) in experimentally infected mice,Mus musculus. J Protozool 31:392–398
Upton SJ, Lindsay DS, Current WL, Barnard SM (1985) Mouse-to-mouse transmission ofCaryospora simplex (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae). J Parasitol 71:395–396
Vivier E, Petitprez A, Landau I (1972) Observations ultrastructurales sur la sporoblastogenèse de l'hémogrégarine,Hepatozoon domerguei, Coccidie, Adeleidea. Protistologica 8:315–333
Wenyon CM (1926) Protozoology: A manual for medical men, veterinarians and zoologists. Baillière, Tindall and Cassel, London
Wozniak EJ, Telford SR (1991) The fate ofHepatozoon species naturally infecting Florida black racers and watersnakes in potential mosquito and soft tick vectors, and histological evidence of pathogenicity in unnatural host species. Int J Parasitol 21:511–516
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, T.G., Desser, S.S. & Martin, D.S. The development ofHepatozoon sipedon sp. nov. (Apicomplexa: Adeleina: Hepatozoidae) in its natural host, the Northern water snake (Nerodia sipedon sipedon), in the culicine vectorsCulex pipiens andC. territans, and in an intermediate host, the Northern leopard frog (Rana pipiens). Parasitol Res 80, 559–568 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00933003
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00933003