Abstract
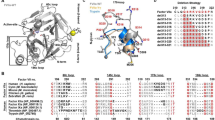
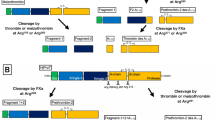
By means of a novel cDNA-based strategy employing the maximum parsimony principle, we have previously deduced probable amino acid sequences for the catalytic domains of the early mammalian ancestors of each of the five extant vitamin K-dependent serine proteases of coagulation, and for their common ancestor from a still earlier stage of vertebrate evolution. In the present study, we employed one of these sequences to construct a molecular model of the catalytic domain of early mammalian protein C and to explore its functional architecture. Following the domain’s progression from the common ancestor of the vitamin K-dependent serine proteases toward extant human protein C, this novel application of homology modelling to a reconstructed amino acid sequence has allowed us to trace the evolution of structural features in a vital coagulation protein.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 23 May 1997 / Accepted: 23 July 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wacey, A., Krawczak, M., Kemball-Cook, G. et al. Homology modelling of the catalytic domain of early mammalian protein C: evolution of structural features. Hum Genet 101, 37–42 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390050582
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390050582