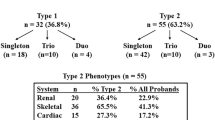
Summary
A human genomic DNA fragment, pAM37 (HGM8; D21S22), was mapped to chromosome 21q2.1-q2.21 by in situ hybridization. This segment is therefore situated on the boundary of the “pathological region” of Down syndrome. A genomic restriction map encompassing 35 kb of chromosome 21 was derived and two restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) were mapped and characterized. A homologous sequence was detected in the mouse genome but no homologous RNA was detected in a range of human tissues. This DNA segment will contribute to the linkage mapping of chromosome 21 and will facilitate delineation of the pathological region of Down syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alwine JC, Kemp DJ, Parker BA, Reiser J, Renart J, Stark GR, Wahl GM (1979) Detection of specific RNAs or specific fragments of DNA by fractionation in gels and transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper. Methods Enzymol 68:220–242
Antonarakis SE, Boehm CD, Giardina PJV, Kazazian HH (1982) Non-random association of polymorphic restriction sites in the beta-globin gene cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:137–141
Antonarakis SE, Kittur SD, Metaxotou C, Watkins PC, Patel AS (1985) Analysis of DNA haplotypes suggests a genetic predisposition to trisomy 21 associated with DNA sequences on chromosome 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:3360–3364
Barker D, Holm T, White R (1984) A locus on chromosome 11p with multiple restriction site polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 36: 1159–1171
Bartels I, Grzeschik K-H, Cooper DN, Schmidtke J (1986) Regional mapping of six cloned DNA sequences on human chromosome 7. Am J Hum Genet 38:280–287
Bech-Hansen NT, Linsley PS, Cox DW (1983) Restriction fragment length polymorphisms associated with immunoglobulin Cγ genes reveal linkage disequeilibrium and genomic organization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:6952–6956
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnick M, Davis RW (1980) Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 32:314–331
Britten RJ (1986) Rates of DNA sequence evolution differ between taxonomic groups. Science 231:1393–1398
Cooper DN, Schmidtke J (1986) Diagnosis of genetic disease using recombinant DNA. Hum Genet 73:1–11
Cooper DN, Smith BA, Cooke HJ, Niemann S, Schmidtke J (1985) An estimate of unique DNA sequence heterozygosity in the human genome. Hum Genet 69:201–205
Crome L, Stern J (1972) Pathology of mental retardation. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh
Davies KE, Harper K, Bonthron D, Krumlauf R, Polkey A, Pembrey ME, Williamson R (1984) Use of a chromosome 21 cloned DNA probe for the analysis of non-disjunction in Down syndrome. Hum Genet 66:54–56
Devine E, Nolin SL, Houck G, Jenkins EC, Miller DL, Brown WT (1984) Isolation and regional localization by in situ hybridization of a unique gene segment to chromosome 21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 121:380–385
Devine EA, Brown WT, Houck GE, Fisher S, Balazs I, Eisenberg A (1985) Molecular quantitation of aneuploid conditions using chromosome 21 as a model. Ann NY Acad Sci 450:85–94
Epstein CJ, Epstein LB (1981) Gene dosage effects in trisomy 21. In: de la Cruz FF, Gerald PS (eds) Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome): research perspectives. University Park Press, Baltimore, pp 253–260
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B (1983) A technique for radiolabelling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132:6–13
Francke U (1981) Gene dosage studies in Down syndrome: a review. In: de la Cruz FF, Geral PS (eds) Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome): research perspectives. University Park Press, Baltimore, pp 237–251
Harris P, Boyd E, Young BD, Ferguson-Smith MA (1986) Determination of the DNA content of human chromosomes by flow cytometry. Cytogenet Cell Genet 41:14–21
Hassld TJ, Jacobs PA (1984) Trisomy in man. Annu Rev Genet 18: 69–97
Hassold T, Chiu D, Yamane JA (1984) Parental origin of autosomal trisomies. Ann Hum Genet 48:129–144
Hassold T, Kumlin E, Takaesu N, Leppert M (1985) Use of restriction fragment length polymorphisms to study the origin of human aneuploidy. Ann NY Acad Sci 450:179–189
Jackson-Cook CK, Flannery DB, Corey LA, Nance WE, Brown JA (1985) Nucleolar organizer region variants as a risk factor for Down syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 37:1049–1061
Joseph AM, Gosden JR, Chandley AC (1984) Estimation of aneuploidy levels in human spermatozoa using chromosome-specific probes and in situ hybridization. Hum Genet 66:234–238
Kaplan BB, Bernstein SL, Gioio AE (1979) An improved method for the rapid isolation of brain ribonucleic acid. Biochem J 183:181–184
Kittur SD, Antonarakis SE, Tanzi RE, Meyers DA, Chakravarti A, Groner Y, Phillips JA, Watkins PC, Gusella JF, Kazazian HH (1985) A linkage map of three anonymous human DNA fragments and SOD-1 on chromosome 21. EMBO J 4:2257–2260
Korenberg JR, Croyle ML, Cox DR (1985) Isolation of human chromosome 21 specific DNA sequences. Cytogenet Cell Genet 40: 673
Kraus JP, Williamson CL, Firgaira FA, Yang-Feng TL, Münke M, Francke U, Rosenberg LE (1986) Cloning and screening with nanogram amounts of immunopurified mRNAs: cDNA cloning and chromosomal mapping of cystathionine β-synthase and the β-subunit of propionyl-CoA carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:2047–2051
Kurnit DM, Neve RL, Morton CC, Bruns GAP, Ma NSF, Cox DR, Klinger HL (1984) Recent evolution of DNA sequence homology in the pericentric regions of human acrocentric chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet 38:99–105
Levanon D, Leiman-Hurwitz J, Dafni N, Wigderson M, Sherman L, Bernstein Y, Laver-Rudich Z, Danciger E, Stein O, Groner Y (1985) Architecture and anatomy of the chromosomal locus in human chromosome 21 encoding the Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase. EMBO J 4:77–84
Litt M, Jorde LB (1986) Linkage disequilibria between pairs of loci within a highly polymorphic region of chromosome 2q. Am J Hum Genet 39:166–178
Millington-Ward A, Wassenaar ALM, Pearson PL (1985) Restriction fragment length polymorphic probes in the analysis of Down's syndrome. Cytogenet Cell Genet 40:699
Mitchell AR, Gosden JR, Miller DA (1985) A cloned sequence, p82H, of the alphoid repeated DNA family found at the centromeres of all human chromosomes. Chromosoma 92:369–377
Nei M (1975) Molecular population genetics and evolution. North Holland, Amsterdam
Schweber M (1985) A possible unitary genetic hypothesis for Alzheimer's disease and Down syndrome. Ann NY Acad Sci 450: 233–238
Skolnick MH, White R (1982) Strategy for detecting and characterizing restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs). Cytogenet Cell Genet 32:58–67
Slate DL, Ruddle FH (1978) Antibodies to chromosome 21-coded cell surface components can block response to human interferon. Cytogenet Cell Genet 22:265–269
Stewart GD, Harris P, Galt J, Ferguson-Smith MA (1984) Cloned DNA probes regionally mapped to human chromosome 21 and their use in determining the origin of non-disjunction. Nucleic Acids Res 13:4125–4132
Summit RL (1981) Specific segments that cause the phenotype of Down syndrome. In: de la Cruz FF, Gerald PS (eds) Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome): research perspectives. University Park Press, Baltimore, pp 225–235
Tanzi R, Watkins P, Gibbons K, Farynairz A, Wallace M, Hallewell R, Conneally PM, Gusella J (1985) A genetic linkage map of human chromosome 21. Cytogenet Cell Genet 40:760
Thomas PS (1980) Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:5201–5205
Tippett R, Kaplan J-C (1985) Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of chromosome 20, 21 and 22. Cytogenet Cell Genet 40:268–279
Van Keuren ML, Goldman D, Merril CR (1982) Protein variations associated with Down's syndrome, chromosome 21 and Alzheimer's disease. Ann NY Acad Sci 396:55–67
Van Keuren ML, Drabkin H, Watkins P, Gusella J, Patterson D (1985) Regional mapping of DNA sequences to chromosome 21. Cytogenet Cell Genet 40:768
Wallis SC, Donald JA, Forrest LA, Williamson R, Humphries SE (1984) The isolation of a genomic clone containing the apolipoprotein CII gene and the detection of linkage disequilibrium between two common DNA polymorphisms around the gene. Hum Genet 68:286–289
Watkins PC, Tanzi RE, Gibbons KT, Tricoli JV, Landes G, Eddy R, Shows RB, Gusella JF (1985) Isolation of polymorphic DNA segments from human chromosome 21. Nucleic Acids Res 13:6075–6088
Watson DK, McWilliams-Smith MJ, Nunn MF, Duesberg PH, O'Brien SJ, Papas TS (1985) Theets sequence from the transforming gene of avian erythroblastosis virus, E26, has unique domains on human chromosomes 11 and 21: both loci are transcriptionally active. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:7294–7298
Whalley LJ (1982) The dementia of Down's syndrome and its relevance to aetiological studies of Alzheimer's disease. Ann NY Acad Sci 396:39–53
Whatley SA, Hall C, Davison AN, Lim L (1984) Alterations in the relative amounts of specific mRNA species in the developing human brain in Down's syndrome. Biochem J 220:179–187
Yokoi T, Lovett M, Epstein CJ (1985) The isolation of single copy human chromosome 21 DNA sequences homologous to mouse fetal cDNA. Am J Hum Genet 37:A185
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cooper, D.N., Niemann, S.C., Gosden, J.R. et al. Regional localization and characterization of a DNA segment on the long arm of chromosome 21. Hum Genet 75, 129–135 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00591073
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00591073