Abstract
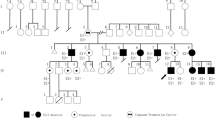
Fragile X syndrome is the most common cause of inherited mental retardation. The incidence has been estimated to be 1 in 1250 males and 1 in 2000 females. Molecular studies have shown that 95% of fragile X syndrome cases are caused by the expansion of a CGG triplet in the FMR1 gene with hypermethylation of the adjacent CpG island. In spite of the high incidence of this syndrome, a female with both FMR1 genes in the expanded form has never been reported. We present here a female from the Canary Islands presenting mental retardation and attention problems. Molecular analysis has revealed that both of her FMR1 genes have the CGG expansion, one with a premutation and the other with a full mutation. We have studied the CGG repeat in the FMR1 gene in 64 members of her family and detected 33 normal individuals, 14 carriers with the premutation (1 male and 13 females), and 18 individuals with full mutations (8 males and 10 females). The index case illustrates that the possibility of both parents being carriers of the fragile X syndrome premutation should be considered in consanguineous families or in small communities.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 4 April 1996 / Revised: 3 May 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Milà, M., Castellví-Bel, S., Giné, R. et al. A female compound heterozygote (pre- and full mutation) for the CGG FMR1 expansion. Hum Genet 98, 419–421 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390050232
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390050232