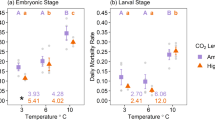
Summary
Acclimation to low salinity induces changes in the ultrastructure of the gill cells of the marine euryhaline amphipod, Gammarus oceanicus. The gills are composed of a single cell type. In 100% artificial sea water, these cells contain moderate numbers of mitochondria which are randomly distributed in the cytoplasm. The plasma membrane is extensively invaginated at the apical, lateral, and basal surfaces. Acclimation to 20% artificial sea water induces a further invagination at the apical cell membrane to form an elaborate apical labyrinth. The extracellular spaces between the folds in the basal cell membrane dilate to 1500 Å or more. Mitochondria are more abundant and in many cells they undergo a change in conformation. The mitochondria are crowded into thin leaflets of cytoplasm between the dilated basal invaginations or into the narrow space between apical and basal cell membranes. Consequently, they lie in close contact with the plasma membrane over much of their surface.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bielawski, J.: Chloride transport and water intake into isolated gills of crayfish. Comp. Biol. chem. Physiol. 13, 423–432 (1964).
Bielawski, J.: Ultrastructure and ion transport in gill epithelium of the crayfish, Astacus leptodactylus Esch. Protoplasma (Wien) 73, 177–190 (1971).
Copeland, D. E.: A study of salt secreting cells in the brine shrimp, (Artemia salina). Protoplasma (Wien) 63, 363–384 (1967).
Copeland, D. E.: Fine structure of salt and water uptake in the land crab, Gecarcinus lateralis. Amer. Zool. 8, 417–432 (1968).
Copeland, D. E., Fitzjarrell, A. T.: The salt absorbing cells in the gills of the blue crab (Callinectes sapidus Rathbun) with notes on modified mitochondria. Z. Zellforsch. 92, 1–22 (1968).
Croghan, P. C.: The mechanism of osmotic regulation in Artemia salina L. The physiology of the branchiae. J. exp. Biol. 35, 234–242 (1958).
Croghan, P. C., Curra, R. A., Lockwood, A. P. M.: The electrical potential difference across the epithelium of isolated gills of the crayfish Austropotamobius pallipes. J. exp. Biol. 42, 463–474 (1965).
Diamond, J. M., Bossert, W. H.: Standing-gradient osmotic flow: a mechanism for coupling of water and solute transport in epithelia. J. gen. Physiol. 50, 2061–2083 (1967).
Diamond, J. M., Bossert, W. H.: Functional consequences of ultrastructural geometry in “backwards” fluid-transporting epithelia. J. Cell Biol. 37, 694–702 (1968).
Horne, F. R.: Active uptake of sodium by the freshwater notostracan Triops longicaudatus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 21, 525–531 (1967).
Jasper, D. K., Bronk, J. R.: Studies on the physiological and structural characteristics of rat intestinal mucosa. Mitochondrial structural changes during amino acid absorption. J. Cell Biol. 38, 277–291 (1968).
Koch, H. J., Evans, J., Schicks, E.: The active absorption of ions by the isolated gills of the crab Eriocheir sinensis. Meded. K. Vlaam, Acad. K. Wet. 16, 1–16 (1954).
Lockwood, A. P. M.: Aspects of the physiology of Crustacea. San Francisco: Freeman & Co. 1967.
Mantel, L. H.: Asymmetry potentials, metabolism and sodium fluxes in gills of the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 20, 743–753 (1967).
Mollenhauer, H. H.: Plastic embedding mixtures for use in electron microscopy. Stain Technol. 39, 111–114 (1964).
Potts, W. T. W., Parry, G.: Osmotic and ionic regulation in animals. New York: MacMillan Co. 1963.
Quinn, D. J., Lane, C. E.: Ionic regulation and Na+-K+-stimulated ATPase activity in the land crab, Cardisoma guanhumi. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 19, 533–543 (1966).
Reynolds, E. S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17, 208–212 (1963).
Shaw, J., Sutcliffe, D. W.: Studies on sodium balance in Gammarus duebeni Lilljeborg and G. pulex pulex (L.). J. exp. Biol. 38, 1–15 (1961).
Sutcliffe, D. W.: Sodium regulation in the fresh-water amphipod, Gammarus pulex (L.). J. exp. Biol. 46, 499–518 (1967a).
Sutcliffe, D. W.: Sodium regulation in the amphipod Gammarus duebeni from brackish-water and fresh-water localities in Britain. J. exp. Biol. 46, 529–550 (1967b).
Sutcliffe, D. W.: Sodium regulation and adaption to fresh water in gammarid crustaceans. J. exp. Biol. 48, 359–380 (1968).
Sutcliffe, D. W., Shaw, J.: The sodium balance mechanism in the fresh-water amphipod, Gammarus lacustris Sars. J. exp. Biol. 46, 519–528 (1967).
Sutcliffe, D. W., Shaw, J.: Sodium regulation in the amphipod Gammarus duebeni Lilljeborg from freshwater localities in Ireland. J. exp. Biol. 48, 339–358 (1968).
Werntz, H. O.: Osmotic regulation in marine and freshwater gammarids (amphipods). Biol. Bull. 124, 225–239 (1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by grants from the United States Public Health Service, 5 RO1 AM13455-03 and PHS FR-07085-04, and by a grant from the National Research Council of Canada administered by Dr. G. P. Morris.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Milne, D.J., Ellis, R.A. The effect of salinity acclimation on the ultrastructure of the gills of Gammarus oceanicus (Segerstråle, 1947) (Crustacea: Amphipoda). Z.Zellforsch 139, 311–318 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00306588
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00306588