Summary
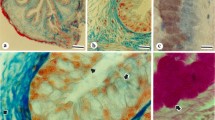
Both ruthenium red and dialyzed iron techniques indicated that anionic protein-carbohydrates were associated with the plasmalemma of secretory cells in mallard salt glands. Digestion of the tissue with neuraminidase prior to dialyzed iron staining provided evidence that much of the anionic nature of this surface was due to sialic acid. These results were confirmed by biochemical assays showing that the salt-gland tissue contained a relatively high sialic-acid content and that the amount of sialic acid increased with salt-water adaptation. Possible roles of these anionic sites are discussed in relation to currently accepted hypotheses of electrolyte transport.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bean, R. C., Shepherd, W. C., Eichner, J. T.: Divalent cation and polycation modification of excitability characteristics in lipid bilayer membranes. Biophys. J. 9, A-31 (1969)
Benedetti, E. L., Emmelot, P.: Studies on plasma membranes. IV. The ultrastructural localization and content of sialic acid in plasma membranes isolated from rat liver and hepatoma. J. Cell Sci. 2, 499–512 (1967)
Bennett, S. H.: Morphological aspects of extracellular polysaccharides. H. Histochem. Cytochem. 11, 14–23 (1963)
Bernal, J. D.: The structure of water and its biological implications. Symp. Soc. expl. Biol. 19, 17–32 (1965)
Bose, A. R., Kar, A. B., Das Gupta, P. R.: Sialic acid in the genital organs of the male rat. Current Sci. 35, 336–337 (1966)
Carroll, P. M., Sereda, D. D.: Sialic acid of uterine muscle membrane; Reappraisal of the serotonin receptor of smooth muscle. Nature (Lond.) 217, 667–668 (1968)
Cook, G. M. W.: Glycoproteins in membranes. Biol. Rev. 43, 363–391 (1968)
Coster, H. G. L., George, E. P., Simons, R.: The electrical characteristics of fixed charge membranes: Solution of the field equations. Biophys. J. 9, 666–684 (1969)
Curran, R. C., Clark, A. E.: The use of colloidal-iron method for acid mucopolysacchaides in electron microscopy. (Abstr.) Biochem. J. 90, 2–3 (1963)
Dannon, D., Howe, C., Lee, L. T.: Interaction of polylysine with soluble components of human erythrocyte membranes. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 101, 201–213 (1965)
Derjaguin, B. V.: Recent research into the properties of water in thin films and in microcapillaries. Symp. Soc. exp. Biol. 19, 55–60 (1965)
Diamond, J. M., Bossert, W. H.: Standing-gradient osmotic flow: a mechanism for coupling of water and solute transport in epithelia. J. gen. Physiol. 50, 2061–2083 (1967)
Diamond, J. M., Bossert, W. H.: Functional consequences of ultrastructural geometry in “backwards” fluid transporting epithelia. J. Cell Biol. 37, 694–702 (1968)
Diamond, J. M., Wright, E. M.: Dependence of alkali cation selectivity on membrane negative charges. (Abstr.) Fed. Proc. 27, 748 (1968)
Dorfman, A.: Polysaccharides of connective tissue. J. Histochem. and Cytochem. 11, 2–13 (1963)
Eisenman, G.: Cation selectivity of glass electrodes and their mode of operation. Biophys. J. 2, 259–323 (1962)
Eisenman, G.: Ion permeation of cell membranes and its models. Fed. Proc. 27, 1249–1251 (1968)
Eisenman, G., Sandblam, J. P., Walker, Jr., J. L.: Membrane structure and ion permeation. Science 155, 965–974 (1967)
Emmelot, P., Bos, C. J.: Differential effect of neuraminidase on the Mg-ATPase, Na-K-Mg-ATPase and 5′-nucleotidase of isolated plasma membrane. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 9, 578–580 (1965)
Emmelot, P., Bos, C. J.: On the participation of neuraminidase-sensitive sialic acid in the K-dependent phosphohydrolysis of p-nitrophenyl phosphate by isolated rat-liver plasma membranes. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 115, 244–247 (1966)
Ernst, A. A.: Transport adenosine triphosphatase cytochemistry I. Biochemical characterization of a cytochemical medium for the ultrastructural localization of ouabain sensitive potassium-dependent phosphatase activity in the avian salt gland. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 20, 13–22 (1972)
Ernst, S. A.: Transport adenosine triphosphatase cytochemistry II. Cytochemical localization of ouabain-sensitive potassium-dependent phosphatase activity in the secretory epithelium of the avian salt gland. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 20, 23–38 (1972)
Ernst, S. A., Goertemiller, C. C., Ellis, R. A.: The effect of salt regimens on the development of (Na-K)-dependent ATPase activity during growth of salt glands of ducklings. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 135, 682–692 (1967)
Ernst, S. A., Philpott, C. W.: Preservation of Na-K-activated and Mg-activated adenosine triphosphatase activities of avian salt gland and teleost gill with formaldehyde as fixative. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 18, 251–263 (1970)
Eylar, E. H., Madoff, M. A., Brody, O. V., Oncley, J. L.: The contribution of sialic acid to the surface charge of the erythrocyte. J. biol. Chem. 237, 1992–2000 (1962)
Faillard, H., Amaral, C. Ferreira de, Blohm, M.: Studies on the enzymic specificity of neuraminidase and N-acylneuraminacetylase with regard to the N-substitution. Happe-Leyless Z. physiol. Chem. 350, 798–802 (1969)
Farber, S. J.: Mucopolysaccharides and sodium metabolism. Circulation 21, 941–953 (1960)
Farquhar, M. G., Palade, G. E.: Cell junctions in amphibian skin. (Abstr.) J. Cell Biol. 19, 22A-23A (1963)
Farquhar, M. G., Palade, G. E.: Cell junctions in amphibian skin. J. Cell Biol. 26, 263–291 (1965)
Fletcher, G. L., Stainer, I. M., Holmes, W. N.: Sequential changes in the adenosinetriphosphatase activity and the electrolyte excretory capacity of the nasal glands of the duck (Anas platyrhynchos) during the period of adaptation to hypertonic saline. J. expl Biol. 47, 375–391 (1967)
Forrester, J. A., Ambrose, E. J., Macphereson, J. A.: Electrophoretic investigations of a clone of hamster fibroblasts and polyomatransformed cells from the same population. Nature (Lond.) 196, 1068–1070 (1962)
Forrester, J. A., Ambrose, E. J., Stoker, M. G. P.: Microelectrophoresis of normal and transformed clones of hamster kidney fibroblasts. Nature (Lond.) 201, 945–946 (1964)
Gasic, G., Gasic, T.: Removal of sialic acid from the cell coat in tumor cells and vascular endothelium, and its effects on metastasis. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 48, 1172–1177 (1962)
Gibbons, R. A.: The sensitivity of the neuraminosidic linkage in mucosubstances towards acid and towards neuraminidase. Biochem. J. 89, 380–381 (1963)
Ginsburg, V., Neufeld, E. F.: Complex heterosaccharides of animals. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 38, 371–388 (1969)
Glaeser, R. M., Mell, H. C.: Microelectrophoretic and enzymic studies concerning the carbohydrate at the surface of rat erythrocytes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 113, 77–82 (1966)
Gliek, J. L., Githens, S., III.: Role of sialic acid in potassium transport of L-1210 leukemia cells. Nature (Lond.) 208, 88–89 (1965)
Glick, J. L., Goldberg, A. R., Pardee, A. B.: The role of sialic acid in the release of proteins from L-1210 leukemia cells. Cancer Res. 26, 1774–1777 (1966)
Gottschalk, A.: The influenza virus neuraminidase. Nature (Lond.) 181, 377–378 (1958)
Hale, C. W.: Histochemical demonstration of acid polysaccharides in animal tissues. Nature (Lond.) 157, 802–803 (1946)
Hartree, E. F., Srivastava, P. N.: Chemical composition of the acrosomes of ram spermatozoa. J. Reprod. Fertil. 9, 47–60 (1965)
Haydon, D. A., Seaman, G. V. F.: Electrokinetic studies on the ultrastructure of the human erythrocyte. I. Electrophoresis at high ionic strengths—the cell as a polyanion. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 122, 126–136 (1967)
Hirst, G. K.: The quantitative determination of influenza virus and antibodies by means of red cell agglutination. J. exp. Med. 75, 49–64 (1942)
Katchalsky, A.: Polyelectrolytes and their biological interactions. Biophys. J. 4 (1), Part 2. 9–10 (1964)
Kemp, R. B.: Effect of the removal of cell surface sialic acids on cell aggregation in vitro. Nature (Lond.) 218, 1255–1256 (1968)
Komnick, H.: Elektronenmikroskopische Lokalisation von Na und Cl in Zellen und Geweben. Protoplasma 55, 414–418 (1962)
Komnick, H.: Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen zur funktionellen Morphologie des Ionentransportes in der Salzdrüse von Larus argentatus. I. Teil: Bau und Feinstruktur der Salzdrüae. Protoplasma 56, 274–314 (1963a)
Komnick, H.: Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen zur funktionellen Morphologie des Ionentransportes in der Salzdrüse von Larus argentatus. II. Teil: Funktionelle Morphologie der Blutgefäße. Protoplasma 56, 385–419 (1963b)
Komnick, H.: Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen zur funktionellen Morphologie des Ionentransportes in der Salzdrüse von Larus argentatus. III. Teil: Funktionelle Morphologie der Tubusepithelzellen. Protoplasma 56, 605–636 (1963c)
Komnick, H.: Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen zur funktionellen Morphologie des Ionentransportes in der Salzdrüse von Larus argentatus. IV. Teil: Funktionelle Morphologie der Epithelzellen des Sammelkanals. Protoplasma 58, 96–127 (1964)
Komnick, H., Komnick, U.: Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen zur funktionellen Morphologie des Ionentransportes in der Salzdrüse von Larus argentatus. V. Teil: Experimenteller Nachweis der Transportwege. Z. Zellforsch. 60, 163–203 (1963)
Kraemer, P. M.: Sialic acid of mammalian cell lines. J. Cell Physiol. 67, 23–34 (1966)
Ling, G. N.: Physiology and anatomy of the cell membrane: the physical state of water in the living cell. Fed. Proc. 24, 103–112 (1965)
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., Randall, R. J.: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951)
Luft, J. H.: Electron microscopy of cell extraneous coats as revealed by ruthenium red staining. (Abstr.) J. Cell Biol. 23, 54A-55A (1964)
Luft, J. H.: Ruthenium red and violet I. Chemistry, purification, methods of use for electron microscopy and mechanism of action. Anat. Rec. 171, 347–368 (1971)
Luft, J. H.: Ruthenium red and violet II. Fine structural localization in animal tissues. Anat. Rec. 171, 369–416 (1971)
Martin, B. J.: Avian Salt Gland: A morphological and cytochemical study of a tissue specialized for electrolyte transport. Ph. D. Thesis, Rice University (1970).
Martin, B. J., Philpott, C. W.: The adaptive response of the salt glands of adult mallard ducks to a salt water regime: An ultrastructural and tracer study. J. exp. Zool. 186, 111–1222 (1973)
Mehrishi, J. N., and Grassetti, D. R.: Sulphydryl groups on the surface of intact Ehrlich ascites tumour cells, human blood platelets and lymphocytes. Nature (Lond.) 224, 563–564 (1969)
McIlwain, H.: Polybasic and polyacidic substances or aggregates and the excitability of cerebral tissues, electrically stimulated in vitro. Biochem. J. 90, 442–448 (1964)
Millonig, G.: Advantages of a phosphate buffer for OsO4 solutions in fixation. J. appl. Physics 32, 1637 (1961)
Mords, B., Candiotti, A., Fabro, J. E.: On the glycocalyx, the external coat of the plasma membrane, of some secretory cells. Z. Zellforsch. 99, 64–73 (1969)
Moore, J. H., Schechter, R. S.: Transfer of ions against their chemical potential gradient through oil membranes. Nature (Lond.) 222, 476–477 (1969)
Morard, J. C.: Etudes histochimiques sur le role des mucopoly-saccharides acides de la medulaire renale dans les processus de la concentration urinaire. C. R. Acad. Sci. (Paris) 264, 2166–2169 (1967)
Nolte, A., Ohkuma, M.: Elektronenmikroskopisch-histochemische Untersuchungen zur Darstellung Saurer Mucopolysaccharide und Sialinsäurehaltiger Glycoproteine in Nierenrinde und innerem Nierenmark der Ratte. Histochemie 17, 17–180 (1969)
Novikoff, A. B.: Their phosphatase controversy: Loves's labours lost. J. Histochem. Cytochem 18, 916 (1970)
Papahadjopoulos, D., Ohki, S.: Stability of asymmetric phospholipid membranes. Science 164, 1075–1077 (1969)
Parsegian, A.: Energy of an ion crossing a low dielectric membrane: Solutions to four relevant electrostatic problems. Nature (Lond.) 221, 844–846 (1969)
Philpott, C. W.: Functional implications of the cell surface: The plasmalemma and surfaceassociated polyanions. In: Cystic fibrosis (Ruth Porter and Meave O'Connor, eds.), p. 109–122, Ciba Foundation Study Group No. 32. London 1968
Pogano, R., Thompson, T. E.: Spherical lipid bilayer membranes: Electrical isotopic studies of ion permeability. J. molec. Biol. 38, 41–57 (1968)
Rajalakshmi, M., Prasad, M. R. N.: Changes in sialic acid in the testis and epididymis of the rat during the onset of puberty. J. Endocr. 44, 379–385 (1969)
Rinehart, J. F., Abul-Haj, S. K.: An improved method for histologic demonstration of acid mucopolysaccharides in tissues. Arch. Path. 52, 189–194 (1951)
Rosenberg, B., Pant, H. C.: Electrochemistry at a bimolecular lipid filmwater interface. (Abstr.) Biophys. J. 9, A-31 (1969)
Rosenthal, A. S., Moses, H. L., Ganote, C. E.: Interpretation of cytochemical data. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 18, 915–916 (1970)
Sabatini, D. D., Bensch, K. G., Barrnett, R. J.: Preservation of ultrastructure and enzymatic activity of aldehyde fixation. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 10, 652–653 (1962)
Skou, J. C.: Enzymatic basis for active transport of Na+ and K+ across cell membrane. Physiol. Rev. 45, 596–617 (1965)
Spicer, S. S., Lev, R.: Histochemical methods for mucosubstances and their application in normal and pathologic states. In: Research on pathogenesis of cystic fibrosis of the pancreas (P. A. di Sant Agnese, ed.), Proc. of Third Internat. Conf., NIH (1967)
Szubinska, B., Luft, J. H.: Ruthenium red and violet. III. Fine structure of the plasma membrane and extraneous coats in Amoeba (A. proteus and Chaos chaos). Anat. Rec. 171, 417–442 (1971)
Thesleff, S., Schmidt-Nielsen, K.: An electrophysiological study of the salt gland of the herring gull. Amer. J. Physiol. 202, 597–600 (1962)
Van Breemen, C., Van Breemen, D.: Accelerated calcium exchange diffusion in a solid ion exchange membrane. Fed. Proc. 28, 547 (1969)
Warren, L.: The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J. biol. Chem. 234, 1971–1975 (1959)
Weinstein, J., Caplan, S.: Charge-mosaic membranes: enhanced permeability and negative osmosis with a symmetrical salt. Science 161, 70–72 (1968)
Weinstein, J. N., Caplan, S. R.: Charge-mosaic membranes: Dialytic separation of electrolytes from nonelectrolytes and amino acids. Science 169, 296–298 (1970)
Weiss, L.: Sialic acid as a structural component of some mammalian tissue cell surfaces. Nature (Lond.) 191, 1108–1109 (1961)
Weiss, L.: Studies on cell deformability. I. Effect of surface charge. J. Cell Biol. 26, 735–739 (1965)
Weiss, L., Levinson, C.: Cell electrophoretic mobility and cationic flux. J. Cell Physiol. 73, 31–36 (1969)
Wesemann, W., Zilliken, F.: Serotoninrezeptor und Neuraminsäurestoffwechsel der glatten Muskulatur. Hoppe-Seylers Z. physiol. Chem. 349, 823–829 (1968)
Wetzel, M. G., Wetzel, B. K., Spicer, S. S.: Ultrastructural localization of acid mucosubstances in the mouse colon with iron-containing stains. J. Cell Biol. 30, 299–315 (1966)
Woolley, D. W., Gommi, B. W.: Serotonin receptors: V. Selective destruction by neuraminidase plus EDTA and reactivation with tissue lipids. Nature (Lond.) 202, 1074–1075 (1964)
Wolley, D. W., Gommi, B. W.: Serotonin receptors. VII. Activities of various pure gangliosides as the receptors. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 53, 959–963 (1965)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Research supported by Public Health Service Grant AM-13705
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martin, B.J., Philpott, C.W. The biochemical nature of the cell periphery of the salt gland secretory cells of fresh and salt water adapted mallard ducks. Cell Tissue Res. 150, 193–211 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222170
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222170