Summary
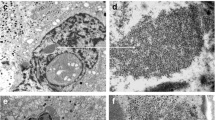
A unique cytoplasmic structure has been observed in Leydig cells of the golden hamster. It consists of a laminar core made up of electron dense material surrounded by a filamentous matrix of lower density, and is tentatively called a dense-cored filamentous body (DCFB). DCFBs vary in overall size and in configuration of the centrally disposed dense lamina. They are typically located in the vicinity of the centrosome and the Golgi complex. The body has no limiting membrane, and may be in contact with virtually every type of organelle. The DCFB is well developed in active Leydig cells, whereas it is small in the quiescent stage of the secretory cell. It is likely that the DCFB is a constant organelle in the hamster Leydig cell and may be involved in the physiological function of the Leydig cell, which remains to be specified.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belt, W.D., Cavazos, L.F.: Fine structure of the interstitial cells of Leydig in the boar. Anat. Rec. 158, 333–350 (1967)
Belt, W.D., Cavazos, L.F.: Fine structure of the interstitial cells of Leydig in the squirrel monkey during seasonal regression. Anat. Rec. 169, 115–128 (1971)
Christensen, A.K., Gillim, S.W.: The correlation of fine structure and function in steroid-secreting cells, with emphasis on those of the gonads. In: The gonads (K.W. McKerns, ed.), pp. 415–488. New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts 1969
Connell, C.J.: The effect of luteinizing hormone on the ultrastructure of the Leydig cell of the chick. Z. Zellforsch. 128, 139–151 (1972)
Connell, C.J., Christensen, A.K.: The ultrastructure of the canine testicular interstitial tissue. Biol. Reprod. 12, 368–382 (1975)
de Kretser, D.M.: The fine structure of the testicular interstitial cells in men of normal androgenic status. Z. Zellforsch. 80, 594–609 (1967)
Fawcett, D.W., Burgos, M.H.: Studies on the fine structure of the mammalian testis. II. The human interstitial tissue. Amer. J. Anat. 107, 245–269 (1960)
Gondos, B., Paup, D.C., Ross, J., Gorski, R.A.: Ultrastructural differentiation of Leydig cells in the fetal and postnatal hamster testis. Anat. Rec. 178, 551–566 (1974)
Gravis, C.J.: Testicular involution following optic enucleation: the Leydig cell. Cell Tissue Res. 185, 303–313 (1977)
Lin, H.-S., Wing, T.-Y.: The influence of activation, removal or denervation of the pineal on the fine structure of the Leydig cell and seminal vesicle epithelium in golden hamsters. Cell Tissue Res. 191, 367–378 (1978)
Rosas, J.C. de, Russo, J.: Pre- and post-natal differentiation of the hamster Leydig cell. Z. Anat. Entwickl.-Gesch. 134, 235–242 (1971)
Setoguti, T., Esumi, H., Shimizu, T.: Specific organization of intracytoplasmic filaments in the dog testicular interstitial cell. Cell Tissue Res. 148, 493–497 (1974)
Spurr, A.R.: A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 26, 31–43 (1969)
Weaker, F.J.: The fine structure of the interstitial tissue of the testis of the nine-banded armadillo. Anat. Rec. 187, 11–28 (1977)
Wing, T.-Y., Lin, H.-S.: A special cytoplasmic structure of Leydig cells in adult golden hamsters (Abstr.) Anat. Rec. 184, 597 (1976)
Wing, T.-Y., Lin, H.-S.: The fine structure of testicular interstitial cells in the adult golden hamster with special reference to seasonal changes. Cell Tissue Res. 183, 385–393 (1977)
Wing, T.-Y., Lin, H.-S.: Electron microscope observations on Leydig cells in the hamster testis. Proc. Natl. Sci. Council, Republic of China 2, 24–32 (1978)
Yates, R.D., Arai, K., Rappoport, D.A.: Fine structure and chemical composition of opaque cytoplasmic bodies of triparanol treated Syrian hamsters. Exp. Cell Res. 47, 459–478 (1967)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported in part by a grant from the National Science Council, the Republic of China (NSC-66B-0412-02-13)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, HS., Wing, TY. A dense-cored filamentous body in Leydig cells of the golden hamster. Cell Tissue Res. 201, 369–376 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00236997
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00236997