Abstract
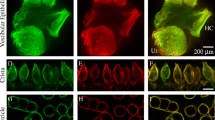
The surface coat, ciliary process, and microvilli of the lamprey neuromast were examined with electron microscopy after tannic acid prefixation and lectin histochemistry. The neuromast was found to exist in the form of a dermal mound with a furrow in the middle. On the bottom of the furrow, the hair cell was characterized by a kinocilium and 15–20 stereocilia, arranged along the longitudinal axis of the furrow. Spanning structures were demonstrated between the kinocilium and stereocilia as well as between stereocilia. The surface coat, enhanced by tannic acid prefixation, was particularly rich over the surface of the supporting cell; by contrast, it was thin over the hair cell. Some lectins (PNA, GS-I, SBA, WGA) showed affinity to the surface coat of the supporting cell as well as the hair cell, and the others (RCA-I, MPA, ConA) showed affinity only to the supporting cell. These differences in the structure and affinities of the surface coat suggest an extracellular milieu highly specialized for the hair cell in this particular form of the mechanoreceptor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainsworth SK, Karnovsky MJ (1972) An ultrastructural staining method for enhancing the size and electron opacity of ferritin in thin sections. J Histochem Cytochem 20:225–229
Blaxter JHS (1983) Structure and development of the free neuromasts and lateral line system of the herring. J Mar Biol Ass UK 63:247–260
Blaxter JHS (1987) Structure and development of the lateral line. Biol Rev 62:471–514
Gil-Loyzaga P, Brownell WE (1988) Wheat germ agglutinin and Helix pomatia agglutinin lectin binding on cochlea hair cells. Hear Res 34:149–156
Gil-Loyzaga P, Raynold J, Gavbrion J (1985) Carbohydrates detected by lectins in the vestibular organ. Hear Res 18:269–272
Hama K (1978) A study of the fine structure of the pit organ of the common Japanese sea eel Conger myriaster. Cell Tissue Res 189:375–388
Hudspeth AJ (1983) Mechanoelectrical transduction by hair cells in the acousticolateralis sensory system. Ann Rev Neurosci 6:187–215
Khan KM, Hatfield JS, Drescher DG (1990) The cell coat of the sensory and supporting cells of the rainbow trout saccular macula as demonstrated by reaction with ruthenium red and tannic acid J Histochem Cytochem 38:1615–1623
Khan KM, Hatfield JS, Drescher DG (1991) Carbohydrates associated with the cell coat surrounding cells of the rainbow trout saccular macula as revealed by lectin probes. Hear Res 53:223–229
Kikuchi T, Takasaka T, Tonosaki A, Watanabe H (1989) Fine structure of guinea pig vestibular kinocilium. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 108:26–30
Lane EB, Whitear M (1982) Sensory structures at the surface of fish skin. II. Lateralis System. Zoological J Linean Soc 76:19–28
Leathem A (1986) Lectin histochemistry. In: Polak JM, Noorden SV (eds) Immunocytochemistry, 2nd edn. Wright, Bristol, pp 167–187
Nagel G, Neugebauer DC, Schmidt B, Thurm U (1991) Structures transmitting stimulatory force to the sensory hairs of vestibular ampullae of fishes and frog. Cell Tissue Res 265:567–578
Ohmori H (1984) Studies of ionic currents in the isolated vestibular hair cell of the chick. J Physiol (Lond) 350:561–581
Osborne MP, Comis SD, Pickles JO (1984) Morphology and crosslinkage of stereocilia in the guinea-pig labyrinth examined without the use of osmium as a fixative. Cell Tissue Res 273:43–48
Pickles JO, Corey DP (1992) Mechanoelectrical transduction by hair cells. Trends Neurosci 15:254–259
Prieto JJ, Merchan JA (1986) Tannic acid staining of the cell coat of the organ of Corti. Hear Res 24:237–241
Rouse GW, Pickles JO (1991) Ultrastructure of free neuromasts of Bathygobius fuscus (Gobiidae) and canal neuromast of Apogon cyanosoma (Apogonidae). J Morphol 209:111–120
Sannes PL, Katsuyama T, Spicer SS (1978) Tannic acid-metal salt sequences for light and electron microscopic localization of complex carbohydrates. J Histochem Cytochem 26:55–61
Sharon N, Lis H (1989) Lectins as cell recognition molecules. Science 246:227–234
Singley CT, Solursh M (1980) The use of tannic acid for the ultrastructural visualization of hyaluronic acid. Histochemistry 65:93–102
Slepecky N, Chamberlain SC (1985) The cell coat of inner ear sensory and supporting cells as demonstrated by ruthenium red. Hear Res 17:281–288
Sugiyama S, Spicer SS, Munyer PD, Schulte BA (1991) Histochemical analysis of glycoconjugates in gelatinous membranes of the gerbil's inner ear. Hear Res 55:263–272
Takumida M, Wersall J, Bagger-Sjoback D (1988) Stereociliary glycocalyx and interconnections in the guinea pig vestibular organs. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 106:130–139
Yamada Y (1973) Fine structure of the ordinary lateral line organ I. The neuromast of lamprey, Entosphenus japonicus. Ultrastruct Res 43:1–17
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katori, Y., Takasaka, T., Ishikawa, M. et al. Fine structure and lectin histochemistry of the apical surface of the free neuromast of Lampetra japonica . Cell Tissue Res 276, 245–252 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00306110
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00306110